Discover how to enhance decision-making in your organization by focusing on three crucial areas: solving the right problem, gathering all the available information, and understanding the intent. Learn to empower your team, foster a purpose-driven culture, and improve organizational clarity for better decision-making.

The Future of the Gig Economy
On Monday, a court in California rejected Uber, and Lyft claims that they didn’t need to treat drivers as employees under AB5, a state law passed in 2019. Under AB5, there are three criteria a company must deem to meet to consider workers, independent contractors, namely:
- Weighing the employer’s control over how the work is performed;
- Whether the services are within the normal course of business; and
- Whether the workers have an independently established role.
Uber CEO, Dara Khosrowshahi, has said that if the court doesn’t reconsider, Uber will shut down its services from the state. This strategy seems to follow Travis Kalanick’s approach – If you own the market, the regulators will have to placate you. Following that strategy should bode well for Uber as the Customer always wins. If Uber were to close down Californian operations, there would a massive cry from both customers and drivers, which could force the state to back down. How this unfolds will be observed by other states, e.g., New Jersey, Massachusetts, and Connecticut, which are using the same standard to determine who is and isn’t a gig worker, and New York and Illinois are considering similar legislation.
Gig work describes independent contractors, remote work, part-time employment, and temporary employment. If someone works for a platform like Fiverr, Uber, or Lyft, then they are part of the gig economy.
While there has been tremendous growth in the gig economy over the last few years, most of it is unskilled work such as driving, delivering, and doing simple errands. A vibrant gig economy for knowledge workers — engineers, consultants, management executives — has not yet materialized.
The Stats and Facts of the Gig Economy
- From nothing in 2014, 57.3MM people performed gig work in the U.S. in 2019.
- 20% of gig workers earned over $100k in 2019.
- 85% of gig workers make less than $500 a month from a single side-job.
- 40% of gig workers had medical insurance.
- 39% of gig workers have no retirement savings.
- 55% of Baby Boomer gig workers have medical insurance.
- 59% of gig workers are satisfied with their financial situation.
- 95% of gig workers say flexibility is essential.
- 19% of gig workers would want a traditional job.
- The main reason for gig work: 18 – 29-year-olds: Need extra money, Gen X: Need money to make ends meet, Men: “Love being their own boss.”
- Only 35% of America’s gig workers are female.
- Almost half of all millennials use online gig economy platforms to find work.
- The total gig income is almost $1 trillion.
- On average, gig workers earn 58% less than full-time employees.
Where are the gig workers?
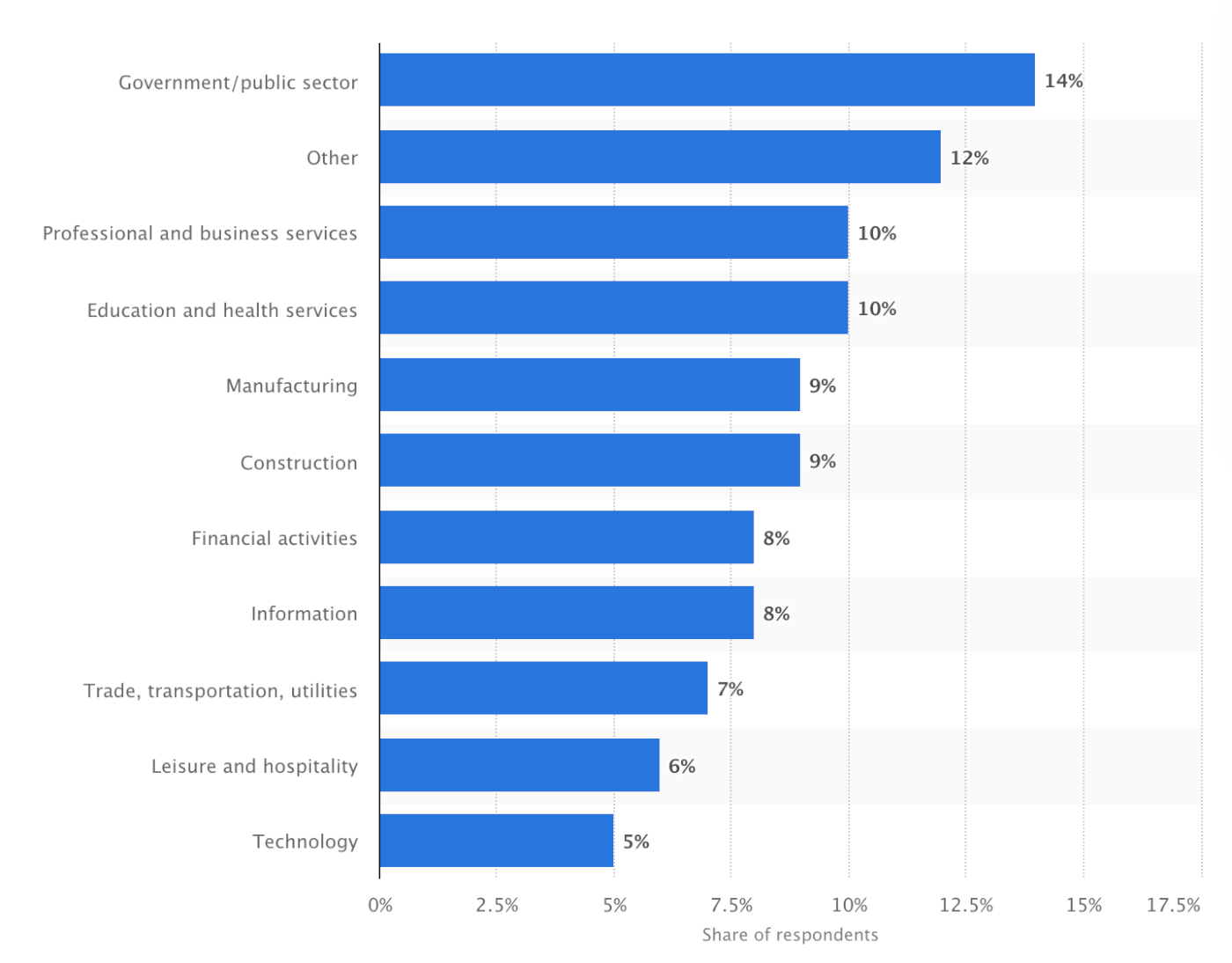
Source: Statista
As can be seen from the above, the Gig economy is significant, is here to stay, and absorbing more jobs and professions. So what are the issues?
Pros of the Gig Economy
- Workers have more flexibility. As noted above, 95% of such workers say flexibility is essential. They use this flexibility to gain the work-life balance they need.
- Gig workers like their independence. As note above, men identified the main reason for gig work is that they “Loved being their own boss.” Gig workers are not micromanaged and can enhance the quality of work for some.
- Gig workers have access to a greater variety of employment opportunities. Freelances often stay in control of their assignment, deciding whether or not to accept a client. They are not stuck with the same monotonous tasks every day.
- Some gig workers work from home, so they have zero commuting costs. Before COVID, this could save $30 to $50 a week commuting to work.
- Lowers companies’ costs. Businesses only have to pay for the labor they receive and don’t have to pay for equipment. Besides, they don’t have to provide benefits or pay state unemployment taxes, and in many cases don’t offer space.
- It allows companies to scale quickly. Startup and small companies find gig workers enable them to scale at a lower cost promptly. They can race to meet market demand and budget restrictions.
- Workers don’t need to cater to the company culture. Gig workers have their own culture. They don’t have to be involved in team-building exercises, corporate rallies, or pander to office politics.
- It is suitable for the creative worker. The variety of work enables some workers to explore their full creativity, increasing the quality of work.
Cons of the Gig Economy
- Less flexibility than thought. While many experienced gig workers, e.g., graphic designers can pick and choose clients and projects, many of the ordinary gig workers don’t have that luxury. Several online platforms use variable pay, rating systems, and notifications to push people to accept specific jobs and work certain hours. These practices, called algorithmic management, limit the flexibility of work.
- No benefits. Most gig workers do not receive any benefits, regardless if they are working 40+ hours a week. Thus they are responsible for their health insurance and retirement contributions, as is seen above. COVID has shown the problems with this. Many gig workers suddenly have no income, but cannot claim unemployment benefits. Furthermore, with a public health crisis, few having health insurance slows the solving of the crisis. Many who don’t have insurance will not seek treatment as they cannot afford it or cannot take time off work to get it, and second those that do, face bankruptcy because they cannot pay for whatever treatment they have.
- More taxes. Since gig workers do have tax withheld, they have to pay income tax and self-employment taxes from their pay, requiring them to withhold 25+% for those purposes. Also, concerning self-employment taxes, gig workers pay both the employee and employer taxes, unlike full-time workers. Finally, gig workers have to manage cash flow as they have to file taxes quarterly, so they will have to save enough to make those payments.
- Gig workers considered lazy. Since many gig workers work from home, many will consider them lazy and nonproductive, which causes social issues.
- Gig workers have high levels of isolation. Gig workers miss the social element of work, discussions around the water cooler, chats with teammates, office events. Lack of the office environment leads to isolation, which can cause mental health issues, as we are seeking with the COVID work from home and suicided rates.
- Gig workers drive more. While gig workers don’t have to commute daily, they end up driving more during a week as they move to pick up and deliver projects or from work site to work site. This increase in driving increases costs and stress.
- More stress for gig workers. Full-time workers know that their employment position is relatively secure. Although layoffs can happen, the risk of such a circumstance is relatively low for the average person. Gig workers have several different stresses. They are always looking out for the next job. They have to be prepared for changes to occur in their current assignments, including being let go in the middle of a task. Thus, their income is never really 100% secure.
- Companies may find their workers are not as reliable. This lack of reliability is a result of workers not adopting the corporate culture. Since gig workers are external, they don’t have to adapt to the corporate culture, and cultural fit is not a hiring requirement. Furthermore, since they are interested in their well being over the corporations, thus, while they will work, they may not work as hard, do what the organization considers “right,” and go the extra mile. Since happy employees lead to satisfied customers, this will reduce customer satisfaction if they interact with customers.
- Gig workers must continuously up-level their skills. Gig workers must continue to up-level their skills to get better because new gig specialists enter this field every day. The levels of industry knowledge that they receive must increase if they want to keep receiving contracts or employment offers. Thus, gig workers have to build in continuing education into their schedules. While this will keep them relevant, it is time that they are not earning.
- Gig workers need to budget for vacations. Gig workers don’t get paid time off, so they need to budget for the fact that while on vacation, they will be spending money and not earning money. Furthermore, many have to give one to three months of advance notice to clients that they will not be available. Finally, if a job comes up as they are about to leave, they may not want to turn it down as they could lose a client.
- It takes longer to build a depth of experience. In an organization, employees are often put on cross-functional teams to address issues. As a result, they create networks and knowledge across many areas of the organization. Gig workers are siloed and don’t build any skills or experience outside their narrow field, limiting their development and earnings potential.
- Us and Them. Many companies have large numbers of gig workers, e.g., Google has more gig workers than full-time workers. Since gig workers are not part of the organization, earn less, and have less opportunity to work in cross-functional areas, they are considered fungible and, in many organizations, are considered less than employees, creating an Us v. Them environment. Furthermore, most gig workers perform specific tasks, not the “package.” The package is more complex and requires working and information sharing across the organization, which gets harder for gig workers who don’t where the information lies due to their lace of organizational knowledge.
- State Tax Revenue. While gig workers have to pay FICA taxes, they are not obliged to pay state unemployment taxes. A study found that if Uber and Lyft had classified its drivers as employees in California, between 2014 and 2018, they would have paid $418 million into the California unemployment insurance fund.
Race to the bottom
A trend that has picked up during COIVD is the race to the bottom. As many people found themselves jobless, they applied for gig jobs. Upwork has seen a 50% increase in freelancer sign-ups since the pandemic began. Talkdesk, which launched a gig economy platform, witnessed 10,000 new applications within ten days. Instacart hired 300,000 additional workers in a month at the beginning of the COVID crisis and, in April, announced it would add 250,000 more.
On platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, many freelancers are already feeling the pinch. With a large number of new workers, given the laws of supply and demand, many gig workers are now vying for freelance work and pitching their services for lower rates to make money.
Now there are too many would-be workers to make the gig economy viable for many of them, and this may be irreversible as companies adapt to the reality of a global recession. By keeping headcounts low, companies will drive more desperate people into the gig economy, expanding the potential labor pool for jobs and driving down the prices that workers can command.
The Recovery
The pandemic has shown that as business recovers, digital economy companies will benefit from their ability to be more flexible than other industries in certain aspects. COVID will probably intensify investors” growing scrutiny of the path to profitability for companies, making them increasingly wary of startups” strategies that favor scale before profitability. Thus gig workers will be vital in meeting this metric.
Also, many governments are now leveraging gig work to fast-track recovery. Having seen how digital platforms have contributed to crisis management and recovery using their nimble operations, flexible thinking, and technological prowess to get things done quickly, India and China are promoting gig work to drive growth in the economy.
So What
Gig work is here to stay, and it will be vital for economic recovery. We must realize; however, that gig workers are not just drivers and delivery people. Presently many occupations are effectively gig jobs, e.g., journalists. However, the issues laid out above are massive and require addressing for gig work to be successful for all. Otherwise, we continue our move to a Hunger Games society.
As Dara Khosrowshahi recently said in an oped in The New York Times, we need to redefine “workers” and have new laws rather than the binary system today. We need to address the reality that this is how millions of people earn some or all of their livings. As a result, we need to ensure that:
- Gig workers can move easily from job to job;
- Gig workers receive healthcare benefits. During a pandemic, we have realized that public health is an essential requirement, and the U.S.healthcare system is not designed to meet it. While ObamaCare causes a visceral reaction for many, much of the thinking behind it was to enable workers to have health insurance not tied to employment. While it may not work well, it needs improving to meet this need for now and the future, not removal and reversion to the past.
- Gig workers receive retirement benefits. Our outdated IRA and 401ks need to restructuring so that gig workers can more easily contribute to them. Today a quarter of Americans have no retirement savings.
- Gig workers need to receive unemployment insurance of some form so that when we have a second COVID like situation, millions are not driven into financial distress due to lack of protections.
- Companies need to contribute towards these benefits so that it doesn’t fall on those who can least afford them, or bore by all taxpayers.
- Changes the balance of power structure between gig workers and corporations in negotiating rates. Our current system encourages a race to the bottom that is detrimental to the gig workers and beneficial to the shareholders. This system reinforces the current U.S. system or rewarding capital at the expense of labor and winnowing out the middle class. It needs addressing, but that will be complex and not easy.
- Companies need to develop better ways of onboarding gig workers to remove the Us v. Them situation. Also, even though these workers are task-specific, smart organizations will start to ensure that gig workers share their core values to ensure that they get better results from them and can use them for the “package.”
If we can address these issues, then the economy should be able to recover quicker and have a flexible, practical framework for future growth while protecting many. If not, the migration to a Hunger Games society will continue, creating more problems and social unrest. However, I believe we up to the task.
Recent Posts
Boosting Common Sense Decision-Making in Your Organization
Do You Understand Your Costs to Ensure Profitability?
You can only determine profitability when you know your costs. I’ve discussed before that you should price according to value, not hours. However, you still need to know your costs to understand the minimum pricing and how it is performing. Do you consider each jobs’ profitability when you price new jobs? Do you know what you should be charging to ensure you hit your profit targets? These discussions about a company’s profitability, and what measure drives profit, are critical for your organization.
Sunk Costs Are Just That, Sunk!
If you were starting your business today, what would you do differently? This thought-provoking question is a valuable exercise, especially when it brings up the idea of “sunk costs” and how they limit us. A sunk cost is a payment or investment that has already been made. Since it is unrecoverable no matter what, a sunk cost shouldn’t be factored into any future decisions. However, we’re all familiar with the sunk cost fallacy: behavior driven by a past expenditure that isn’t recoupable, regardless of future actions.
Do You REALLY Know Your Business Model?
Bringing clarity to your organization is a common theme on The Disruption! blog. Defining your business model is a worthwhile exercise for any leadership team. But how do you even begin to bring clarity into your operations? If you’re looking for a place to start, Josh Kaufman’s “Five Parts of Every Business” offers an excellent framework. Kaufman defines five parts of every business model that all flow into the next, breaking it down into Value Creation, Marketing, Sales, Value Delivery, and Finance.
Ideation! Harder Than It Sounds
Bringing in new ideas, thoughts, understanding, and logic is key as your organization faces the challenges of a changing environment. But when you do an ideation session in your organization… how does it go? For so many organizations, many times, after a few ideas have been thrown out and rejected, the thought process slows down very quickly, and a form of hopelessness takes over. How does your organization have better ideation? I’ve come across a new approach with a few teams lately.
Recruit, Recruit, Recruit!
An uptick in business has begun this quarter, and companies are rushing to hire to meet this surge in demand. What amazes me is how many are so unprepared to hire. Continual recruiting is key to the survival of a company. It isn’t the same thing as hiring—continuous recruiting is building a pipeline of people that you would hire if you needed to fill a position, or “A players” you would hire if they were available.
We All Need Clarity
If your organization is focused on obscurity over clarity, whether intentionally or not, your “A” player employees are vulnerable. There is a looming talent crunch. As we start to emerge from COVID, demand is increasing, and many are scrambling to fill positions to meet that demand. Headhunters and recruiters are soon going to be calling your key “A” employees. Have you been giving them a reason to stay?
Not Another **** Meeting
As Leonard Bernstein put it so well, “To achieve great things, two things are needed: a plan and not quite enough time.” Your meetings can be shorter, more fruitful, and engaging, with better outcomes for the organization, employees, and managers. It’s time to examine your meeting rhythms and how you set meeting agendas. This week, I break down daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, annual, and individual meeting rhythms, with sample agendas for each.
Is Your Company Scalable?
Let’s start here: Why should your company be scalable at all? If your business is scalable, you have business freedom–freedom with time, money, and options. Many business leaders get stuck in the “owner’s trap”, where you need to do everything yourself. Sound familiar? If you want a scalable business that gives you freedom, you need to be intentional about what you sell, and how.
Are you ready for the Talent Crunch?
Companies are gearing up to hire. Unfortunately, many are competing within the same talent pool. Some experts are currently predicting a strong economic recovery starting in May or June. But as the economy booms, there is going to be fierce competition for talent. How will you fare in the looming talent crisis? Your organization should be creating a plan, now, so you can attract the talent you need in the year ahead.














