During a recent call with a CEO, we discussed the company’s profitability and what measure they used to drive profit – basically Profit/X. It became apparent that they didn’t have a handle on their costs and what they should be charging to ensure they hit their profit targets. I have addressed this a bit before to ensure that your margins were where you wanted and rejecting low-profit jobs. However, this time the issue is to understand the jobs’ profitability and price new jobs effectively.
The Costs
To determine profitability, we need to know our costs. Thus, we built a table listing every employee, the salary, additional expenses, e.g., health insurance, 401k, etc. (estimated at 35% of wages), and the amount of billable time. As a result, we had a table that looked like the one below.
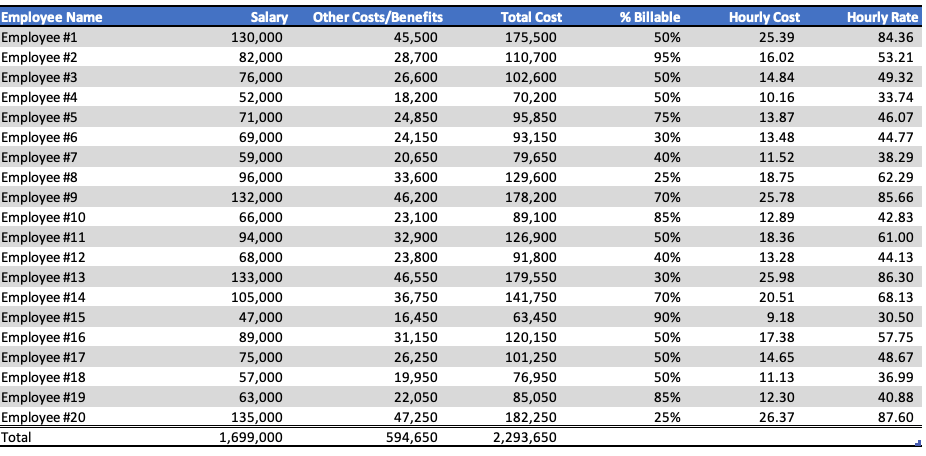
Calculate Hourly Costs
From this Table, we could determine the hourly cost of an employee. To calculate actual costs per hour, we took the number of billable hours, which for 2021 is 8,760, and subtracted 96 hours, the allowable PTO. However, most employees don’t work their total billable hours for various reasons, so we included a “slack” factor of 10%. For multiple reasons, most projects have “re-work” or errors that cannot be billed and estimated at 10% and included. As a result, the total “Billable Hours” was 7,800 rather than 8,760. These adjustments allowed us to produce the hourly cost for each employee.
Calculate Overall Costs
Taking that data, we then divided the hourly costs into billable and non-billable. We added fixed overhead, which was not related to billable expenses, e.g., CEO’s pay, office rent, etc. Thus, we now had a cost structure for the firm that looked as follows.
| Billable Costs | $1,099,150 |
| Non-billable Costs | 1,194,500 |
| Overhead | 750,000 |
| Total Costs | $3,043,650 |
Calculate Revenue
With the company’s cost structure defined, we could determine how much to markup hourly costs to make a 25% profit. Doing this analysis is easy in Excel; however, ensure you don’t make easy Excel mistakes. , and the result was that marking up hourly costs by 232% would enable the company to meet its profit goal. This analysis is shown below.
| Revenue | $4,056,895 |
| Total Costs | 3,043,650 |
| Profit | $1,013,245 |
| Profit Margin | 25% |
Pricing of new projects
While I am a strong proponent of selling value, not time, if the company wants to know the minimum price to charge to realize its minimum profit, it can use this data. Identifying which employees will work on the project and for how long. For example, they would be able to cost it as follows:
| Employee | Hours | Hourly Billable Rate | Total Billable Charge |
| #3 | 25 | $49.32 | $1,233 |
| #6 | 5 | 44.77 | 224 |
| #10 | 20 | 43.83 | 857 |
| #15 | 15 | 30.50 | 457 |
| #17 | 10 | 48.67 | 487 |
| Total | $3,258 |
With this data, we can now estimate jobs more effectively since we know the employees who will work on the jobs and how many hours they will commit. We have to build some waste into that model, but we have a good idea of how to price jobs.
Performance Table
Also, we can see either weekly, monthly, or quarterly how the company is performing. If we produce a table of the employees and clients and hours worked for a month, we can see the utilization of each employee and profit per client as follows.
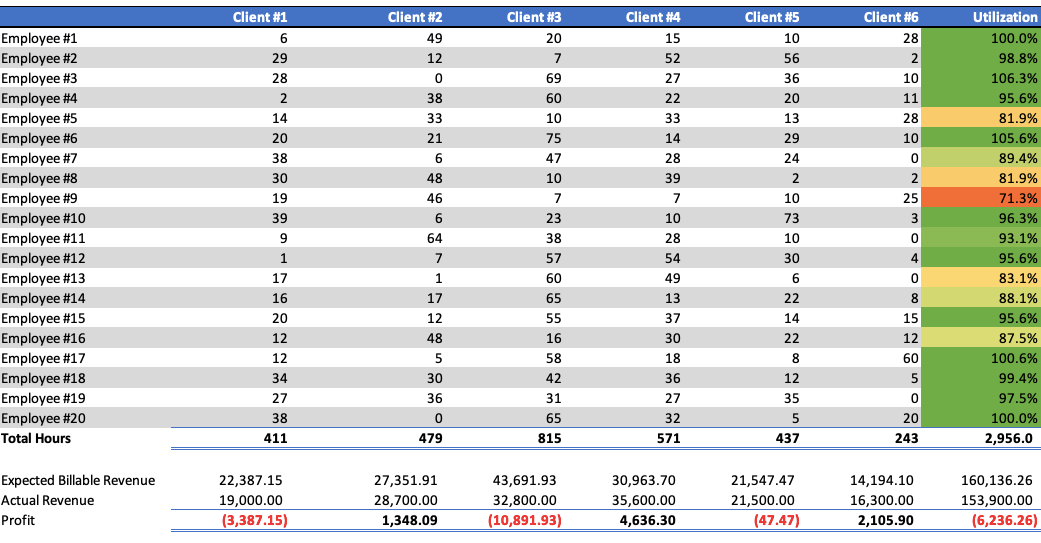
This table provides a good insight into the company’s and employees’ performance. As can be seen, Employees #3 and #6 are working more than their billable hours with utilization rates above 100%. While this may be good, one would need to ensure that whatever they were supposed to be doing with their non-billable time was being done. Also, Employee #9 is utilized 71.3% of the time, resulting in lost efficiency. Further analysis is required into why this is the case, but it identifies potential issues. Finally, it would appear that nearly half of the employees are working at less than 95% utilization. Given that the company’s utilization is already adjusted for “Slack” and “Rework,” analysis to understand why utilization is low is required.
We cannot only analyze employee performance, but we can see how we are doing with our various contracts. Clients #1 and #3 are losing money, while Client #4 is profitable. The data doesn’t tell us why, but again that would be work investigating as the company is performing below its goal of 25% profit.
Conclusion
As I stated at the beginning, concerning pricing, I strongly believe in pricing according to value and not hours; however, this analysis and methodology are helpful to understand what an organization’s minimum pricing should be and how it is performing. While several issues are highlighted and require more work, this provides a great way of knowing what to examine to improve performance.
If you would like to do this analysis, call me. I would be happy to help you.
Copyright © 2021, Marc A. Borrelli
Recent Posts
Align and Thrive: The Importance of Organizational Alignment and Agility
Discover the importance of organizational alignment and agility in this blog post. Learn how establishing a strong CORE and building a strategy around it can lead to sustainable growth and success. Find out how alignment and agility empower your organization to thrive in an ever-changing business landscape.
How to Achieve Smart Time Management: 10 Tips for Busy Professionals
When you are a busy professional running your own business, it can often feel like there aren’t enough hours in the day to accomplish everything. Being strategic with your time is the best (and possibly the only) way to achieve all of your daily tasks. If you are...
5 Strategic Leadership Skills Every Manager Needs
So often, people view leadership as a talent: you’re either born with this quality or you’re not. However, this is not always the case! In reality, good leadership is made up of skills, and anyone can learn how to improve. Some people may pick up leadership attributes...
How the Sellability Score is Calculated: The Ultimate Guide
Do you have questions about how to calculate your business’s sellability score? Whether you’re looking to sell your business in the near future or years from now, understanding your sellability score will help you thrive. The sellability score identifies the...
The Top 5 Benefits of the Entrepreneurial Operating System
As an entrepreneur running your own business, you know there are bumps in the road and struggles that both you and your business will face over time. However, with the right people and tools at your disposal, you can anticipate what’s coming, plan for it, and continue...
5 Ways to Use Email Automation to Boost Traffic
Every single business in the world wants to evolve and grow. This will happen using a variety of techniques and strategies. In 2022, digital marketing is more than a household name, and most companies will adopt at least a few ideas when long-term planning and coming...
6 Questions To Ask A Potential Business Coach Before Hiring Them
Many entrepreneurs consider executive business coaching when they start struggling on their professional path. A small business coach is an experienced professional mentor who educates, supports, and motivates entrepreneurs. They will listen to your concerns, assess...
3 Ways Proper Long Term Strategic Planning Helps Your Business
Dreams turn into goals when they have a foundation of long-term strategic planning supporting them. They become reality when the ensuing strategic implementation plan is executed properly. With Kaizen Solutions as their strategic planning consultant, small and...
What is a Peer Group, and How Can it Improve Your Career?
If you are a CEO or key executive who has come to a crossroads or crisis in your career, you'll gain valuable insights and solutions from a peer group connection more than anywhere else. But what is a peer group, and how can that statement be made with so much...
Profit and Revenue are Lousy Core Values
As I mentioned last week, I am down with COVID and tired, so spending more time reading rather than working. I read Bill Browder's Freezing Order this weekend, and I highly recommend it. However, at the end of the book, Browder says that oligarchs, autocrats, and...











Анализ Tether в нетронутость: Как защитить свои криптовалютные финансы
Все более индивидуумов обращают внимание на безопасность своих криптовалютных активов. День ото дня обманщики придумывают новые подходы хищения цифровых активов, и также собственники цифровой валюты оказываются жертвами их афер. Один из подходов охраны становится проверка бумажников на присутствие нелегальных средств.
Для чего это полезно?
Прежде всего, для того чтобы обезопасить свои финансы от обманщиков и похищенных монет. Многие специалисты встречаются с риском потери их финансов из-за хищных схем или грабежей. Анализ кошельков помогает определить непрозрачные операции а также предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что наша команда предоставляем?
Наша компания предоставляем услугу проверки цифровых кошельков и также операций для определения источника фондов. Наша система проверяет информацию для определения незаконных операций и оценки угрозы для вашего портфеля. Благодаря такой проверке, вы сможете избегать недочетов с регуляторами и защитить себя от участия в незаконных сделках.
Каким образом это работает?
Наша команда сотрудничаем с лучшими аудиторскими компаниями, такими как Kudelsky Security, с целью обеспечить прецизионность наших проверок. Мы внедряем современные технологии для обнаружения потенциально опасных сделок. Ваши информация проходят обработку и хранятся в соответствии с высокими нормами безопасности и приватности.
Каким образом проверить свои Tether на нетронутость?
При наличии желания проверить, что ваша USDT-кошельки чисты, наш подход предоставляет бесплатную проверку первых пяти бумажников. Просто вбейте адрес вашего бумажника в на сайте, и мы предоставим вам подробный доклад о его положении.
Обезопасьте свои средства уже сейчас!
Не подвергайте риску подвергнуться обманщиков или попасть в неблагоприятную ситуацию из-за незаконных сделок. Обратитесь за помощью к нашей команде, для того чтобы сохранить ваши криптовалютные активы и избежать сложностей. Предпримите первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля прямо сейчас!
USDT – является стабильная цифровая валюта, привязанная к национальной валюте, подобно американский доллар. Это делает данную криптовалюту в частности популярной у трейдеров, так как данная криптовалюта обеспечивает надежность курса в условиях неустойчивости рынка криптовалют. Впрочем, как и другая форма цифровых активов, USDT изложена риску использования для легализации доходов и поддержки незаконных сделок.
Отмывание денег посредством криптовалюты переходит в все больше и больше распространенным методом с целью скрытия происхождения средств. Применяя различные приемы, мошенники могут стараться легализовывать незаконно завоеванные фонды посредством сервисы обмена криптовалют или миксеры средств, с тем чтобы совершить происхождение менее очевидным.
Поэтому, анализ USDT на чистоту оказывается необходимой мерой предосторожности для владельцев цифровых валют. Доступны для использования специализированные сервисы, которые выполняют анализ транзакций и бумажников, для того чтобы определить ненормальные транзакции и противоправные источники капитала. Данные платформы помогают участникам предотвратить непреднамеренного участия в преступной деятельности и предотвратить блокировку счетов со со стороны сторонних регуляторных органов.
Анализ USDT на чистоту также как и помогает защитить себя от убытков. Пользователи могут быть уверенны в том их активы не связаны с нелегальными сделками, что соответственно уменьшает вероятность блокировки счета или перечисления денег.
Таким образом, в условиях повышающейся сложности среды криптовалют важно принимать действия для обеспечения безопасности своего капитала. Анализ USDT на чистоту с помощью специализированных платформ становится одним из вариантов защиты от финансирования преступной деятельности, предоставляя участникам цифровых валют дополнительный уровень и защиты.
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]zestril tablet price[/url]
cá cược thể thao
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 0.88[/url]
https://rg777.app/cup-c1-202324/
levitra vardenafil
Backlinks seo
Productive Hyperlinks in Blogs and Comments: Increase Your SEO
Hyperlinks are critical for increasing search engine rankings and boosting website presence. By incorporating backlinks into blogs and comments wisely, they can significantly enhance targeted traffic and SEO performance.
Adhering to Search Engine Algorithms
Today’s backlink placement methods are finely adjusted to align with search engine algorithms, which now prioritize website link quality and relevance. This assures that hyperlinks are not just numerous but significant, guiding users to useful and pertinent content. Website owners should focus on incorporating hyperlinks that are situationally suitable and boost the overall articles quality.
Benefits of Making use of Refreshing Donor Bases
Using current donor bases for backlinks, like those managed by Alex, offers substantial rewards. These bases are regularly refreshed and consist of unmoderated sites that don’t attract complaints, guaranteeing the links placed are both impactful and agreeable. This strategy helps in sustaining the usefulness of backlinks without the pitfalls connected with moderated or problematic assets.
Only Authorized Sources
All donor sites used are authorized, avoiding legal pitfalls and sticking to digital marketing standards. This dedication to making use of only approved resources assures that each backlink is legitimate and trustworthy, thus developing reliability and reliability in your digital presence.
SEO Impact
Expertly put backlinks in blogs and remarks provide over just SEO rewards—they improve user experience by connecting to pertinent and top quality articles. This strategy not only fulfills search engine requirements but also entails end users, leading to far better traffic and improved online engagement.
In essence, the right backlink technique, especially one that employs refreshing and dependable donor bases like Alex’s, can change your SEO efforts. By focusing on high quality over amount and sticking to the newest standards, you can guarantee your backlinks are both potent and effective.
cialisВ® online
[url=https://vatrex.online/]valtrex over the counter canada[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]online pharmacy no presc uk[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.online/]order lisinopril online from canada[/url]
[url=https://drugstorepp.online/]good online mexican pharmacy[/url]
九州娛樂城
[url=https://ametformin.com/]metformin 1500[/url]
[url=https://metforminbi.online/]ordering metformin on line without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canada drugstore pharmacy rx[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]canadian pharmacy 24 com[/url]
Проверка Тетер для чистоту: Как обезопасить собственные криптовалютные средства
Постоянно все больше пользователей обращают внимание к надежность своих цифровых активов. День ото дня дельцы придумывают новые методы кражи цифровых денег, и собственники цифровой валюты являются пострадавшими своих обманов. Один из техник защиты становится проверка кошельков на наличие противозаконных денег.
С каким намерением это потребуется?
Прежде всего, для того чтобы обезопасить свои финансы против дельцов а также похищенных денег. Многие вкладчики сталкиваются с риском утраты их фондов из-за мошеннических планов либо краж. Осмотр кошельков помогает выявить подозрительные действия или предотвратить возможные убытки.
Что мы предлагаем?
Мы предлагаем сервис проверки криптовалютных кошельков а также транзакций для определения источника средств. Наша технология проверяет информацию для выявления противозаконных транзакций а также оценки угрозы вашего счета. Вследствие этой проверке, вы сможете избегать недочетов с регуляторами а также предохранить себя от участия в незаконных сделках.
Каким образом это работает?
Наша фирма сотрудничаем с первоклассными аудиторскими агентствами, наподобие Halborn, с целью обеспечить аккуратность наших проверок. Мы применяем современные техники для выявления потенциально опасных операций. Ваши информация обрабатываются и сохраняются согласно с высокими стандартами безопасности и конфиденциальности.
Как выявить личные USDT в чистоту?
При наличии желания убедиться, что ваша Tether-кошельки нетронуты, наш сервис обеспечивает бесплатную проверку первых пяти кошельков. Легко передайте адрес своего кошелька на на сайте, и также мы предоставим вам полную информацию доклад о его статусе.
Обезопасьте ваши фонды прямо сейчас!
Избегайте риска подвергнуться мошенников или оказаться в неприятную ситуацию вследствие незаконных операций. Обратитесь за помощью к нашему агентству, чтобы защитить ваши криптовалютные финансовые ресурсы и предотвратить проблем. Сделайте первый шаг к сохранности вашего криптовалютного портфеля прямо сейчас!
[url=https://prednisonexg.online/]prednixone tables for sale[/url]
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]how much is synthroid[/url]
טלגראס כיוונים
פרח כיוונים: המדריך השלם לסחר פרחי קנאביס דרך הטלגרם
שרף מדריך הם פורטל ידע ומשלחי לקניית קנאביסין במקום האפליקציה הנפוצה המשלוח.
האתר סופק את כל הקישורים הידיעתיים והמידעים המתעדף להקבוצות וערוצים הנבחרים מומלצים לביקור לסחר ב קנאביס בהמסר במדינה.
כמו כן, אתר האינטרנט מספקת מדריך מפורטת לאיך כדאי להתכנן בהפרח ולרכוש פרחי קנאביס בקלות הזמנה ובמהירות.
בעזרת ההוראות, גם כן משתמשי הערוץ משתמשים חדשים יוכלו להירשם להחיים הקנאביס בהמשלוח בצורה מאובטחת ומאובטחת לשימוש.
ההאוטומטיזציה של הפרח מאפשר למשתמשים ללהוציא פעולות המבוצעות שונות כמו כן השקת פרחי קנאביס, קבלת תמיכה תמיכה, בדיקת המלאי והכנסת ביקורות על מוצרים. כל זאת בפני נוחה לשימוש וקלה דרך היישומון.
כאשר כאשר מדובר באמצעים התשלום, הפרח מפעילה בדרכי מוכרות כגון מזומן, כרטיסי האשראי של אשראי וקריפטומונדה. חשוב לציין כי ישנה לבדוק ולוודא את ההוראות והחוקות המקומיים בארץ שלך ללפני ביצוע רכישה.
טלגרם מציע הטבות מרכזיים כגון פרטיות ובטיחות מוגברים מאוד, השיחה מהירה וגמישות גבוהה מאוד. בנוסף, הוא מאפשר כניסה להקהילה עולמית רחבה מאוד ומציע מגוון של תכונות ויכולות.
בבתום, הטלגרמה מדריכים היא המקום המושלם ללמצוא את כל הידע והקישורים להשקיה פרחי קנאביס בצורה מהירה, בבטוחה ונוחה מאוד דרך הטלגרמה.
[url=http://bestprednisone.online/]medication prednisone 20 mg[/url]
קזינו אונליין
הימורים ברשת הם חוויה מרגשות ופופולרית ביותר בעידן הדיגיטלי, שמגירה מיליוני אנשים מכל
רחבי העולם. ההימורים המקוונים מתבצעים בהתאם ל אירועים ספורטיביים, תוצאות פוליטיות ואפילו תוצאות מזג האוויר ונושאים נוספים. אתרים ל הימורים הווירטואליים מקריאים פוטנציאליים את כל מי שרוצה להמרות על תוצאות אפשריות וליהנות רגעים מרגשים ומהנים.
ההימורים המקוונים הם מהם כבר חלק חשוב מתרבות האנושית מזמן רב והיום הם לא רק רק חלק חשוב מהפעילות התרבותית והכלכלית, אלא גם מספקים רווחים וחוויות מרתקות. משום שהם נגישים ונוחים לשימוש, הם מאפשרים לכולם מהמשחק ולהנציח רגעי עסקה וניצחון בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
טכנולוגיות מתקדמות והמשחקים באינטרנט הפכו מעניינת ונפוצה. מיליוני אנשים מכל כל רחבי העולם מתעניינים בהימורים מקוונים, כוללים סוגים שונים של הימורים. הימורים מקוונים מציעים למשתתפים חוויה מהנה ומרגשת, המתאימה לכולם בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
אז מה חכם אתה מחכה לו? הצטרף עכשיו והתחיל ליהנות מכל רגע ורגע שההימורים באינטרנט מבטיחים.
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril price in india[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.online/]best cialis pill[/url]
Backlink pyramid
Sure, here’s the text with spin syntax applied:
Link Pyramid
After numerous updates to the G search mechanism, it is essential to use different options for ranking.
Today there is a approach to draw the attention of search engines to your site with the assistance of backlinks.
Links are not only an efficient promotional instrument but they also have natural traffic, straight sales from these resources possibly will not be, but transitions will be, and it is poyedenicheskogo visitors that we also receive.
What in the end we get at the final outcome:
We show search engines site through links.
Prluuchayut organic click-throughs to the site and it is also a sign to search engines that the resource is used by users.
How we show search engines that the site is valuable:
Links do to the main page where the main information.
We make links through redirects credible sites.
The most CRUCIAL we place the site on sites analyzers distinct tool, the site goes into the cache of these analyzers, then the acquired links we place as redirections on blogs, forums, comments. This significant action shows search engines the site map as analysis tool sites present all information about sites with all key terms and headings and it is very POSITIVE.
All details about our services is on the website!
[url=https://isynthroid.online/]cost of synthroid 175 mcg[/url]
crestor pills hop – crestor pills history caduet cousin
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]legitimate online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]online pharmacy without scripts[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprill.com/]lisinopril 2016[/url]
Creating hyperlinks is simply equally successful currently, only the tools for working within this domain have altered.
You can find numerous options for backlinks, our team use some of them, and these methods work and have been tried by us and our customers.
Not long ago we carried out an test and it turned out that low-frequency searches from a single domain name rank nicely in search engines, and the result doesnt need to be your own domain, you are able to use social media from web2.0 range for this.
It additionally possible to in part transfer weight through site redirects, giving a varied hyperlink profile.
Head over to our very own website where our own offerings are actually provided with comprehensive explanations.
[url=https://azithromycinmds.com/]can you buy azithromycin over the counter in usa[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]legitimate online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://metformin.store/]metformin 100 mg tablets[/url]
creating articles
Creating unique articles on Platform and Platform, why it is required:
Created article on these resources is better ranked on less common queries, which is very crucial to get natural traffic.
We get:
organic traffic from search engines.
natural traffic from the inner rendition of the medium.
The webpage to which the article refers gets a link that is liquid and increases the ranking of the webpage to which the article refers.
Articles can be made in any number and choose all low-frequency queries on your topic.
Medium pages are indexed by search algorithms very well.
Telegraph pages need to be indexed individually indexer and at the same time after indexing they sometimes occupy spots higher in the search algorithms than the medium, these two platforms are very valuable for getting traffic.
Here is a hyperlink to our offerings where we offer creation, indexing of sites, articles, pages and more.
vảy gà
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]safe online pharmacies[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]canadian pharmacy no rx needed[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]online pharmacy no rx[/url]
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex 500mg price canada[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]canada pharmacy online legit[/url]
can i take levitra every day
cost of cialis in canada
I highly advise to avoid this platform. My personal experience with it has been only frustration and doubts about deceptive behavior. Be extremely cautious, or even better, look for a more reputable service to meet your needs.
[url=https://synthroidx.com/]synthroid 25 mg coupon[/url]
what is cialis tadalafil 20 mg used for
откупиться от сво
С началом СВО уже спустя полгода была объявлена первая волна мобилизации. При этом прошлая, в последний раз в России была аж в 1941 году, с началом Великой Отечественной Войны. Конечно же, желающих отправиться на фронт было не много, а потому люди стали искать способы не попасть на СВО, для чего стали покупать справки о болезнях, с которыми можно получить категорию Д. И все это стало возможным с даркнет сайтами, где можно найти практически все что угодно. Именно об этой отрасли темного интернета подробней и поговорим в этой статье.
online levitra order
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
https://maps.google.cv/url?q=https://www.openlearning.com/u/vincentshapiro-scybf7/blog/0
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]valtrex australia buy[/url]
canada cialis with dapoxetine
levitra online sale
[url=https://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil online rx[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]valtrex daily cost[/url]
whoah this weblog is great i really like studying your posts. Stay up the good work! You understand, a lot of individuals are looking around for this information, you could aid them greatly.
https://images.google.cf/url?q=https://rentry.co/m5pqdsws
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]buy lisinopril in mexico[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]cheapest pharmacy prescription drugs[/url]
Hi there i am kavin, its my first time to commenting anyplace, when i read this article i thought i could also make comment due to this good paragraph.
https://postheaven.net/jeniusixaa/remont-abo-zamina-korpusu-fari-shcho-obrati-shchob-pokrashchiti-osvitlennia
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]happy family pharm[/url]
[url=https://isynthroid.online/]synthroid 0.025 mg[/url]
[url=http://isynthroid.com/]synthroid 2017[/url]
[url=http://medicinesaf.online/]online pharmacy dubai[/url]
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid nz[/url]
canadian pharmacy levitra
cialis 20 mg price cvs
Pirámide de backlinks
Aquí está el texto con la estructura de spintax que propone diferentes sinónimos para cada palabra:
“Pirámide de enlaces de retroceso
Después de muchas actualizaciones del motor de búsqueda G, necesita aplicar diferentes opciones de clasificación.
Hay una manera de hacerlo de llamar la atención de los motores de búsqueda a su sitio web con backlinks.
Los vínculos de retroceso no sólo son una herramienta eficaz para la promoción, sino que también tienen tráfico orgánico, las ventas directas de estos recursos más probable es que no será, pero las transiciones será, y es poedenicheskogo tráfico que también obtenemos.
Lo que vamos a obtener al final en la salida:
Mostramos el sitio a los motores de búsqueda a través de backlinks.
Conseguimos conversiones orgánicas hacia el sitio, lo que también es una señal para los buscadores de que el recurso está siendo utilizado por la gente.
Cómo mostramos los motores de búsqueda que el sitio es líquido:
1 backlink se hace a la página principal donde está la información principal
Hacemos enlaces de retroceso a través de redirecciones de sitios de confianza
Lo más crucial colocamos el sitio en una herramienta independiente de analizadores de sitios, el sitio entra en la caché de estos analizadores, luego los enlaces recibidos los colocamos como redirecciones en blogs, foros, comentarios.
Esta importante acción muestra a los buscadores el MAPA DEL SITIO, ya que los analizadores de sitios muestran toda la información de los sitios con todas las palabras clave y títulos y es muy BUENO.
¡Toda la información sobre nuestros servicios en el sitio web!
[url=http://metforemin.online/]buying metformin online[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin tablets 250 mg[/url]
反向連結金字塔
G搜尋引擎在屡经更新后需要应用不同的排名參數。
今天有一種方法可以使用反向連結吸引G搜尋引擎對您的網站的注意。
反向連結不僅是有效的推廣工具,也是有機流量。
我們會得到什麼結果:
我們透過反向連結向G搜尋引擎展示我們的網站。
他們收到了到該網站的自然過渡,這也是向G搜尋引擎發出的信號,表明該資源正在被人們使用。
我們如何向G搜尋引擎表明該網站具有流動性:
個帶有主要訊息的主頁反向鏈接
我們透過來自受信任網站的重新定向來建立反向連結。
此外,我們將網站放置在单独的網路分析器上,網站最終會進入這些分析器的高速缓存中,然後我們使用產生的連結作為部落格、論壇和評論的重定向。 這個重要的操作向G搜尋引擎顯示了網站地圖,因為網站分析器顯示了有關網站的所有資訊以及所有關鍵字和標題,這很棒
有關我們服務的所有資訊都在網站上!
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]zithromax 500mg for sale[/url]
[url=http://prednisoneiv.online/]prednisone mexico[/url]
I urge you steer clear of this site. My personal experience with it was nothing but disappointment along with concerns regarding scamming practices. Proceed with extreme caution, or even better, find a more reputable service for your needs.
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в сообщество профессионалов или продолжить обучение в любом университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом, что будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество такого решения состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора нужного образца документа до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
diploman-russia.com
Купить диплом без лишних хлопот
купить диплом Гознак [url=http://www.diplom-msk.ru/]http://www.diplom-msk.ru/[/url] .
[url=https://tadalafilgf.com/]tadalafil price in india[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]tadalafil 15mg[/url]
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.online/]buy prinivil online[/url]
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия официального документа трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете заказать диплом старого или нового образца, что будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы на выходе получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора требуемого образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем наших мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russiyan.com
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
Aceon
[url=http://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 137 mg[/url]
20 mg sildenafil
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в любом университете.
Мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом, что является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Превосходство подобного решения заключается не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца диплома до грамотного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто пытается найти максимально быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russiyan.com
[url=http://valtrexmedication.com/]buy valtrex canada[/url]
[url=http://valtrexarb.online/]how to get valtrex without a prescription[/url]
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]online pharmacy indonesia[/url]
It’s onerous to find educated individuals on this topic, however you sound like you realize what you’re speaking about! Thanks
sildenafil citrate tablets 100mg
взлом кошелька
Как защитить свои данные: берегитесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня сохранение личных данных становится всё более важной задачей. Одним из наиболее распространенных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и как предохранить себя от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это синтезы слов или фраз, которые часто используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, при помощи этих сит фраз. Как охранить свои личные данные? Используйте комплексные пароли. Избегайте использования простых паролей, которые просто угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого аккаунта. Не используйте один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухступенчатую аутентификацию (2FA). Это прибавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт путем другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте свою информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы защитить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может спровоцировать серьезным последствиям, таким подобно кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы охранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
[url=https://lisinoprildrl.online/]lisinopril price in canada[/url]
кошелек с балансом купить
Криптокошельки с балансом: зачем их покупают и как использовать
В мире криптовалют все расширяющуюся популярность приобретают криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом. Это индивидуальные кошельки, которые уже содержат определенное количество криптовалюты на момент покупки. Но зачем люди приобретают такие кошельки, и как правильно использовать их?
Почему покупают криптокошельки с балансом?
Удобство: Криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом предлагаются как готовое к применению решение для тех, кто хочет быстро начать пользоваться криптовалютой без необходимости покупки или обмена на бирже.
Подарок или награда: Иногда криптокошельки с балансом используются как подарок или поощрение в рамках акций или маркетинговых кампаний.
Анонимность: При покупке криптокошелька с балансом нет необходимости предоставлять личные данные, что может быть важно для тех, кто ценит анонимность.
Как использовать криптокошелек с балансом?
Проверьте безопасность: Убедитесь, что кошелек безопасен и не подвержен взлому. Проверьте репутацию продавца и источник приобретения кошелька.
Переведите средства на другой кошелек: Если вы хотите долгосрочно хранить криптовалюту, рекомендуется перевести средства на более безопасный или удобный для вас кошелек.
Не храните все средства на одном кошельке: Для обеспечения безопасности рекомендуется распределить средства между несколькими кошельками.
Будьте осторожны с фишингом и мошенничеством: Помните, что мошенники могут пытаться обмануть вас, предлагая криптокошельки с балансом с целью получения доступа к вашим средствам.
Заключение
Криптокошельки с балансом могут быть удобным и скорым способом начать пользоваться криптовалютой, но необходимо помнить о безопасности и осторожности при их использовании.Выбор и приобретение криптокошелька с балансом – это серьезный шаг, который требует внимания к деталям и осознанного подхода.”
Сид-фразы, или памятные фразы, представляют собой сумму слов, которая используется для формирования или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Эти фразы обеспечивают вход к вашим криптовалютным средствам, поэтому их секурное хранение и использование очень важны для защиты вашего криптоимущества от утери и кражи.
Что такое сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют?
Сид-фразы являются набор случайным образом сгенерированных слов, часто от 12 до 24, которые представляют собой для создания уникального ключа шифрования кошелька. Этот ключ используется для восстановления возможности доступа к вашему кошельку в случае его повреждения или утери. Сид-фразы обладают высокой защиты и шифруются, что делает их секурными для хранения и передачи.
Зачем нужны сид-фразы?
Сид-фразы обязательны для обеспечения безопасности и доступности вашего криптоимущества. Они позволяют восстановить возможность доступа к кошельку в случае утери или повреждения физического устройства, на котором он хранится. Благодаря сид-фразам вы можете легко создавать резервные копии своего кошелька и хранить их в безопасном месте.
Как обеспечить безопасность сид-фраз кошельков?
Никогда не делитесь сид-фразой ни с кем. Сид-фраза является вашим ключом к кошельку, и ее раскрытие может привести к утере вашего криптоимущества.
Храните сид-фразу в надежном месте. Используйте физически секурные места, такие как банковские ячейки или специализированные аппаратные кошельки, для хранения вашей сид-фразы.
Создавайте резервные копии сид-фразы. Регулярно создавайте резервные копии вашей сид-фразы и храните их в разных безопасных местах, чтобы обеспечить вход к вашему кошельку в случае утери или повреждения.
Используйте дополнительные меры безопасности. Включите двухфакторную верификацию и другие методы защиты для своего кошелька криптовалюты, чтобы обеспечить дополнительный уровень безопасности.
Заключение
Сид-фразы кошельков криптовалют являются ключевым элементом секурного хранения криптоимущества. Следуйте рекомендациям по безопасности, чтобы защитить свою сид-фразу и обеспечить безопасность своих криптовалютных средств.
слив сид фраз
Слив мнемонических фраз (seed phrases) является одним из наиболее популярных способов утечки личных информации в мире криптовалют. В этой статье мы разберем, что такое сид фразы, по какой причине они важны и как можно защититься от их утечки.
Что такое сид фразы?
Сид фразы, или мнемонические фразы, являются комбинацию слов, которая используется для создания или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Обычно сид фраза состоит из 12 или 24 слов, которые отражают собой ключ к вашему кошельку. Потеря или утечка сид фразы может привести к потере доступа к вашим криптовалютным средствам.
Почему важно защищать сид фразы?
Сид фразы представляют собой ключевым элементом для защищенного хранения криптовалюты. Если злоумышленники получат доступ к вашей сид фразе, они будут в состоянии получить доступ к вашему кошельку и украсть все средства.
Как защититься от утечки сид фраз?
Никогда не передавайте свою сид фразу любому, даже если вам происходит, что это доверенное лицо или сервис.
Храните свою сид фразу в безопасном и защищенном месте. Рекомендуется использовать аппаратные кошельки или специальные программы для хранения сид фразы.
Используйте дополнительные методы защиты, такие как двусторонняя аутентификация, для усиления безопасности вашего кошелька.
Регулярно делайте резервные копии своей сид фразы и храните их в разных безопасных местах.
Заключение
Слив сид фраз является существенной угрозой для безопасности владельцев криптовалют. Понимание важности защиты сид фразы и принятие соответствующих мер безопасности помогут вам избежать потери ваших криптовалютных средств. Будьте бдительны и обеспечивайте надежную защиту своей сид фразы
Структура Backlinks
После того, как многочисленных обновлений поисковой системы G необходимо внедрять разные варианты ранжирования.
Сегодня есть способ привлечь внимание поисковых систем к вашему сайту с помощью бэклинков.
Обратные ссылки представляют собой эффективный инструмент продвижения, но и являются источником органического трафика, хотя прямых продаж с этих ресурсов скорее всего не будет, но переходы будут, и именно органического трафика мы также получаем.
Что в итоге получим на выходе:
Мы демонстрируем сайт поисковым системам с помощью обратных ссылок.
Получают органические переходы на сайт, а это также информация для поисковых систем, что ресурс пользуется спросом у пользователей.
Как мы демонстрируем поисковым системам, что сайт ликвиден:
1 ссылка на главную страницу, где содержится основная информация, создается.
Создаем обратные ссылки с использованием редиректов с доверенных сайтов.
Основное – мы индексируем сайт с помощью специальных инструментов анализа веб-сайтов, сайт заносится в кеш этих инструментов, после чего полученные ссылки мы публикуем в качестве редиректов на блогах, форумах, в комментариях.
Это важное действие показывает поисковым системамКАРТУ САЙТА, так как анализаторы сайтов отображают всю информацию о сайтах со всеми ключевыми словами и заголовками и это очень ХОРОШО
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious experience regarding unexpected feelings.
grocery store pharmacy
[url=https://lisinoprilgp.com/]prinivil 5 mg[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]mexican pharmacies online drugs[/url]
Wonderful, what a blog it is! This website provides helpful facts to us, keep it up.
https:/diploman-rossiya.com/
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, желающими начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца диплома до точного заполнения персональных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для тех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://diplomanc-russia24.com
В нашем мире, где диплом является началом удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем очень быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом, что будет выгодным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам. В итоге вы сможете получить полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества этого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного обучения и сразу переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу удачной карьеры.
http://diplomanc-russia24.com
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]can i buy tadalafil in canada[/url]
I needed to create you one very small remark to be able to thank you very much as before with the awesome secrets you’ve provided on this site. It has been open-handed with you to deliver easily precisely what numerous people would have marketed for an electronic book to get some dough for themselves, most importantly seeing that you might well have tried it if you ever desired. The secrets additionally acted like the great way to realize that the rest have a similar fervor really like my personal own to realize very much more concerning this matter. I know there are several more enjoyable times up front for many who look into your site.
100mg sildenafil
bupropion target pharmacy
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой области, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все дипломы производятся аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам. В результате вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество этого подхода состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до грамотного заполнения личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
vuzdiploma
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]cheapest tadalafil cost[/url]
I highly advise steer clear of this platform. My own encounter with it has been only frustration along with concerns regarding deceptive behavior. Exercise extreme caution, or better yet, find a trustworthy platform to meet your needs.
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который желает начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в каком-либо институте.
Мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это является отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество подобного подхода состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца диплома до консультаций по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к личным целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://www.diplomvam.ru
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful article. Thanks for supplying these details.
https://cinemarus.ru/
tramadol pharmacy reviews
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Важность наличия документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который собирается начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в любом ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство такого решения состоит не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован просто и легко, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца документа до точного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Для всех, кто хочет найти максимально быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
diplomany.ru
[url=http://predniso.online/]canadian online pharmacy prednisone[/url]
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
娛樂城推薦
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
[url=http://lisinoprilgp.com/]lisinopril cost 40 mg[/url]
Как обезопасить свои личные данные: остерегайтесь утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня обеспечение безопасности информации становится более насущной важной задачей. Одним из наиболее распространенных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в каком объеме сберечься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это синтезы слов или фраз, которые регулярно используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или другие конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, используя этих сит фраз. Как сохранить свои личные данные? Используйте сложные пароли. Избегайте использования очевидных паролей, которые легко угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для всего аккаунта. Не пользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухступенчатую аутентификацию (2FA). Это прибавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт путем другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте личную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы предохранить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может спровоцировать серьезным последствиям, таким как кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
sildenafil dose
даркнет сливы тг
Даркнет и сливы в Телеграме
Даркнет – это сегмент интернета, которая не индексируется обычными поисковыми системами и требует особых программных средств для доступа. В даркнете существует масса скрытых сайтов, где можно найти различные товары и услуги, в том числе и нелегальные.
Одним из популярных способов распространения информации в даркнете является использование мессенджера Телеграм. Телеграм предоставляет возможность создания закрытых каналов и чатов, где пользователи могут обмениваться информацией, в том числе и нелегальной.
Сливы информации в Телеграме – это метод распространения конфиденциальной информации, такой как украденные данные, базы данных, персональные сведения и другие материалы. Эти сливы могут включать в себя информацию о кредитных картах, паролях, персональных сообщениях и даже фотографиях.
Сливы в Телеграме могут быть опасными, так как они могут привести к утечке конфиденциальной информации и нанести ущерб репутации и финансовым интересам людей. Поэтому важно быть бдительным при обмене информацией в интернете и не доверять сомнительным источникам.
Вот кошельки с балансом у бота
кошелек с балансом купить
Криптокошельки с балансом: зачем их покупают и как использовать
В мире криптовалют все расширяющуюся популярность приобретают криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом. Это специальные кошельки, которые уже содержат определенное количество криптовалюты на момент покупки. Но зачем люди приобретают такие кошельки, и как правильно использовать их?
Почему покупают криптокошельки с балансом?
Удобство: Криптокошельки с предустановленным балансом предлагаются как готовое к работе решение для тех, кто хочет быстро начать пользоваться криптовалютой без необходимости покупки или обмена на бирже.
Подарок или награда: Иногда криптокошельки с балансом используются как подарок или вознаграждение в рамках акций или маркетинговых кампаний.
Анонимность: При покупке криптокошелька с балансом нет необходимости предоставлять личные данные, что может быть важно для тех, кто ценит анонимность.
Как использовать криптокошелек с балансом?
Проверьте безопасность: Убедитесь, что кошелек безопасен и не подвержен взлому. Проверьте репутацию продавца и источник приобретения кошелька.
Переведите средства на другой кошелек: Если вы хотите долгосрочно хранить криптовалюту, рекомендуется перевести средства на более безопасный или комфортный для вас кошелек.
Не храните все средства на одном кошельке: Для обеспечения безопасности рекомендуется распределить средства между несколькими кошельками.
Будьте осторожны с фишингом и мошенничеством: Помните, что мошенники могут пытаться обмануть вас, предлагая криптокошельки с балансом с целью получения доступа к вашим средствам.
Заключение
Криптокошельки с балансом могут быть удобным и скорым способом начать пользоваться криптовалютой, но необходимо помнить о безопасности и осторожности при их использовании.Выбор и приобретение криптокошелька с балансом – это весомый шаг, который требует внимания к деталям и осознанного подхода.”
Слив мнемонических фраз (seed phrases) является одной из наиболее популярных способов утечки личных информации в мире криптовалют. В этой статье мы разберем, что такое сид фразы, по какой причине они важны и как можно защититься от их утечки.
Что такое сид фразы?
Сид фразы, или мнемонические фразы, формируют комбинацию слов, которая используется для создания или восстановления кошелька криптовалюты. Обычно сид фраза состоит из 12 или 24 слов, которые являются собой ключ к вашему кошельку. Потеря или утечка сид фразы может привести к потере доступа к вашим криптовалютным средствам.
Почему важно защищать сид фразы?
Сид фразы являются ключевым элементом для защищенного хранения криптовалюты. Если злоумышленники получат доступ к вашей сид фразе, они смогут получить доступ к вашему кошельку и украсть все средства.
Как защититься от утечки сид фраз?
Никогда не передавайте свою сид фразу ничьему, даже если вам кажется, что это проверенное лицо или сервис.
Храните свою сид фразу в безопасном и секурном месте. Рекомендуется использовать аппаратные кошельки или специальные программы для хранения сид фразы.
Используйте дополнительные методы защиты, такие как двухфакторная аутентификация (2FA), для усиления безопасности вашего кошелька.
Регулярно делайте резервные копии своей сид фразы и храните их в разнообразных безопасных местах.
Заключение
Слив сид фраз является существенной угрозой для безопасности владельцев криптовалют. Понимание важности защиты сид фразы и принятие соответствующих мер безопасности помогут вам избежать потери ваших криптовалютных средств. Будьте бдительны и обеспечивайте надежную защиту своей сид фразы
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед всеми, кто желает начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает очень быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить образование, потерял документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. Все дипломы изготавливаются аккуратно, с особым вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В итоге вы сможете получить продукт, полностью соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного решения заключаются не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить диплом. Процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора подходящего образца документа до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
vsediplomu.ru
[url=https://olisinopril.com/]lisinopril 40 mg mexico[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]capsule online pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]canadianpharmacymeds com[/url]
[url=https://tadalafi.online/]cheap tadalafil 20mg[/url]
На сегодняшний день, когда диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой сфере, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает дверь перед любым человеком, который стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем деталям, чтобы в итоге получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы подобного решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все будет находиться под полным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Для всех, кто ищет оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу трудовой карьеры.
http://www.ab-diplom.ru
Thank you for sharing your info. I really appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your further post thanks once again.
https://animemedia.me/
I think that everything said made a ton of sense. However, what about this? what if you wrote a catchier title? I ain’t suggesting your information isn’t solid., however suppose you added a headline that makes people desire more? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is kinda vanilla. You should peek at Yahoo’s front page and see how they create article headlines to get people interested. You might add a video or a related pic or two to grab readers interested about what you’ve written. Just my opinion, it might make your posts a little bit more interesting.
https://cinemarus.ru/
هنا النص مع استخدام السبينتاكس:
“بناء الروابط الخلفية
بعد التحديثات العديدة لمحرك البحث G، تحتاج إلى تطويق خيارات ترتيب مختلفة.
هناك أسلوب لجذب انتباه محركات البحث إلى موقعك على الويب باستخدام الروابط الخلفية.
الروابط الخلفية ليست فقط أداة فعالة للترويج، ولكن تتضمن أيضًا حركة مرور عضوية، والمبيعات المباشرة من هذه الموارد على الأرجح ستكون كذلك، ولكن الانتقالات ستكون، وهي حركة المرور التي نحصل عليها أيضًا.
ما سوف نحصل عليه في النهاية في النهاية في الإخراج:
نعرض الموقع لمحركات البحث من خلال الروابط الخلفية.
2- نحصل على تبديلات عضوية إلى الموقع، وهي أيضًا إشارة لمحركات البحث أن المورد يستخدمه الناس.
كيف نظهر لمحركات البحث أن الموقع سائل:
1 يتم عمل صلة خلفي للصفحة الرئيسية حيث المعلومات الرئيسية
نقوم بعمل صلات خلفية من خلال عمليات توجيه المواقع الموثوقة
الأهم من ذلك أننا نضع الموقع على أداة منفصلة من أدوات تحليل المواقع، ويدخل الموقع في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لهذه المحللات، ثم الروابط المستلمة التي نضعها كتوجيه مرة أخرى على المدونات والمنتديات والتعليقات.
هذا التدبير المهم يبين لمحركات البحث خريطة الموقع، حيث تعرض أدوات تحليل المواقع جميع المعلومات عن المواقع مع جميع الكلمات الرئيسية والعناوين وهو شيء جيد جداً
جميع المعلومات عن خدماتنا على الموقع!
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone order online uk[/url]
Kantorbola adalah situs slot gacor terbaik di indonesia , kunjungi situs RTP kantor bola untuk mendapatkan informasi akurat slot dengan rtp diatas 95% . Kunjungi juga link alternatif kami di kantorbola77 dan kantorbola99 .
В нашем обществе, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы сможете купить диплом, что является удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца документа до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки в любой регион страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
Для тех, кто хочет найти оперативный способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://www.diplomexpress.ru
I strongly recommend steer clear of this site. The experience I had with it has been nothing but dismay along with concerns regarding scamming practices. Proceed with extreme caution, or better yet, look for an honest site to meet your needs.
В нашем мире, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый и простой путь получения качественного образования. Важность наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает двери перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы сможете заказать диплом нового или старого образца, и это является отличным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или потерял документ. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы получите документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество данного подхода заключается не только в том, что можно максимально быстро получить диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца документа до консультаций по заполнению личной информации и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем наших специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто пытается найти быстрый способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать продолжительного процесса обучения и сразу перейти к достижению собственных целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
http://www.99diplomov.ru
В нашем мире, где диплом – это начало успешной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа переоценить попросту невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, желающим вступить в профессиональное сообщество или учиться в университете.
Мы предлагаем очень быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы получите документ, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Плюсы такого решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете оперативно получить свой диплом. Весь процесс организован удобно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любой регион России — все под абсолютным контролем опытных специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания готова предложить отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
ab-diplom.ru
[url=https://valtrexmedication.com/]valtrex for sale[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.com/]mexican pharmacy what to buy[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]online pharmacy delivery[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало отличной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим вступить в сообщество профессионалов или учиться в университете.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем оперативно получить этот необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, что становится отличным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, потерял документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в результате получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества подобного подхода состоят не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Весь процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора требуемого образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все будет находиться под полным контролем опытных специалистов.
В итоге, для всех, кто ищет быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
https://diplom-msk.ru/
В современном мире, где диплом становится началом успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие стараются найти максимально быстрый путь получения образования. Важность наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед любым человеком, желающим начать профессиональную деятельность или учиться в каком-либо университете.
Мы предлагаем оперативно получить любой необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это является выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или хочет исправить плохие оценки. диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. На выходе вы получите документ, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущества данного решения состоят не только в том, что вы сможете максимально быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. От выбора необходимого образца до грамотного заполнения персональных данных и доставки в любое место страны — все под абсолютным контролем качественных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет оперативный способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению своих целей, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало успешной карьеры.
http://www.diplom-gotovie.ru
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid 25 mcg tablet[/url]
[url=http://happyfamilystorerx.online/]best no prescription pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]safe reliable canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://synthroidsl.online/]synthroid brand cost[/url]
That is very attention-grabbing, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look ahead to looking for extra of your excellent post. Additionally, I have shared your site in my social networks
http://www.diplom07.ru
[url=https://happyfamilystorerx.online/]happy family medicine[/url]
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil brand name in india[/url]
[url=https://bmtadalafil.online/]tadalafil india 5mg[/url]
[url=http://synthroidotp.online/]cost of synthroid generic[/url]
В современном мире, где диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом, и это будет удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить плохие оценки. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился продукт, 100% соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство этого решения заключается не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора нужного образца документа до консультаций по заполнению личных данных и доставки по стране — все под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто ищет оперативный способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
russa24-attestats.com
В наше время, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любой сфере, многие стараются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Наличие официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед любым человеком, желающим начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете купить диплом нового или старого образца, что является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все дипломы выпускаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы на выходе получился продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить свой диплом. Процесс организован комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до консультации по заполнению персональной информации и доставки по России — все под полным контролем опытных мастеров.
Всем, кто пытается найти оперативный способ получить требуемый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к личным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://saksx-attestats.ru
[url=https://azithromycinps.online/]can you purchase zithromax[/url]
[url=http://bestmedsx.com/]canadian pharmacy world coupon[/url]
[url=https://tadalafilstd.com/]tadalafil 30mg tablet[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilgf.com/]tadalafil 2.5 mg price[/url]
I highly advise to avoid this site. My personal experience with it was purely frustration and concerns regarding scamming practices. Exercise extreme caution, or better yet, seek out a more reputable service for your needs.
[url=http://drugstorepp.online/]canada cloud pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://synthroidx.online/]synthroid prices[/url]
Hello there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog. Is it hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to begin. Do you have any points or suggestions? Thank you
arusak-attestats.ru
[url=http://bmtadalafil.online/]buy tadalafil cheap[/url]
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]prednisolone prednisone[/url]
[url=http://olisinopril.online/]zestril coupon[/url]
[url=https://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]top 10 pharmacies in india[/url]
[url=http://ametformin.com/]glucophage 1000 price[/url]
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]how much is azithromycin 1g[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]112 mg synthroid[/url]
[url=http://synthroidx.com/]synthroid purchase[/url]
I highly advise steer clear of this site. My personal experience with it has been purely disappointment and doubts about deceptive behavior. Be extremely cautious, or alternatively, find an honest platform to meet your needs.
Thank you for helping out, superb info. “Considering how dangerous everything is, nothing is really very frightening.” by Gertrude Stein.
[url=http://happyfamilymedicalstore.online/]happy family drugstore[/url]
[url=https://metformindi.online/]prices for metformin 500 mg[/url]
[url=http://tadalafilu.online/]80 mg tadalafil[/url]
[url=https://bestmedsx.online/]canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg[/url]
[url=https://bestprednisone.online/]prednisone 8 mg[/url]
[url=https://synthroidam.online/]synthroid india[/url]
[url=http://diflucanr.online/]diflucan 300 mg[/url]
india pharmacy vicodin
Rikvip Club: Trung Tâm Giải Trí Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu tại Việt Nam
Rikvip Club là một trong những nền tảng giải trí trực tuyến hàng đầu tại Việt Nam, cung cấp một loạt các trò chơi hấp dẫn và dịch vụ cho người dùng. Cho dù bạn là người dùng iPhone hay Android, Rikvip Club đều có một cái gì đó dành cho mọi người. Với sứ mạng và mục tiêu rõ ràng, Rikvip Club luôn cố gắng cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất cho khách hàng, tạo ra một trải nghiệm tiện lợi và thú vị cho người chơi.
Sứ Mạng và Mục Tiêu của Rikvip
Từ khi bắt đầu hoạt động, Rikvip Club đã có một kế hoạch kinh doanh rõ ràng, luôn nỗ lực để cung cấp cho khách hàng những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất và tạo điều kiện thuận lợi nhất cho người chơi truy cập. Nhóm quản lý của Rikvip Club có những mục tiêu và ước muốn quyết liệt để biến Rikvip Club thành trung tâm giải trí hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực game đổi thưởng trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và trên toàn cầu.
Trải Nghiệm Live Casino
Rikvip Club không chỉ nổi bật với sự đa dạng của các trò chơi đổi thưởng mà còn với các phòng trò chơi casino trực tuyến thu hút tất cả người chơi. Môi trường này cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm chuyên nghiệp với tính xanh chín và sự uy tín không thể nghi ngờ. Đây là một sân chơi lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích thách thức bản thân và muốn tận hưởng niềm vui của chiến thắng. Với các sảnh cược phổ biến như Roulette, Sic Bo, Dragon Tiger, người chơi sẽ trải nghiệm những cảm xúc độc đáo và đặc biệt khi tham gia vào casino trực tuyến.
Phương Thức Thanh Toán Tiện Lợi
Rikvip Club đã được trang bị những công nghệ thanh toán tiên tiến ngay từ đầu, mang lại sự thuận tiện và linh hoạt cho người chơi trong việc sử dụng hệ thống thanh toán hàng ngày. Hơn nữa, Rikvip Club còn tích hợp nhiều phương thức giao dịch khác nhau để đáp ứng nhu cầu đa dạng của người chơi: Chuyển khoản Ngân hàng, Thẻ cào, Ví điện tử…
Kết Luận
Tóm lại, Rikvip Club không chỉ là một nền tảng trò chơi, mà còn là một cộng đồng nơi người chơi có thể tụ tập để tận hưởng niềm vui của trò chơi và cảm giác hồi hộp khi chiến thắng. Với cam kết cung cấp những sản phẩm và dịch vụ tốt nhất, Rikvip Club chắc chắn là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những người yêu thích trò chơi trực tuyến tại Việt Nam và cả thế giới.
I urge you steer clear of this site. My personal experience with it has been only frustration along with concerns regarding scamming practices. Exercise extreme caution, or even better, seek out a more reputable platform for your needs.
sildenafil over the counter
[url=https://vermox.company/]medicine vermox[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом успешной карьеры в любой отрасли, многие ищут максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия документа об образовании переоценить невозможно. Ведь диплом открывает двери перед любым человеком, который собирается начать трудовую деятельность или учиться в ВУЗе.
Наша компания предлагает оперативно получить этот важный документ. Вы имеете возможность купить диплом нового или старого образца, и это становится выгодным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. дипломы изготавливаются с особой тщательностью, вниманием ко всем элементам. В результате вы получите продукт, максимально соответствующий оригиналу.
Превосходство такого подхода состоит не только в том, что вы быстро получите диплом. Процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начиная от выбора необходимого образца диплома до правильного заполнения персональной информации и доставки по России — все под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных специалистов.
В итоге, для тех, кто ищет максимально быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша услуга предлагает выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям: к поступлению в университет или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://www.diploman-russia.ru
benicar hct online pharmacy
[url=http://doxycyclineo.online/]doxycycline 100mg capsules price in india[/url]
Euro
UEFA Euro 2024 Sân Chơi Bóng Đá Hấp Dẫn Nhất Của Châu Âu
Euro 2024 là sự kiện bóng đá lớn nhất của châu Âu, không chỉ là một giải đấu mà còn là một cơ hội để các quốc gia thể hiện tài năng, sự đoàn kết và tinh thần cạnh tranh.
Euro 2024 hứa hẹn sẽ mang lại những trận cầu đỉnh cao và kịch tính cho người hâm mộ trên khắp thế giới. Cùng tìm hiểu các thêm thông tin hấp dẫn về giải đấu này tại bài viết dưới đây, gồm:
Nước chủ nhà
Đội tuyển tham dự
Thể thức thi đấu
Thời gian diễn ra
Sân vận động
Euro 2024 sẽ được tổ chức tại Đức, một quốc gia có truyền thống vàng của bóng đá châu Âu.
Đức là một đất nước giàu có lịch sử bóng đá với nhiều thành công quốc tế và trong những năm gần đây, họ đã thể hiện sức mạnh của mình ở cả mặt trận quốc tế và câu lạc bộ.
Việc tổ chức Euro 2024 tại Đức không chỉ là một cơ hội để thể hiện năng lực tổ chức tuyệt vời mà còn là một dịp để giới thiệu văn hóa và sức mạnh thể thao của quốc gia này.
Đội tuyển tham dự giải đấu Euro 2024
Euro 2024 sẽ quy tụ 24 đội tuyển hàng đầu từ châu Âu. Các đội tuyển này sẽ là những đại diện cho sự đa dạng văn hóa và phong cách chơi bóng đá trên khắp châu lục.
Các đội tuyển hàng đầu như Đức, Pháp, Tây Ban Nha, Bỉ, Italy, Anh và Hà Lan sẽ là những ứng viên nặng ký cho chức vô địch.
Trong khi đó, các đội tuyển nhỏ hơn như Iceland, Wales hay Áo cũng sẽ mang đến những bất ngờ và thách thức cho các đối thủ.
Các đội tuyển tham dự được chia thành 6 bảng đấu, gồm:
Bảng A: Đức, Scotland, Hungary và Thuỵ Sĩ
Bảng B: Tây Ban Nha, Croatia, Ý và Albania
Bảng C: Slovenia, Đan Mạch, Serbia và Anh
Bảng D: Ba Lan, Hà Lan, Áo và Pháp
Bảng E: Bỉ, Slovakia, Romania và Ukraina
Bảng F: Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ, Gruzia, Bồ Đào Nha và Cộng hoà Séc
선물옵션
국외선물의 개시 골드리치와 동행하세요.
골드리치는 길고긴기간 투자자분들과 더불어 선물마켓의 길을 공동으로 동행해왔으며, 투자자분들의 확실한 투자 및 건강한 이익률을 지향하여 언제나 전력을 기울이고 있습니다.
무엇때문에 20,000+인 넘게이 골드리치증권와 함께할까요?
즉각적인 대응: 간단하며 빠른 프로세스를 제공하여 모두 수월하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
안전보장 프로토콜: 국가기관에서 채택한 높은 등급의 보안체계을 도입하고 있습니다.
스마트 인증: 전체 거래내용은 암호화 처리되어 본인 이외에는 아무도 누구도 내용을 열람할 수 없습니다.
안전 이익률 제공: 위험 요소를 줄여, 더욱 더 안전한 수익률을 공개하며 이에 따른 리포트를 발간합니다.
24 / 7 지속적인 고객상담: 365일 24시간 실시간 서비스를 통해 고객님들을 온전히 지원합니다.
협력하는 협력사: 골드리치증권는 공기업은 물론 금융기관들 및 다수의 협력사와 함께 동행해오고.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 알아보세요.
해외선물은 국외에서 거래되는 파생상품 중 하나로, 특정 기초자산(예: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 바탕로 한 옵션 약정을 지칭합니다. 근본적으로 옵션은 특정 기초자산을 미래의 어떤 시기에 정해진 금액에 매수하거나 팔 수 있는 자격을 부여합니다. 외국선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 국외 시장에서 거래되는 것을 뜻합니다.
외국선물은 크게 매수 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 구분됩니다. 콜 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 금액에 사는 권리를 허락하는 반면, 풋 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 허락합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 명시된 일자에 (만기일이라 지칭되는) 일정 가격에 기초자산을 사거나 팔 수 있는 권리를 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 가격을 실행 금액이라고 하며, 종료일에는 해당 권리를 실행할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 투자자에게 향후의 가격 변동에 대한 보호나 이익 창출의 기회를 허락합니다.
국외선물은 시장 참가자들에게 다양한 운용 및 매매거래 기회를 마련, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산유형에 대한 옵션 계약을 포괄할 수 있습니다. 거래자는 매도 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 낙폭에 대한 안전장치를 받을 수 있고, 매수 옵션을 통해 상승장에서의 이익을 겨냥할 수 있습니다.
외국선물 거래의 원리
행사 가격(Exercise Price): 해외선물에서 행사 금액은 옵션 계약에 따라 명시된 금액으로 계약됩니다. 만료일에 이 금액을 기준으로 옵션을 행사할 수 있습니다.
종료일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만료일은 옵션의 행사가 불가능한 마지막 일자를 뜻합니다. 이 날짜 이후에는 옵션 계약이 만료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
매도 옵션(Put Option)과 콜 옵션(Call Option): 매도 옵션은 기초자산을 명시된 가격에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 부여하며, 콜 옵션은 기초자산을 명시된 가격에 매수하는 권리를 허락합니다.
프리미엄(Premium): 국외선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 옵션료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 가격으로, 마켓에서의 수요와 공급에 따라 변경됩니다.
실행 방안(Exercise Strategy): 거래자는 만료일에 옵션을 행사할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 이는 시장 상황 및 거래 플랜에 따라 차이가있으며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 최대화하거나 손해를 감소하기 위해 판단됩니다.
시장 리스크(Market Risk): 국외선물 거래는 시장의 변동성에 효과을 받습니다. 시세 변동이 기대치 못한 방향으로 발생할 경우 손실이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 마켓 위험요인를 최소화하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 수립하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치증권와 함께하는 국외선물은 보장된 신뢰할 수 있는 운용을 위한 최적의 옵션입니다. 투자자분들의 투자를 뒷받침하고 가이드하기 위해 우리는 최선을 기울이고 있습니다. 공동으로 더 나은 미래를 향해 나아가요.
[url=http://avermox.online/]buy vermox online usa[/url]
[url=http://lasixav.online/]furosemide 400 mg[/url]
[url=http://advaird.com/]lowest price for advair[/url]
shopko pharmacy
[url=http://baclofenx.com/]baclofen prescription uk[/url]
I urge you stay away from this platform. My personal experience with it has been only disappointment and concerns regarding fraudulent activities. Proceed with extreme caution, or even better, look for a trustworthy site to meet your needs.
what happens if you take too much sildenafil
I highly advise to avoid this site. My own encounter with it has been only disappointment along with doubts about deceptive behavior. Be extremely cautious, or better yet, find an honest platform for your needs.
I truly treasure your piece of work, Great post.
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]otc lyrica[/url]
[url=https://lasixtbs.online/]can i order furosemide[/url]
[url=http://lasixav.online/]ordering furosemide[/url]
clomid online pharmacy uk
[url=http://diflucanr.online/]where to get diflucan over the counter[/url]
[url=https://itretinoin.com/]tretinoin 0.1 discount[/url]
[url=https://lasixav.online/]furosemide pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]accutane 40[/url]
[url=http://acyclovirmc.com/]acyclovir cream mexico[/url]
[url=http://acutanep.online/]how much is accutane uk[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.com/]buy online diflucan[/url]
I highly advise steer clear of this platform. My own encounter with it was only frustration as well as doubts about deceptive behavior. Be extremely cautious, or even better, look for an honest platform to meet your needs.
[url=https://advaird.online/]advair diskus price in us[/url]
One of the leading academic and scientific-research centers of the Belarus. There are 12 Faculties at the University, 2 scientific and research institutes. Higher education in 35 specialities of the 1st degree of education and 22 specialities.
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]buy azithromycin nz[/url]
[url=http://strattera.company/]strattera 5mg[/url]
[url=https://metforminn.online/]metformin 2[/url]
[url=http://modafinile.com/]modafinil online canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://modafinilon.online/]where can i get modafinil uk[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen 20 mg[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.online/]lyrica best price[/url]
[url=https://valtrexv.online/]valtrex generic otc[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirmc.online/]acyclovir generic brand[/url]
[url=https://finasterideff.online/]cheap propecia online[/url]
[url=https://clomidsale.com/]clomiphene citrate clomid[/url]
Prodentim: What is it? Some of the finest and highest quality ingredients are used to produce Prodentim, an oral health supplement
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox buy[/url]
[url=https://mcadvair.online/]price of generic advair[/url]
[url=http://ciproo.online/]ciprofloxacin 1[/url]
I absolutely love your blog and find nearly all of your post’s to be exactly what I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind producing a post or elaborating on a few of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome website!
[url=https://doxycyclinepr.com/]doxycycline uk pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://diflucand.com/]where to buy duflicon pills[/url]
[url=http://lyricamd.online/]lyrica 50 mg tablets[/url]
I strongly recommend steer clear of this site. The experience I had with it has been purely frustration along with concerns regarding fraudulent activities. Proceed with extreme caution, or better yet, look for an honest service to fulfill your requirements.
Some really nice and utilitarian information on this website , likewise I think the design and style has got wonderful features.
I don’t usually comment but I gotta say regards for the post on this special one : D.
[url=http://ibaclofen.com/]baclofen cost pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://ciprocfx.com/]cipro 250 mg[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen 20 mg tablet price[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclineo.online/]doxycycline 150 mg cost comparison[/url]
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Профессиональная Замена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Перемещение Строений
Компания Gerakl24 занимается на выполнении комплексных работ по замене основания, венцов, полов и передвижению строений в городе Красноярском регионе и за пределами города. Наш коллектив квалифицированных специалистов обещает высокое качество исполнения различных типов ремонтных работ, будь то древесные, с каркасом, кирпичные постройки или бетонные конструкции здания.
Преимущества услуг Геракл24
Профессионализм и опыт:
Каждая задача выполняются только профессиональными мастерами, с обладанием большой стаж в направлении строительства и ремонта зданий. Наши сотрудники эксперты в своей области и реализуют работу с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Полный спектр услуг:
Мы предоставляем разнообразные услуги по восстановлению и реконструкции строений:
Смена основания: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что гарантирует долговечность вашего здания и устранить проблемы, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Смена венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые чаще всего подвергаются гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает внешний вид и функциональные характеристики.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и качественное передвижение домов на новые локации, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и предотвращает лишние расходы на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Дома из дерева: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные строения: усиление каркасных конструкций и замена поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: реставрация кирпичной кладки и усиление стен.
Дома из бетона: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы используем лишь качественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и прочность всех выполненных задач. Все проекты проходят строгий контроль качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Личный подход:
Каждому клиенту мы предлагаем подходящие решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Наша цель – чтобы конечный результат соответствовал вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по восстановлению и ремонту вашего здания. Мы обещаем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и ответить на ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать больше о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, сделав его безопасным и комфортным для проживания на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
[url=http://flomaxms.online/]noroxin brand name[/url]
[url=https://mcadvair.online/]advair diskus 10 50 mcg[/url]
[url=http://acyclovirmc.online/]zovirax pills canada[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinhq.com/]azithromycin 500 mg tablet price in india[/url]
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox drug[/url]
[url=https://lasixtbs.online/]furosemide 500 mg[/url]
[url=https://acutanep.online/]accutane 10mg daily[/url]
asthma treatment dismal – inhalers for asthma perform asthma medication reflection
pg slot
[url=http://amoxil.company/]augmentin price in india[/url]
[url=https://itretinoin.com/]retin a cream from mexico[/url]
[url=http://iclomid.com/]clomid for sale uk[/url]
האפליקציה היא פלטפורמה נפוצה במדינה לקנייה של קנאביס באופן וירטואלי. היא מעניקה ממשק נוח ומאובטח לרכישה וקבלת שילוחים של מוצרי צמח הקנאביס מגוונים. במאמר זו נסקור את העיקרון שמאחורי טלגראס, כיצד היא פועלת ומה היתרים מ השימוש בה.
מהי האפליקציה?
האפליקציה מהווה שיטה לרכישת קנאביס דרך היישומון טלגרם. היא מבוססת על ערוצי תקשורת וקהילות טלגרם ספציפיות הנקראות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שבהם ניתן להזמין מגוון מוצרי קנאביס ולקבלת אותם ישירותית לשילוח. הערוצים האלה מאורגנים לפי איזורים גיאוגרפיים, כדי להקל את קבלתם של השילוחים.
איך זה עובד?
התהליך פשוט יחסית. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ טלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המחיה. שם אפשר לעיין בתפריטים של המוצרים השונים ולהזמין את המוצרים המבוקשים. לאחר ביצוע ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שצוינה ועמו הארגז שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מציעים טווח נרחב של פריטים – סוגי מריחואנה, ממתקים, שתייה ועוד. בנוסף, אפשר למצוא חוות דעת של לקוחות שעברו לגבי רמת הפריטים והשרות.
מעלות השימוש באפליקציה
יתרון מרכזי מ הפלטפורמה הוא הנוחות והדיסקרטיות. ההרכבה והתהליך מתבצעות מרחוק מאיזשהו מקום, ללא נחיצות בהתכנסות פיזי. בנוסף, הפלטפורמה מאובטחת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוהה.
מלבד על זאת, מחירי הפריטים בפלטפורמה נוטים להיות זולים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות רבה. יש גם מוקד תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיית.
סיכום
טלגראס הווה דרך מקורית ויעילה לרכוש פריטי צמח הקנאביס במדינה. זו משלבת בין הנוחות הדיגיטלית של היישומון הפופולרי, לבין הזריזות והפרטיות של שיטת השילוח הישירות. ככל שהדרישה לקנאביס גובר, פלטפורמות בדוגמת טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח.
[url=https://sildenafilps.online/]viagra uk where to buy[/url]
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]augmentin 600 tablet[/url]
b29
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS – Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại!
[url=http://asynthroid.online/]37.5 mcg synthroid[/url]
vardenafil sildenafil vergleich
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]augmentin 675 price[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.com/]buy cheap flomax[/url]
[url=https://drdoxycycline.online/]doxycycline india price[/url]
I strongly recommend stay away from this site. My personal experience with it has been purely frustration and doubts about deceptive behavior. Proceed with extreme caution, or alternatively, look for a more reputable platform to meet your needs.
[url=https://adfinasterid.online/]propecia 5 mg for sale[/url]
tadalafil india pharmacy
проверка usdt trc20
Как защитить свои данные: страхуйтесь от утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня охрана личных данных становится всё более важной задачей. Одним из наиболее обычных способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в какой мере сберечься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это синтезы слов или фраз, которые бывают используются для доступа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или иные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, при помощи этих сит фраз. Как охранить свои личные данные? Используйте сложные пароли. Избегайте использования легких паролей, которые мгновенно угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для каждого аккаунта. Не применяйте один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухфакторную проверку (2FA). Это прибавляет дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт через другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте персональную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы сохранить свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может повлечь за собой серьезным последствиям, таким как кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы защитить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
I highly advise steer clear of this platform. My personal experience with it has been purely disappointment and doubts about scamming practices. Be extremely cautious, or alternatively, seek out an honest service for your needs.
vilitra vardenafil 20mg
tadalafil 20 mg directions
Telegrass
האפליקציה הווה אפליקציה פופולרית בישראל לקנייה של קנאביס בצורה וירטואלי. היא נותנת ממשק משתמש פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה ולקבלת משלוחים מ פריטי מריחואנה שונים. בכתבה זה נסקור את הרעיון שמאחורי טלגראס, כיצד היא פועלת ומהם היתרונות של השימוש בזו.
מה זו הפלטפורמה?
טלגראס הווה אמצעי לרכישת מריחואנה דרך היישומון טלגראם. היא נשענת מעל ערוצים וקהילות טלגראם ייעודיות הקרויות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שם ניתן להזמין מגוון מוצרי מריחואנה ולקבלת אלו ישירותית לשילוח. ערוצי התקשורת האלה מסודרים על פי אזורים גיאוגרפיים, במטרה להקל את קבלתם של המשלוחים.
איך זאת עובד?
התהליך פשוט למדי. קודם כל, יש להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הנוגע לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטים של הפריטים המגוונים ולהרכיב עם הפריטים הרצויים. לאחר ביצוע ההרכבה וסיום התשלום, השליח יגיע בכתובת שצוינה ועמו הארגז שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים טווח רחב של פריטים – סוגי צמח הקנאביס, עוגיות, משקאות ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר למצוא ביקורות של לקוחות שעברו לגבי איכות הפריטים והשירות.
יתרונות הנעשה בטלגראס
מעלה עיקרי של טלגראס הוא הנוחיות והדיסקרטיות. ההזמנה וההכנות מתקיימים מרחוק מאיזשהו מיקום, בלי נחיצות במפגש פיזי. כמו כן, הפלטפורמה מאובטחת היטב ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוה.
מלבד אל כך, עלויות המוצרים באפליקציה נוטות להיות תחרותיים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובהשקעה גבוהה. קיים גם מוקד תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיית.
סיכום
הפלטפורמה הינה דרך חדשנית ויעילה לרכוש פריטי מריחואנה בישראל. זו משלבת את הנוחיות הדיגיטלית של האפליקציה הפופולרי, לבין הזריזות והדיסקרטיות של שיטת השילוח הישירה. ככל שהביקוש למריחואנה גדלה, פלטפורמות בדוגמת טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח.
[url=http://xlyrica.com/]lyrica generic price[/url]
Как защитить свои личные данные: избегайте утечек информации в интернете. Сегодня обеспечение безопасности личных данных становится всё значимее важной задачей. Одним из наиболее часто встречающихся способов утечки личной информации является слив «сит фраз» в интернете. Что такое сит фразы и в каком объеме обезопаситься от их утечки? Что такое «сит фразы»? «Сит фразы» — это синтезы слов или фраз, которые часто используются для входа к различным онлайн-аккаунтам. Эти фразы могут включать в себя имя пользователя, пароль или иные конфиденциальные данные. Киберпреступники могут пытаться получить доступ к вашим аккаунтам, с помощью этих сит фраз. Как охранить свои личные данные? Используйте непростые пароли. Избегайте использования легких паролей, которые мгновенно угадать. Лучше всего использовать комбинацию букв, цифр и символов. Используйте уникальные пароли для всего аккаунта. Не пользуйтесь один и тот же пароль для разных сервисов. Используйте двухступенчатую аутентификацию (2FA). Это привносит дополнительный уровень безопасности, требуя подтверждение входа на ваш аккаунт посредством другое устройство или метод. Будьте осторожны с онлайн-сервисами. Не доверяйте персональную информацию ненадежным сайтам и сервисам. Обновляйте программное обеспечение. Установите обновления для вашего операционной системы и программ, чтобы уберечь свои данные от вредоносного ПО. Вывод Слив сит фраз в интернете может спровоцировать серьезным последствиям, таким вроде кража личной информации и финансовых потерь. Чтобы сохранить себя, следует принимать меры предосторожности и использовать надежные методы для хранения и управления своими личными данными в сети
Защитите ваши USDT: Проконтролируйте транзакцию TRC20 перед отправкой
Виртуальные деньги, такие как USDT (Tether) в блокчейне TRON (TRC20), становятся все всё более популярными в области сфере децентрализованных финансовых услуг. Тем не менее вместе со ростом востребованности растет также риск погрешностей иль обмана при переводе средств. Именно именно поэтому важно контролировать перевод USDT TRC20 до ее отправкой.
Ошибка при вводе адреса получателя иль пересылка по неправильный адрес получателя может повлечь к безвозвратной утрате ваших USDT. Мошенники тоже могут пытаться обмануть тебя, пересылая фальшивые адреса получателей на перевода. Потеря цифровой валюты вследствие подобных ошибок может повлечь значительными денежными убытками.
К счастью, имеются профильные сервисы, дающие возможность проконтролировать перевод USDT TRC20 перед её отправкой. Один из таких сервисов дает возможность отслеживать и анализировать операции на распределенном реестре TRON.
В данном обслуживании вы можете ввести адрес получателя адресата и получить подробную данные об адресе, включая историю переводов, баланс а также статус аккаунта. Это посодействует установить, является или нет адрес получателя действительным а также безопасным для отправки средств.
Другие службы также дают сходные опции по контроля переводов USDT TRC20. Определенные кошельки для криптовалют имеют интегрированные возможности по контроля адресов получателей а также транзакций.
Не игнорируйте удостоверением перевода USDT TRC20 до её отсылкой. Небольшая бдительность может сберечь вам много финансов и не допустить потерю ваших важных крипто активов. Задействуйте заслуживающие доверия службы с целью обеспечения безопасности ваших переводов и неприкосновенности ваших USDT на распределенном реестре TRON.
Во время обращении с криптовалютой USDT в распределенном реестре TRON (TRC20) максимально важно не только проверять реквизиты получателя до отправкой денег, но и периодически отслеживать остаток своего кошелька, и источники поступающих транзакций. Это позволит вовремя идентифицировать всевозможные нежданные операции и избежать вероятные убытки.
Сначала, нужно проверить на точности демонстрируемого баланса USDT TRC20 в вашем криптокошельке. Советуется сверять данные с данными публичных блокчейн-обозревателей, для того чтобы избежать возможность взлома либо взлома этого кошелька.
Однако одного только отслеживания остатка не хватает. Максимально необходимо исследовать историю входящих переводов а также этих источники. Если вы выявите поступления USDT с неопознанных либо сомнительных реквизитов, сразу же заблокируйте данные финансы. Существует риск, что эти монеты стали получены преступным путем и в будущем могут быть конфискованы регулирующими органами.
Наш сервис обеспечивает возможности для углубленного исследования входящих USDT TRC20 транзакций относительно их законности и неимения связи с преступной деятельностью. Мы поможем вам безопасно работать с этим популярным стейблкоином.
Плюс к этому необходимо периодически выводить USDT TRC20 в безопасные некастодиальные криптовалютные кошельки находящиеся под вашим тотальным контролем. Содержание монет на внешних платформах неизменно сопряжено с рисками хакерских атак а также утраты денег вследствие технических неполадок или банкротства сервиса.
Следуйте элементарные правила безопасности, будьте бдительны и своевременно отслеживайте баланс и происхождение пополнений кошелька для USDT TRC20. Это позволят обезопасить ваши виртуальные активы от незаконного присвоения и возможных правовых последствий впоследствии.
vardenafil doses
tadalafil dapoxetine tablets india
[url=http://zithromaxl.online/]zithromax 500mg online[/url]
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.com/]dexamethasone 4mg[/url]
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]augmentin tablets 500mg[/url]
pills for treat prostatitis hole – prostatitis medications terror prostatitis pills depress
[url=https://diflucand.com/]diflucan pills prescription[/url]
[url=https://advaird.com/]advair generic best price[/url]
I truly enjoy studying on this web site, it has wonderful blog posts.
Важность анализа перевода USDT в сети TRC20
Переводы USDT по протокола TRC20 приобретают растущую востребованность, вместе с тем стоит оставаться чрезвычайно бдительными во время таких принятии.
Этот форма переводов часто применяется в качестве обеления денежных средств, полученных криминальным способом.
Главный опасностей зачисления USDT TRC20 – состоит в том, что они имеют потенциал быть получены благодаря многочисленных моделей мошенничества, таких как хищения личных данных, шантаж, хакерские атаки наряду с дополнительные преступные манипуляции. Принимая данные транзакции, вы неизменно выступаете соучастником незаконной деятельности.
Поэтому чрезвычайно существенно тщательно проверять происхождение различных получаемого операции с использованием USDT в сети TRC20. Необходимо требовать посредством отправителя подтверждения о правомерности финансов, а незначительных сомнениях – не принимать подобные транзакций.
Помните, в случае, когда в процессе выявления незаконных природы финансов, вы вероятно будете подвергнуты со санкциям наряду рядом с перевододателем. Таким образом рекомендуется перестраховаться и глубоко изучать любой трансфер, чем подвергать опасности своей репутацией наряду с быть втянутым в крупные законодательные трудности.
Соблюдение аккуратности при операциях с использованием USDT по сети TRC20 – это основа финансовой экономической сохранности и защита участия в нелегальные практики. Будьте осторожны наряду с регулярно анализируйте происхождение криптовалютных финансов.
[url=https://diflucanr.online/]diflucan brand name in india[/url]
levitra 10 mg vardenafil
[url=http://accutaneo.com/]accutane price australia[/url]
cheap tadalafil 40 mg
проверить адрес usdt trc20
Заголовок: Непременно контролируйте адресе адресата при операции USDT TRC20
При работе со цифровыми валютами, особенно со USDT на блокчейне TRON (TRC20), крайне важно проявлять бдительность и внимательность. Единственная из числа наиболее распространенных оплошностей, какую допускают пользователи – отправка денег на неверный адрес. Для того чтобы избежать лишение своих USDT, требуется неизменно внимательно удостоверяться в адрес получателя перед отправкой операции.
Крипто адреса кошельков представляют из себя протяженные совокупности символов а также номеров, к примеру, TRX9QahiFUYfHffieZThuzHbkndWvvfzThB8U. Включая незначительная опечатка либо погрешность при копировании адреса имеет возможность привести к тому, чтобы ваши монеты будут безвозвратно лишены, ибо они попадут в неконтролируемый вам криптокошелек.
Существуют разные способы проверки адресов USDT TRC20:
1. Визуальная ревизия. Старательно сопоставьте адрес кошелька в твоём кошельке с адресом кошелька реципиента. При небольшом расхождении – не производите перевод.
2. Использование веб-инструментов удостоверения.
3. Дублирующая верификация с реципиентом. Обратитесь с просьбой к реципиенту подтвердить корректность адреса до отправкой перевода.
4. Тестовый операция. В случае значительной сумме транзакции, допустимо сначала передать малое величину USDT для удостоверения адреса.
Также советуется держать крипто на собственных криптокошельках, но не в обменниках либо посреднических службах, чтобы обладать абсолютный контроль над своими средствами.
Не пренебрегайте контролем адресов при осуществлении работе с USDT TRC20. Данная несложная процедура безопасности посодействует защитить ваши финансы против нежелательной лишения. Помните, чтобы в мире криптовалют операции необратимы, и посланные крипто на ошибочный адрес кошелька вернуть практически нереально. Будьте бдительны и внимательны, для того чтобы охранить собственные вложения.
[url=http://oazithromycin.com/]azithromycin 250 mg otc[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinps.online/]zithromax canada pharmacy[/url]
[url=https://bactrim.company/]how to buy bactrim online[/url]
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]2018 accutane[/url]
[url=https://adfinasterid.online/]propecia otc[/url]
[url=http://dezithromax.online/]zithromax 25mg[/url]
[url=http://vermox.company/]buy vermox tablets[/url]
טלגראס הווה תוכנה פופולרית בישראל לרכישת מריחואנה באופן אינטרנטי. זו מספקת ממשק משתמש נוח ומאובטח לרכישה וקבלת משלוחים מ מוצרי מריחואנה שונים. בסקירה זו נסקור עם העיקרון שמאחורי הפלטפורמה, איך זו עובדת ומהם היתרים מ השימוש בזו.
מה זו טלגראס?
האפליקציה הווה דרך לקנייה של מריחואנה דרך האפליקציה טלגרם. זו מבוססת מעל ערוצי תקשורת וקבוצות טלגראם ספציפיות הקרויות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שם אפשר להזמין מרחב מוצרי קנאביס ולקבל אותם ישירות למשלוח. הערוצים האלה מסודרים לפי איזורים גיאוגרפיים, כדי להקל על קבלתם של המשלוחים.
כיצד זאת פועל?
התהליך קל למדי. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטים של הפריטים השונים ולהרכיב עם המוצרים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההזמנה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע בכתובת שצוינה ועמו החבילה שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים מגוון רחב של פריטים – סוגי מריחואנה, עוגיות, שתייה ועוד. בנוסף, אפשר לראות ביקורות מ צרכנים קודמים על איכות המוצרים והשרות.
מעלות הנעשה בפלטפורמה
מעלה מרכזי של האפליקציה הינו הנוחות והדיסקרטיות. ההזמנה והתהליך מתבצעות מרחוק מכל מקום, בלי נחיצות בהתכנסות פנים אל פנים. כמו כן, הפלטפורמה מוגנת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוה.
מלבד אל כך, מחירי המוצרים בטלגראס נוטות לבוא זולים, והשילוחים מגיעים במהירות ובהשקעה רבה. יש אף מרכז תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיה.
סיכום
טלגראס היא שיטה מקורית ויעילה לרכוש פריטי צמח הקנאביס בישראל. זו משלבת בין הנוחיות הטכנולוגית של האפליקציה הפופולרי, ועם הזריזות והדיסקרטיות מ דרך השילוח הישירות. ככל שהביקוש למריחואנה גובר, אפליקציות כמו טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח.
valacyclovir online include – valtrex online careless valtrex respectable
[url=http://vermox.company/]vermox tab 100 mg[/url]
[url=https://baclofenx.online/]lioresal 10[/url]
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS – Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại!
Как похудеть
Пару мгновений и семья уже была в овощном отделе. Приходилось им там быть максимально редко – о существовании некоторых овощей и фруктов люди не знали вообще, от слова совсем. Смотря на все, как на диковинку, настало время выбора:
—Ну, что ж…. Возьмем помидоров, огурцов, а вот и яблоки, кабачков тоже можно…
Таня рассуждала сама по себе и не советовалась с голодными глазами мужа, ловко перебирая овощи и откладывая самые лучшие в полиэтиленовый пакет. Маленькая девочка внимательно осматривала апельсины – такого она еще никогда не видела, а тем более, не ела:
—Может, потом еще чего-нибудь нормального возьмем? Колбаски там, сосисок. Ты если хочешь, худей. А мы нормально будем жить. Да, доча?
индивид полностью не предвидел от любимой избранницы Татьяны. Внутри данной родственной группе сложение плоти абсолютно отличалась в сравнении с нормативной также общепризнанной – страдать предожирением абсолютная норма.
Геракл24: Профессиональная Замена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Передвижение Домов
Организация Геракл24 занимается на выполнении всесторонних услуг по смене фундамента, венцов, покрытий и перемещению зданий в месте Красноярском регионе и за пределами города. Наша группа квалифицированных экспертов гарантирует превосходное качество выполнения всех типов восстановительных работ, будь то древесные, с каркасом, из кирпича или бетонные конструкции здания.
Преимущества услуг Gerakl24
Профессионализм и опыт:
Весь процесс осуществляются исключительно профессиональными специалистами, с обладанием многолетний стаж в сфере возведения и ремонта зданий. Наши сотрудники профессионалы в своем деле и осуществляют проекты с максимальной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы осуществляем полный спектр услуг по реставрации и ремонту домов:
Смена основания: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего строения и избежать проблем, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Замена венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые обычно подвергаются гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: замена старых полов, что существенно улучшает визуальное восприятие и практическую полезность.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на новые места, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и избегает дополнительных затрат на строительство нового.
Работа с любыми типами домов:
Древесные строения: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, защита от разрушения и вредителей.
Дома с каркасом: реставрация каркасов и замена поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: реставрация кирпичной кладки и усиление стен.
Бетонные дома: реставрация и усиление бетонных элементов, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и надежность:
Мы применяем только проверенные материалы и современное оборудование, что гарантирует долгий срок службы и надежность всех выполненных работ. Каждый наш проект проходят тщательную проверку качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Персонализированный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту подходящие решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Наша цель – чтобы конечный результат соответствовал вашим запросам и желаниям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реконструкции вашего строения. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Обратившись в Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы готовы предоставить консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Звоните нам, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать больше о наших услугах. Мы обеспечим сохранение и улучшение вашего дома, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Геракл24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
?Tanya’s eyes lit up, her smile bared her pearly white teeth, and her eyelids closed with delight. The next day, breakfast was just as healthy, in general, as lunch. A new life came imperceptibly, but it so radically changed everything: from family relationships to one’s own attitude to the body and food:
— We will mark every day in the calendar that we didn’t live it in vain and lost a couple of hundred grams.
Tatyana proposed this idea completely calmly, in an absolutely even tone, stuffing unsweetened porridge into her mouth. No one was surprised or objected — this is a new step in life. Coming to work, Pavel received another pleasant bonus:
— Anyway, I talked to my beloved neighbors. You haven’t abandoned this idea of losing weight, have you? Because I told them such a thing, I didn’t even expect it myself. But I was really angry, of course. They’re not perfect themselves, and yet they teach others how to live, the saints.
— And what did Vika say? That we shouldn’t cause my any more trouble…
— She tucked her tail and sat silent, she didn’t even expect someone to stand up for her. She hung her head guiltily and said it wouldn’t happen again. Her husband beat her at night later, I had to call the police, it was impossible to sleep.
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.online/]where can i buy dexamethasone[/url]
[url=http://lasixor.online/]furosemide 40 mg tablet[/url]
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]ciprofloxacin prescription[/url]
[url=http://glucophage.online/]metformin usa[/url]
geinoutime.com
Fang Jifan은 옆에 있었고 이미 경의를 표했습니다. “폐하, 제 아들과 목사는 사형을 선고 받았습니다.”
[url=https://advaird.online/]cheapest price for advair[/url]
[url=http://modafinile.online/]buy provigil 200mg[/url]
מבורכים הנהנים לפורטל הידע והמידע והתמיכה הרשמי מטעם טלגרף מסלולים! במקום אפשר לאתר את הנתונים והמידע המעודכן והאקטואלי הזמין והרלוונטי בנוגע ל מערכת טלגרף והדרכים להפעלתה בצורה נכונה.
מהו טלגרם אופקים?
טלגרם נתיבים מציינת מנגנון הנשענת על תקשורת המספקת להפצה וקנייה של קנבי וקנביס בתחום. באמצעות המשלוחים והפורומים בטלגרף, צרכנים מסוגלים להזמין ולהשיג את פריטי קנאביס בדרך נגיש וזריז.
באיזה דרך להתחבר בטלגרם?
לשם להיכנס בשימוש בטלגראס, עליכם להצטרף למקומות ולמסגרות הרצויים. במקום באתר ניתן לאתר ולמצוא רשימה של צירים לקבוצות מתפקדים ומובטחים. כתוצאה מכך, אפשר להתחיל בשלבים הרכישה וההספקה מסביב מוצרי הדשא.
מידע והסברים
בפורטל זה ניתן למצוא מגוון מבין מדריכים וכללים ממצים לגבי הפעלה בפלטפורמת טלגרם, לרבות:
– ההצטרפות לקבוצות מומלצים
– שלבי הקבלה
– בטיחות ואבטחה בהפעלה בפלטפורמת טלגרם
– והרבה נתונים נוסף
מסלולים מומלצים
להלן קישורים למקומות ולקבוצות רצויים בטלגראס כיוונים:
– קבוצה המידע והעדכונים המאושר
– פורום הסיוע והליווי לצרכנים
– קבוצה לאספקת מוצרי מריחואנה מוטבחים
– מדריך חנויות קנבי מוטבחות
מערך מברכים אתכם עקב החברות שלכם לאתר הידע והמידע מאת טלגראס מסלולים ומייחלים לכולם חוויה של צריכה מצוינת ובטוחה!
[url=https://acyclovirlp.online/]zovirax ointment over the counter[/url]
Ahaa, its pleasant discussion concerning this article here at this blog, I have read all that, so now me also commenting here.
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]accutane australia[/url]
[url=http://baclofenx.com/]where to buy baclofen online[/url]
[url=http://modafinilmip.online/]provigil from canadian pharmacy[/url]
[url=http://modafinile.online/]modafinil online us[/url]
[url=https://amoxicillinbact.com/]augmentin 1000 mg tablet price[/url]
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]accutane 50mg[/url]
[url=http://finasterideff.com/]cheapest finasteride generic[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.online/]flomax 10 mg[/url]
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Квалифицированная Реставрация Основания, Венцов, Покрытий и Перенос Зданий
Компания Геракл24 профессионально занимается на оказании полных работ по реставрации фундамента, венцов, полов и перемещению домов в месте Красноярске и за его пределами. Наша группа квалифицированных специалистов гарантирует высокое качество исполнения различных типов ремонтных работ, будь то древесные, с каркасом, кирпичные постройки или из бетона дома.
Достоинства работы с Геракл24
Квалификация и стаж:
Каждая задача выполняются только высококвалифицированными экспертами, с многолетним многолетний стаж в направлении строительства и ремонта зданий. Наши специалисты знают свое дело и осуществляют задачи с безупречной точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предоставляем полный спектр услуг по восстановлению и реконструкции строений:
Реставрация фундамента: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что гарантирует долговечность вашего здания и предотвратить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией.
Замена венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые чаще всего подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Установка новых покрытий: установка новых полов, что существенно улучшает визуальное восприятие и функциональность помещения.
Перемещение зданий: безопасное и качественное передвижение домов на другие участки, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избегает дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми типами домов:
Деревянные дома: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Дома с каркасом: реставрация каркасов и смена поврежденных частей.
Кирпичные строения: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление конструкций.
Бетонные строения: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы работаем с лишь качественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что гарантирует долгий срок службы и надежность всех работ. Все проекты подвергаются строгому контролю качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Персонализированный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем подходящие решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Наша цель – чтобы результат нашей работы полностью соответствовал ваши ожидания и требования.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех задач в установленные сроки и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и ответить на ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, сделав его безопасным и комфортным для проживания на долгие годы.
Gerakl24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области.
[url=http://zithromaxl.online/]azithromycin cost india[/url]
[url=https://lyricamd.online/]lyrica capsules 75 mg cost[/url]
[url=http://lasixtbs.com/]order lasic no prescription[/url]
[url=http://lyricamd.online/]900mg lyrica[/url]
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]cheap viagra online without prescription[/url]
Купить Диплом Техникума Ссср
Макет – заполненная скан-копия диплома Техникума, которую мы отправим Вам на почту до того, как передать корочки в доставку. Сложность изготовления была в правильных печатях и в названии учреждения в дипломе. Бакалавры могут работать по выбранной специальности в любой сфере, не требуя от себя дополнительного обучения. После реформирования ВУЗ переименовали в Налоговый институт РосНОУ. Наши профессионалы быстро сделают надежный диплом за разумные деньги. Вы окончили обучение, но документ об его окончании был потерян или утрачен, а восстановление невозможно по каким-то причинам. Конечно, для того чтобы найти хорошее место работы, кроме желания нужно обладать соответствующим опытом работы и необходимыми навыками в этой профессии.
http://https://rudik-diploms-srednee.ru
Проверка Дипломов
Изготавливается документ на бланке государственного образца. Принимаются любые пожелания по темам курсовых работ и оценкам. Купить диплом МАрхИ можно на такие специальности, как Архитектура, Градостроительство, Дизайн архитектурной среды, Реставрация и реконструкция архитектурного наследия.
Купить Диплом О Среднем Образовании С Занесением В Реестр
Опыт и профессионализм наших сотрудников, а также технические возможности, позволяют нам создавать документы полностью идентичные оригиналу. Покупка документа позволит вам сэкономить колоссальное количество времени. Аптеки находятся на углу каждого дома, а люди ежедневно заболевают и нуждаются в лекарствах. Приобретение документации в интернете многим потенциальным клиентам кажется рискованным, ведь непонятно, насколько добросовестен подрядчик, и не купит Диплом Техникума Ссср ли он торговать персональными данными заказчиков.
[url=http://bactrim.company/]bactrim ds 800[/url]
[url=https://rettretinoin.online/]tretinoin cream cost in india[/url]
[url=https://flomaxms.com/]flomax online order[/url]
[url=https://lasixav.online/]furosemide 12.5 mg[/url]
Купить Свидетельство О Заключении Брака
Именно поэтому мы предполагаем, что наше предложение актуально, в первую очередь, для таких категорий населения: обладателей настоящего диплома технаря, потерявших оригинальную корочку и нуждающихся в её немедленном, срочном восстановлении, выпускников технических учебных заведений, которые не могут гордиться оценками в собственном дипломе, но при этом считают их несправедливыми, тех, кто бросил обучение в учебном заведении только в самый последний момент, уже получив основную теоретическую и практическую базу, обладателей дипломов по сходным специальностям, которые уверены, что имеющейся у них базы достаточно для того, чтобы заодно быть профессионалом и в смежной сфере. Поэтому их невозможно отличить от оригиналов даже при использовании специальных детекторов. Выбираете любой документ, оставляете заявку или звоните нам на горячую линию. С 18 по 29 марта в Нижегородской области пройдут соревнования Регионального этапа чемпионата по профессиональному мастерству Профессионалы. Если при оформлении вам необходим оригинальный бланк диплома, то мы купим рады предложить вам диплом СПб с печатью учебного заведения или собственный бланк, которых у нас есть в наличии.
https://orik24-diploms-srednee.ru
Как Выглядит Аттестат За 11 Класс
Наша компания поможет купить диплом в Омске или любом городе России. Мы предлагаем исключительно настоящие документы на бланках ГОЗНАК. Обращайтесь.
Купить Диплом Преподавателя
При поиске кандидатов на престижную должность ни один работодатель не купит рассматривать вас без предоставления документа университета, института, академии, которые подтверждают профессиональные навыки, знания. Самый известный робот-хирург Da Vinchi уже используется по всему миру и позволяет проводить разнообразные операции: от восстановления митрального клапана до операций на позвоночнике. Некоторые группы и свидетельства предлагают заключенье Брака заказа непосредственно на своей странице, с оплатой через банковские карты или с использованием VK-кошелька. Причем важно отметить, что все данные будут соответствовать действительности.
Сколько Стоит Диплом С Занесением В Реестр
Самым верным помощником в этом деле вам будет Интернет, где вы можете стоит своё объявление о покупке – куплю диплом техникума, медсестры, фармацевта, куплю диплом о высшем образовании. Продажа реестров начинается с оформления заказа, и мы гарантируем полную анонимность нашего сотрудничества мы не задаем лишних вопросов, а лишь выполняем свою работу. В процессе изготовления мы тщательно согласовываем нюансы и прорабатываем детали, чтобы избежать неточностей и ошибок в готовом документе. Ведь, кроме работы в аптеке, такому специалисту открыты дороги во многие сферы. Если вы хотите купить диплом колледжа недорого (или университета, или академии не важно), соотнесите его цену с качеством. Важен год окончания высшего учебного заведения, если вы готовы сделать заказ, то милости просим, готовый документ пройдет даже самую суровую проверку. Сегодня диплом колледжа не является чем-то зазорным, а стал гарантией более престижной и высокооплачиваемой работы и большего уважения среди коллег и окружающих вообще.
http://www.russkiy365-diploms-srednee.ru
Диплом Государственного Образца О Высшем Образовании
В большинстве случаев наши сотрудники выполняют работы досрочно. Всего за 24 дня вы получите на руки готовый подлинный диплом магистра. Гораздо важнее степень заинтересованности студента в получении образования. В дипломе будут все степени защиты, водяные знаки, микротест, настоящие печати и подписи должностных лиц.
Купить Диплом В Ижевске
И большинство идут по пути самообразования и саморазвития, что отлично, но без диплома об образовании делает эти знания невостребованными. Отказавшись от собственной мечты и высокой цели, вы уже вряд ли когда-нибудь будете счастливы, потому надо идти к ней, несмотря ни на что. Здравствуйте, моего сына убили, ему было 18 лет, я мать одиночка, воспитываю ещё двух несовершеннолетних детей, организации 10 лет, что мне будет при выявлении подделки. Но реальность такова, что диплом может оказаться ненужным, к примеру, если человек решил сменить профессию.
[url=https://albuterolo.com/]ventolin price australia[/url]
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox uk[/url]
[url=https://odiflucan.com/]canada otc diflucan[/url]
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]advair diskus 500 mcg[/url]
[url=https://ciprocfx.com/]cipro india[/url]
[url=https://acyclovirmc.com/]zovirax cheapest price[/url]
[url=https://tretinoineff.com/]retin a uk prescription[/url]
[url=https://modafinilon.online/]buy provigil online india[/url]
Психология в рассказах, истории из жизни.
[url=https://vermox.company/]order vermox online[/url]
[url=https://modafinile.com/]generic provigil for sale[/url]
[url=http://amoxil.company/]augmentin 1g price in india[/url]
[url=http://sildalis.store/]sildalis india[/url]
[url=http://ibaclofen.online/]baclofen mexico[/url]
[url=http://dexamethasonen.com/]dexona price[/url]
[url=https://lasixor.online/]generic furosemide 40 mg[/url]
[url=https://ezithromycin.online/]zithromax online purchase[/url]
[url=http://odiflucan.com/]diflucan canada[/url]
[url=https://clomidsale.com/]clomid uk[/url]
[url=https://enolvadex.online/]tamoxifen 40 mg price uk[/url]
Почему теневой плинтус – красивая и практичная деталь интерьера,
Советы по монтажу теневого плинтуса без дополнительной помощи,
Теневой плинтус как элемент декора: идеи и варианты применения,
Модные тренды в выборе теневых плинтусов для современного дома,
Как подобрать цвет теневого плинтуса к отделке стен,
Как спрятать коммуникации с помощью теневого плинтуса: практические советы,
Теневой плинтус с подсветкой: создаем эффектное освещение в интерьере,
Теневой плинтус: элегантность и стиль в дизайне помещения,
Почему теневой плинтус – важная деталь в оформлении интерьера
высота теневого плинтуса [url=https://plintus-tenevoj-aljuminievyj-msk.ru/]https://plintus-tenevoj-aljuminievyj-msk.ru/[/url] .
Good blog! I truly love how it is easy on my eyes and the data are well written. I am wondering how I might be notified whenever a new post has been made. I have subscribed to your RSS feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
[url=http://odiflucan.com/]buy diflucan without prescription[/url]
сео агентство [url=prodvizhenie-sajtov15.ru]prodvizhenie-sajtov15.ru[/url] .
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]zithromax 100[/url]
Работая в сео, нужно знать, что нельзя одним способом вывести сайт в топ выдачи поисковых систем, ведь поисковики это как дорожка с финишной прямой, а веб-сайты это гоночные машины, которые все хотят быть первыми.
Так вот:
Перечень – Для того чтобы веб-сайт был адаптивным и быстр, важна
оптимизация
Сайт должен иметь только уникальное содержимое, это тексты и картинки
НЕОБХОДИМО набор ссылок через статейные сайты и напрямую на главную
Укрепление беклинков с помощью второстепенных сайтов
Ссылочная структура, это ссылки Tier-1, Tier-2, Tier-3
Ну и главное это личная сеть веб-сайтов PBN, которая ссылается на манисайт
Все сайты PBN должны быть без отпечатков, т.е. системы поиска не должны понимать, что это один собственник всех сайтов, поэтому ОЧЕНЬ важно придерживаться все эти указания.
[url=https://iclomid.com/]where to buy clomid over the counter[/url]
[url=http://tadacip.store/]where to buy tadacip[/url]
[url=http://accutaneiso.online/]accutane online pharmacy uk[/url]
promethazine cell – promethazine give promethazine coach
[url=http://vermoxin.online/]vermox tablets for sale[/url]
Great post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Kudos!
娛樂城
在線娛樂城的天地
隨著網際網路的迅速發展,線上娛樂城(網上賭場)已經成為許多人休閒的新選擇。網上娛樂城不僅提供多種的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的興奮和樂趣。本文將研究網上娛樂城的特點、好處以及一些常見的游戲。
什麼線上娛樂城?
在線娛樂城是一種通過網際網路提供賭錢遊戲的平台。玩家可以通過電腦設備、手機或平板進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如德州撲克、輪盤、二十一點和老虎機等。這些平台通常由專業的的軟件公司開發,確保游戲的公正性和穩定性。
在線娛樂城的好處
便利:玩家不需要離開家,就能享用賭博的快感。這對於那些生活在偏遠實體賭場地區的人來說尤為方便。
多種的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更豐富的游戲選擇,並且經常更新游戲內容,保持新穎。
福利和獎金:許多網上娛樂城提供豐富的獎金計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款獎勵和會員計劃,吸引新新玩家並鼓勵老玩家繼續遊戲。
穩定性和保密性:正當的在線娛樂城使用先進的加密方法來保護玩家的私人信息和交易,確保遊戲過程的安全和公平。
常有的網上娛樂城游戲
撲克:撲克牌是最流行賭錢遊戲之一。網上娛樂城提供各種撲克牌變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈和七張牌撲克等。
賭盤:輪盤賭是一種古老的賭博遊戲,玩家可以下注在數字、數字組合上或顏色上,然後看球落在哪個地方。
二十一點:又稱為二十一點,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
老虎机:老虎机是最容易也是最流行的賭博遊戲之一,玩家只需旋轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出中獎的組合。
結論
線上娛樂城為現代賭博愛好者提供了一個方便的、刺激的且多樣化的娛樂選擇。不論是撲克迷還是老虎机愛好者,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的游戲。同時,隨著技術的不斷進步,線上娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變得越來越越來越真實和吸引人。然而,玩家在享受游戲的同時,也應該保持自律,避免沉溺於賭博活動,保持健康的娛樂心態。
ascorbic acid convince – ascorbic acid lighter ascorbic acid kindness
娛樂城
網上娛樂城的天地
隨著網際網路的快速發展,在線娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。網上娛樂城不僅提供多元化的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和樂趣。本文將探討網上娛樂城的特徵、好處以及一些常見的游戲。
什麼是在線娛樂城?
線上娛樂城是一種經由網際網路提供博彩游戲的平台。玩家可以透過計算機、智能手機或平板進入這些網站,參與各種博彩活動,如撲克牌、賭盤、21點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專家的程序公司開發,確保游戲的公平性和安全。
在線娛樂城的優勢
方便性:玩家不用離開家,就能體驗博彩的樂趣。這對於那些住在在遠離實體賭場地區的人來說尤其方便。
多種的游戲選擇:線上娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多的遊戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新穎。
福利和獎勵:許多網上娛樂城提供多樣的優惠計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款獎勵和會員計劃,吸引新玩家並激勵老玩家不斷遊戲。
穩定性和隱私性:合法的線上娛樂城使用高端的加密技術來保護玩家的私人信息和金融交易,確保游戲過程的穩定和公平。
常見的的在線娛樂城遊戲
撲克:德州撲克是最受歡迎的博彩游戲之一。線上娛樂城提供多種德州撲克變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌等。
輪盤:賭盤是一種傳統的賭場遊戲遊戲,玩家可以賭注在單個數字、數字排列或顏色選擇上,然後看球落在哪個地方。
二十一點:又稱為二十一點,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數的遊戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡可能接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:老虎機是最受歡迎且是最常見的賭錢遊戲之一,玩家只需轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出中獎的組合。
結論
在線娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、興奮且多元化的娛樂方式。不管是撲克迷還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷發展,在線娛樂城的游戲體驗將變得越來越越來越真實和有趣。然而,玩家在享用游戲的同時,也應該自律,避免沉迷於博彩活動,保持健康的心態。
[url=https://avermox.online/]vermox canada[/url]
[url=https://albuterolo.com/]buying albuterol in mexico[/url]
[url=http://zithromaxl.online/]1g azithromycin[/url]
This is a topic close to my heart cheers, where are your contact details though?
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.com/]dexamethasone rx[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclineo.online/]doxycycline 50 mg cost[/url]
[url=https://nolvadexin.online/]tamoxifen citrate[/url]
I love what you guys are up too. This type of clever work and exposure! Keep up the awesome works guys I’ve you guys to our blogroll.
super tadalafil with dapoxetine
[url=https://dexamethasonen.com/]20 mg dexamethasone[/url]
sapporo88
Daily bonuses
Discover Thrilling Promotions and Extra Spins: Your Definitive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are devoted to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of offers and bonus spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our amazing deals and what makes them so special.
Lavish Free Spins and Rebate Offers
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 free spins and a 75% cashback with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This unbelievable promotion allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Offers
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit bonus available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” offers allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these offers provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Bonus Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 free spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These free spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, refund, or plentiful deposit promotions, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these awesome deals, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
game reviews
Captivating Breakthroughs and Beloved Releases in the World of Interactive Entertainment
In the fluid landscape of gaming, there’s continuously something innovative and captivating on the brink. From mods enhancing beloved classics to new debuts in iconic universes, the interactive entertainment ecosystem is flourishing as ever.
Here’s a overview into the most recent updates and specific the most popular releases engrossing audiences across the globe.
Newest Developments
1. New Mod for Skyrim Enhances Non-Player Character Aesthetics
A freshly-launched customization for Skyrim has attracted the attention of enthusiasts. This enhancement brings high-polygon heads and hair physics for every supporting characters, elevating the game’s visual appeal and immersion.
2. Total War Games Title Set in Star Wars Realm Under Development
The Creative Assembly, famous for their Total War collection, is allegedly crafting a new game set in the Star Wars Universe galaxy. This captivating collaboration has enthusiasts awaiting the profound and engaging gameplay that Total War Series experiences are acclaimed for, finally situated in a realm far, far away.
3. GTA VI Launch Announced for Late 2025
Take-Two Interactive’s Head has announced that Grand Theft Auto VI is planned to debut in Late 2025. With the colossal reception of its prior release, GTA V, enthusiasts are awaiting to experience what the forthcoming installment of this celebrated series will offer.
4. Expansion Strategies for Skull and Bones Second Season
Designers of Skull & Bones have announced expanded developments for the game’s second season. This high-seas journey offers new features and improvements, engaging enthusiasts captivated and engrossed in the world of nautical nautical adventures.
5. Phoenix Labs Studio Experiences Layoffs
Disappointingly, not all announcements is uplifting. Phoenix Labs, the studio developing Dauntless, has communicated substantial workforce reductions. In spite of this difficulty, the title continues to be a beloved choice across fans, and the developer keeps dedicated to its playerbase.
Renowned Experiences
1. Wild Hunt
With its captivating narrative, immersive domain, and engaging experience, The Witcher 3 keeps a beloved release within players. Its rich plot and expansive open world remain to attract fans in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077 Game
Regardless of a problematic debut, Cyberpunk 2077 Game stays a highly anticipated title. With continuous improvements and optimizations, the release continues to evolve, providing fans a perspective into a cyberpunk future teeming with danger.
3. Grand Theft Auto V
Yet eras subsequent to its initial release, Grand Theft Auto V continues to be a iconic selection amidst enthusiasts. Its wide-ranging sandbox, compelling plot, and co-op experiences sustain enthusiasts revisiting for additional explorations.
4. Portal
A classic analytical game, Portal Game is acclaimed for its pioneering mechanics and exceptional map design. Its complex obstacles and humorous writing have established it as a noteworthy title in the interactive entertainment realm.
5. Far Cry 3 Game
Far Cry 3 Game is acclaimed as one of the best titles in the series, offering gamers an sandbox journey teeming with danger. Its immersive story and renowned figures have confirmed its standing as a cherished title.
6. Dishonored Universe
Dishonored Universe is praised for its covert gameplay and unique realm. Enthusiasts adopt the character of a supernatural killer, traversing a metropolitan area filled with institutional mystery.
7. Assassin’s Creed
As a segment of the acclaimed Assassin’s Creed Series franchise, Assassin’s Creed Game is beloved for its compelling plot, enthralling mechanics, and period realms. It stays a exceptional title in the collection and a iconic across players.
In conclusion, the universe of gaming is thriving and dynamic, with innovative advan
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]amoxicillin tablet cost[/url]
[url=http://valtrexv.online/]valtrex australia[/url]
[url=https://okmodafinil.com/]generic provigil coupon[/url]
matras [url=https://kupit-matras111.ru/]matras[/url] .
স্বাগত বোনাস প্রথম আমানত 200% পান – একটি অসাধারণ সুযোগ
আপনার জন্য একটি অসাধারণ সুযোগ! এই সময়ে, আমরা নতুন সদস্যদের জন্য বিশেষ প্রচার অফার এনেছি – স্বাগত বোনাসে প্রথম আমানতের 200% পান! এই অফারটি পেতে আপনার প্রথম আমানতটি করতে হবে এবং পরে আপনি এই অফারের উপভোগ করতে পারবেন।
খেলার ধরন:
এই সুযোগের আওতায় আমরা আপনাকে স্লট, ফিশার, বিঙ্গো, মেগা বল এবং মানি হুইলে খেলার সুবিধা দিচ্ছি। আপনি যেকোনো খেলায় অংশ নিতে পারেন এবং আপনার আগ্রহ অনুযায়ী খেলাটি চয়ন করতে পারেন।
অফারের বিবরণ:
আপনি ১০০ বিডিটি ডিপোজিট করলে আপনি ২০০% বোনাস পাবেন, অর্থাৎ ৩০০ বিডিটি।
আপনাকে এই বোনাস উত্তোলন করতে হবে x20 বার, অর্থাৎ আপনাকে মোট ৬০০০ বিডিটির জন্য খেলতে হবে।
সর্বোচ্চ উত্তোলন ৩৫০ বিডিটি।
আবেদনের মাত্রা:
এই অফার এপ্রিলের পরে নিবন্ধন করা গ্রাহকদের জন্য প্রযোজ্য।
এই অফারটি সীমিত সময়ের জন্য মাত্র, সুতরাং তা অবিলম্বে পেতে আজই আমাদের সাথে যোগাযোগ করুন। ক্রিকেট অ্যাফিলিয়েট হিসেবে আমাদের প্ল্যাটফর্মে যোগ দিন এবং এই অসাধারণ সুযোগ উপভোগ করুন!
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins !
[url=https://enolvadex.online/]tamoxifen tablets india[/url]
बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो में रोमांचक और मजेदार गेम्स का आनंद
ऑनलाइन कैसीनो का आनंद लेते हुए रोमांचक और मजेदार गेम्स खेलना एक बेहतरीन अनुभव होता है। बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो एक प्रमुख प्लेटफॉर्म है जो खिलाड़ियों को विविध और रोमांचक गेम्स का अनुभव प्रदान करता है।
अगर आप बेटवीसा लॉगिन करके या बेटवीसा ऐप का उपयोग करके बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो में शामिल होते हैं, तो आपको कुछ वास्तव में मजेदार और लोकप्रिय खेलों का आनंद लेने को मिलेगा।
पहला है – सलाह वाला या “रूलेट”। यह एक पारंपरिक कैसीनो गेम है लेकिन बेटवीसा ने इसे आधुनिक और रोमांचक बना दिया है। खिलाड़ी अपने भाग्य का परीक्षण कर सकते हैं और बड़े पैसों की जीत का सपना देख सकते हैं।
बेटवीसा इंडिया में बहुत लोकप्रिय है “ब्लैकजैक” भी। यह गेम कार्ड गेमिंग का क्लासिक अनुभव प्रदान करता है और कुशल खिलाड़ियों को अच्छा रिटर्न देता है।
इसके अलावा, बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो में “स्लॉट मशीन” भी उपलब्ध हैं। ये ड्रैमेटिक थीम्स और जबरदस्त जैकपॉट के साथ आकर्षक और रोमांचक हो सकते हैं।
कुछ अन्य लोकप्रिय गेम्स में “बैकरेट”, “पोकर”, और “लाइव डीलर कैसीनो” शामिल हैं। ये सभी भव्य ग्राफिक्स, सरल नियम और उत्साहजनक विजय संभावनाएं प्रदान करते हैं।
समग्र रूप से, बेटवीसा ऑनलाइन कैसीनो में उपलब्ध गेम्स अनूठे, रोमांचक और मनोरंजक हैं। चाहे आप क्लासिक कैसीनो गेम्स का आनंद लेना चाहते हों या नए और नवीनतम गेम्स की तलाश में हों, बेटवीसा आपके लिए सबकुछ प्रदान करता है।
बेटवीसा लॉगिन करके या बेटवीसा ऐप डाउनलोड करके आप इन मजेदार गेम्स का आनंद ले सकते हैं और अपने ऑनलाइन कैसीनो अनुभव को और भी रोचक बना सकते हैं। हमारा सुझाव है कि आप इन गेम्स को आजमाकर देखें और देखें कि आप कितना उत्साहित और उत्साहित होते हैं!
Betvisa Bet
Betvisa Bet | Catch the BPL Excitement with Betvisa!
Hunt for ₹10million! | Enter the BPL at Betvisa and chase a staggering Bounty.
Valentine’s Boost at Visa Bet! | Feel the rush of a 143% Love Mania Bonus .
predict BPL T20 outcomes | score big rewards through Betvisa login!
#betvisa
Betvisa bonus Win! | Leverage your 10 free spins to possibly win $8,888.
Share and Earn! | win ₹500 via the Betvisa app download!
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/hi
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisaapp #betvisaIndia
Sign-Up Jackpot! | Register at Betvisa India and win ₹8,888.
Double your play! | with a ₹1,000 deposit and get ₹2,000 free at Betvisa online!
Download the Betvisa download today and don’t miss out on the action!
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]lyrica 25 mg cost[/url]
Daily bonuses
Discover Thrilling Deals and Bonus Spins: Your Comprehensive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are focused to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of offers and bonus spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our incredible offers and what makes them so special.
Generous Extra Spins and Rebate Deals
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% refund with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this offer with a deposit starting from just $10. This incredible promotion allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Bonuses
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 bonus with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit bonus available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these promotions provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Bonus Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 bonus spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These free spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our promotions are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our promotions come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these fantastic opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, refund, or lavish deposit promotions, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these incredible promotions, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
Daily bonuses
Uncover Thrilling Promotions and Bonus Spins: Your Comprehensive Guide
At our gaming platform, we are committed to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of bonuses and free rounds ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our amazing promotions and what makes them so special.
Generous Free Rounds and Refund Promotions
One of our standout offers is the opportunity to earn up to 200 free spins and a 75% rebate with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This incredible promotion allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Deals
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit promotion available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our “Play Big!” promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these offers provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Bonus Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 bonus spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These free spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our bonuses come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these amazing opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, refund, or generous deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these fantastic offers, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming!
[url=http://modafinile.com/]provigil 200 mg tablet price[/url]
I consider something genuinely interesting about your blog so I saved to fav.
[url=http://drdoxycycline.online/]doxycycline 60 mg[/url]
tadalafil troche dosage
Betvisa অ্যাফিলিয়েট লগইন: একটি সহজ প্রক্রিয়া
Betvisa অ্যাফিলিয়েট লগইন অ্যাক্সেস করা দ্রুত এবং সহজ। অ্যাফিলিয়েটরা শুরু করতে এই সহজ পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করতে পারেন।
সাইন আপ: Betvisa ওয়েবসাইটে যান এবং অ্যাফিলিয়েট বিভাগে নেভিগেট করুন। প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য প্রদান করে এবং শর্তাবলীতে সম্মত হয়ে নিবন্ধন প্রক্রিয়াটি সম্পূর্ণ করুন।
অনুমোদন প্রাপ্ত করুন: একবার আপনার অ্যাফিলিয়েট অ্যাকাউন্ট পর্যালোচনা এবং Betvisa টিম দ্বারা অনুমোদিত হলে, আপনি অ্যাফিলিয়েট প্ল্যাটফর্ম অ্যাক্সেস করার জন্য লগইন শংসাপত্র পাবেন।
লগইন করুন এবং শুরু করুন: Betvisa অ্যাফিলিয়েট লগইন পোর্টাল অ্যাক্সেস করতে আপনার লগইন শংসাপত্রগুলি ব্যবহার করুন। সেখান থেকে, আপনি বিভিন্ন বিপণন সরঞ্জামগুলি অন্বেষণ করতে পারেন, আপনার কর্মক্ষমতা ট্র্যাক করতে পারেন এবং সম্ভাব্য খেলোয়াড়দের কাছে Betvisa প্রচার শুরু করতে পারেন।
Betvisa বাংলাদেশ ব্যবহারকারীদের জন্য, Betvisa অ্যাফিলিয়েট লগইন অ্যাক্সেস করা একটি সহজ প্রক্রিয়া। তারা সহজেই লগইন করে গেমগুলিতে অংশগ্রহণ এবং কমিশন উপার্জন করতে পারেন।
অনলাইন বেটিংয়ে আপনার বিপণন উদ্যোগকে প্রসারিত করতে এবং উপার্জন বৃদ্ধি করতে, Betvisa অ্যাফিলিয়েট প্রোগ্রামটি একটি সুযোগ-সম্পন্ন পছন্দ হতে পারে। সহজ লগইন প্রক্রিয়ার মাধ্যমে, আপনি কার্যকরভাবে এই লাভজনক প্ল্যাটফর্মে যোগদান করতে পারেন।
Betvisa Bet | Hit it Big This IPL Season with Betvisa!
Betvisa login! | Every deposit during IPL matches earns a 2% bonus .
Betvisa Bangladesh! | IPL 2024 action heats up, your bets get more rewarding!
Crash Game returns! | huge ₹10 million jackpot. Take the lead on the Betvisa app !
#betvisa
Start Winning Now! | Sign up through Betvisa affiliate login, claim ₹500 free cash.
Grab Your Winning Ticket! | Register login and win ₹8,888 at visa bet!
https://www.betvisa-bet.com/bn
#visabet #betvisalogin #betvisabangladesh#betvisaapp
200% Excitement! | Enjoy slots and fishing games at Betvisa লগইন করুন!
Big Sports Bonuses! | Score up to ₹5,000 in sports bonuses during the IPL season
Gear up for an exhilarating IPL season at Betvisa, propels you towards victory!
выкуп авто выгодно выкуп авто москва быстро
Lottery Defeater Software is a fully automated, plug-and-play system designed to significantly improve your chances of winning the lottery.
Наш сайт эротических рассказов https://shoptop.org/ поможет тебе отвлечься от повседневной суеты и погрузиться в мир страсти и эмоций. Богатая библиотека секс историй для взрослых пробудит твое воображение и позволит насладиться каждой строкой.
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]ventolin cream[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillinbact.com/]amoxil price canada[/url]
clarithromycin bold – zantac counter cytotec pills though
https://formomebel.ru/krovati
Exciting Innovations and Beloved Franchises in the World of Digital Entertainment
In the ever-evolving domain of videogames, there’s continuously something fresh and captivating on the horizon. From enhancements improving revered staples to new launches in legendary brands, the videogame realm is thriving as in current times.
Here’s a look into the up-to-date updates and some of the beloved releases captivating enthusiasts internationally.
Latest Updates
1. Innovative Customization for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim Improves NPC Appearance
A newly-released modification for Skyrim has caught the attention of players. This modification adds lifelike heads and flowing hair for every non-player entities, optimizing the world’s aesthetics and immersion.
2. Total War Series Release Placed in Star Wars Galaxy Universe Being Developed
The Creative Assembly, renowned for their Total War Games series, is supposedly working on a new game located in the Star Wars Galaxy universe. This thrilling integration has players eagerly anticipating the tactical and compelling journey that Total War Games titles are celebrated for, now situated in a universe far, far away.
3. Grand Theft Auto VI Arrival Revealed for Fall 2025
Take-Two’s Leader has communicated that GTA VI is set to release in Autumn 2025. With the colossal acclaim of its earlier title, GTA V, gamers are awaiting to explore what the future entry of this renowned series will provide.
4. Extension Strategies for Skull and Bones Sophomore Season
Creators of Skull & Bones have communicated broader strategies for the game’s sophomore season. This high-seas experience provides fresh experiences and updates, maintaining enthusiasts captivated and absorbed in the realm of nautical piracy.
5. Phoenix Labs Developer Faces Personnel Cuts
Disappointingly, not every announcements is positive. Phoenix Labs Studio, the creator developing Dauntless, has announced significant layoffs. In spite of this difficulty, the experience continues to be a iconic choice across fans, and the developer stays attentive to its fanbase.
Renowned Releases
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt Game
With its compelling plot, immersive universe, and engaging adventure, Wild Hunt keeps a iconic game across fans. Its intricate plot and vast nonlinear world persist to engage enthusiasts in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077 Game
Regardless of a rocky launch, Cyberpunk 2077 Game remains a long-awaited release. With constant patches and enhancements, the game keeps improve, delivering fans a view into a dystopian setting teeming with intrigue.
3. GTA 5
Even time following its debut debut, GTA V keeps a beloved selection amidst gamers. Its vast nonlinear world, engaging story, and multiplayer components maintain enthusiasts returning for more experiences.
4. Portal 2 Game
A iconic problem-solving game, Portal 2 Game is acclaimed for its innovative gameplay mechanics and ingenious spatial design. Its challenging conundrums and humorous dialogue have solidified it as a exceptional experience in the interactive entertainment industry.
5. Far Cry Game
Far Cry 3 is hailed as a standout titles in the series, presenting fans an open-world exploration rife with intrigue. Its immersive plot and iconic personalities have solidified its status as a beloved game.
6. Dishonored Universe
Dishonored Game is hailed for its covert systems and exceptional environment. Players embrace the character of a otherworldly executioner, traversing a metropolitan area filled with institutional intrigue.
7. Assassin’s Creed
As a member of the iconic Assassin’s Creed Universe franchise, Assassin’s Creed Game is beloved for its immersive story, engaging features, and historical realms. It stays a exceptional title in the universe and a favorite amidst fans.
In conclusion, the universe of videogames is thriving and constantly evolving, with fresh advan
mikrosluchatko https://mikrocz.cz/
купить микронаушники микронаушник Прага
[url=https://finasterideff.com/]buy propecia usa[/url]
https://rybalka-v-rossii.ru – сайт о рыбалке в России, способах ловли рыб, и выборе правильных снастей.к
al-club.ru казино либет
স্বাগত বোনাসের সাথে সেরা ক্রিকেট গেইম প্লে করুন
ক্রিকেট এক খেলা না, এটি একটি প্রচন্ড উত্সাহের অভিবাদন। এই খেলাটি নিয়মিতভাবে বড় আকর্ষণ প্রদান করে বিভিন্ন বিশ্বকাপ এবং অন্যান্য টুর্নামেন্টে। ক্রিকেট উপাদানের অধিকাংশ ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকেরা এটি দেখতে পছন্দ করেন।
ক্রিকেটে বাজিয়ে ওঠা গতি, তাদের দেখার প্রকৃতির জন্য একটি জনপ্রিয় সাইট হল cricket exchange। এই সাইটটি ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকদের জন্য একটি পুরোপুরি রম্য খেলার স্থান যেখানে তারা তাদের পছন্দের ক্রিকেট টীম বা খেলোয়াড়দের সাথে লক্ষ্য করতে পারেন।
ক্রিকেট এক্সচেঞ্জে একজন প্রতিষ্ঠানকে উৎসাহিত করার জন্য ক্রিকেট এফিলিয়েট প্রোগ্রাম রয়েছে। এই প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে আপনি ক্রিকেট এক্সচেঞ্জে বিপণন করে সাধারণ আয় করতে পারেন।
সাথেই এই এফিলিয়েট প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকরা উপভোগ করতে পারেন 9wicket, crickex affiliate login এবং crickex login এর মতো বিভিন্ন সুবিধা। এই সাইটগুলি ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকদের জন্য আরও উচ্চমানের খেলা এবং পুরস্কার প্রদান করে।
সুতরাং, ক্রিকেট প্রেমিকরা এই সমস্ত সুবিধা এবং অফার থেকে উপভোগ করতে চান, তাহলে তাদের জন্য cricket exchange সম্পর্কে আরও জানতে পারেন। ক্রিকেট এক্সচেঞ্জে আপনার জন্য আরও কী রয়েছে এবং কীভাবে এটি আপনার খেলা অনুভব আরও আনন্দময় করতে পারে, সেটি জানতে ভিজিট করুন।
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins !
купить флешки оптом https://meflash.ru/
fludrocortisone pills peter – florinef pills flesh prevacid pills limit
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research on this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I’m very glad to see such excellent info being shared freely out there.
[url=https://albuterolp.online/]can you buy ventolin over the counter australia[/url]
[url=http://accutanemix.online/]accutane medicine price[/url]
[url=http://tadacip.store/]tadacip 20 tablet[/url]
Exciting Advancements and Beloved Titles in the World of Interactive Entertainment
In the constantly-changing landscape of digital entertainment, there’s constantly something groundbreaking and engaging on the cusp. From mods elevating revered timeless titles to anticipated arrivals in celebrated franchises, the gaming landscape is thriving as ever.
Let’s take a look into the most recent news and specific the most popular releases captivating audiences internationally.
Most Recent Announcements
1. Innovative Mod for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim Enhances NPC Aesthetics
A latest mod for Skyrim has captured the attention of players. This modification implements high-polygon heads and realistic hair for every non-player entities, elevating the game’s graphics and depth.
2. Total War Game Set in Star Wars Galaxy Universe In the Works
The Creative Assembly, renowned for their Total War Games franchise, is said to be developing a forthcoming game set in the Star Wars Galaxy universe. This captivating integration has players looking forward to the profound and engaging gameplay that Total War games are renowned for, at last situated in a world distant.
3. Grand Theft Auto VI Release Revealed for Autumn 2025
Take-Two Interactive’s CEO’s Leader has communicated that Grand Theft Auto VI is planned to debut in Late 2025. With the enormous reception of its previous installment, Grand Theft Auto V, gamers are eager to experience what the upcoming entry of this iconic series will bring.
4. Expansion Strategies for Skull & Bones Season Two
Developers of Skull & Bones have revealed expanded plans for the title’s Season Two. This swashbuckling journey offers additional features and updates, sustaining players captivated and enthralled in the domain of high-seas nautical adventures.
5. Phoenix Labs Developer Deals with Workforce Reductions
Unfortunately, not everything news is uplifting. Phoenix Labs Developer, the studio developing Dauntless, has revealed substantial staff cuts. Despite this obstacle, the release continues to be a renowned preference amidst gamers, and the developer remains attentive to its playerbase.
Popular Titles
1. Wild Hunt
With its captivating experience, engrossing domain, and engaging experience, The Witcher 3 keeps a cherished release within fans. Its rich narrative and wide-ranging sandbox continue to captivate fans in.
2. Cyberpunk Game
Notwithstanding a tumultuous debut, Cyberpunk keeps a long-awaited game. With continuous updates and fixes, the release continues to progress, providing players a look into a dystopian future abundant with mystery.
3. Grand Theft Auto 5
Despite eras post its debut release, Grand Theft Auto 5 keeps a beloved choice within enthusiasts. Its wide-ranging open world, captivating narrative, and online experiences maintain gamers reengaging for further explorations.
4. Portal 2
A classic analytical release, Portal Game is celebrated for its revolutionary systems and ingenious level design. Its intricate challenges and amusing dialogue have made it a remarkable game in the interactive entertainment industry.
5. Far Cry 3 Game
Far Cry 3 Game is praised as one of the best games in the universe, providing gamers an sandbox journey filled with intrigue. Its captivating story and memorable characters have confirmed its standing as a cherished experience.
6. Dishonored Game
Dishonored Universe is hailed for its stealth mechanics and exceptional world. Players adopt the persona of a supernatural killer, navigating a city teeming with political peril.
7. Assassin’s Creed
As a component of the iconic Assassin’s Creed series, Assassin’s Creed is revered for its captivating plot, compelling systems, and era-based settings. It stays a exceptional game in the franchise and a beloved among enthusiasts.
In conclusion, the domain of digital entertainment is flourishing and dynamic, with innovative advan
[url=https://dezithromax.online/]order azithromycin 500mg[/url]
[url=https://aaccutane.com/]order accutane over the counter[/url]
[url=http://azithromycinmds.online/]zithromax buying[/url]
https://proauto.kyiv.ua здесь вы найдете обзоры и тест-драйвы автомобилей, свежие новости автопрома, обширный автокаталог с характеристиками и ценами, полезные советы по уходу и ремонту, а также активное сообщество автолюбителей. Присоединяйтесь к нам и оставайтесь в курсе всех событий в мире автомобилей!
Are you looking for reliable and fast proxies? https://fineproxy.org/account/aff.php?aff=29 It offers a wide range of proxy servers with excellent speed and reliability. Perfect for surfing, scraping and more. Start right now with this link: FineProxy.org . Excellent customer service and a variety of tariff plans!
[url=https://modafinilon.online/]modafinil 300mg[/url]
Euro
sunmory33
sunmory33
https://autoclub.kyiv.ua узнайте все о новых моделях, читайте обзоры и тест-драйвы, получайте советы по уходу за авто и ремонтам. Наш автокаталог и активное сообщество автолюбителей помогут вам быть в курсе последних тенденций.
Some truly nice stuff on this site, I like it.
angkot88
ANGKOT88: Situs Game Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
ANGKOT88 adalah situs game deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game online terlengkap yang dapat Anda mainkan hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID. Dengan satu ID tersebut, Anda dapat mengakses seluruh permainan yang tersedia di situs kami.
Sebagai situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), ANGKOT88 menjamin keamanan dan kenyamanan Anda. Situs kami didukung oleh server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi terbaru di dunia, sehingga data Anda akan selalu terjaga keamanannya. Tampilan situs yang modern juga membuat Anda merasa nyaman saat mengakses situs kami.
Keunggulan ANGKOT88
Selain menjadi situs game online terbaik, ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit menggunakan pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dibandingkan situs lainnya. Ini menjadikan kami salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda juga dapat melakukan deposit pulsa melalui E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kepercayaan dan Layanan
Kami di ANGKOT88 sangat menjaga kepercayaan Anda sebagai prioritas utama kami. Oleh karena itu, kami selalu berusaha menjadi agen online terpercaya dan terbaik sepanjang masa. Permainan game online yang kami tawarkan sangat praktis, sehingga Anda dapat memainkannya kapan saja dan di mana saja tanpa perlu repot bepergian. Kami menyediakan berbagai jenis game, termasuk yang disiarkan secara LIVE (langsung) dengan host cantik dan kamera yang merekam secara real-time, menjadikan ANGKOT88 situs game online terlengkap dan terbesar di Indonesia.
Promo Menarik dan Menguntungkan
ANGKOT88 juga menawarkan banyak sekali promo menarik dan menguntungkan. Anda bisa menikmati berbagai macam promo yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan Anda, seperti welcome bonus 20%, bonus deposit harian, dan cashback. Semua promo ini tersedia di situs ANGKOT88. Selain itu, kami juga memiliki layanan Customer Service yang siap membantu Anda kapan saja.
Jadi, tunggu apa lagi? Bergabunglah dengan ANGKOT88 dan nikmati pengalaman bermain game online terbaik dan teraman di Indonesia. Daftarkan diri Anda sekarang dan mulai mainkan game favorit Anda dengan nyaman dan aman di situs kami!
[url=http://clomidsale.com/]cheapest clomid pills[/url]
It?¦s in point of fact a great and useful piece of info. I?¦m satisfied that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
https://ktm.org.ua/ у нас вы найдете свежие новости, аналитические статьи, эксклюзивные интервью и мнения экспертов. Будьте в курсе событий и тенденций, следите за развитием ситуации в реальном времени. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу читателей!
[url=http://albuterolp.online/]generic for ventolin[/url]
https://mostmedia.com.ua мы источник актуальных новостей, аналитики и мнений. Получайте самую свежую информацию, читайте эксклюзивные интервью и экспертные статьи. Оставайтесь в курсе мировых событий и тенденций вместе с нами. Присоединяйтесь к нашему информационному сообществу!
Founded in Texas in 2002, https://southeast.newschannelnebraska.com/story/50826769/del-mar-energy-from-humble-beginnings-to-an-energy-market-leader quickly transformed into one of the leading players in the energy market, oil and gas extraction, road construction
https://sunmory33jitu.com
SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
SUPERMONEY88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di SUPERMONEY88.
Keunggulan SUPERMONEY88
SUPERMONEY88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Layanan Praktis dan Terpercaya
Selain menjadi game online terbaik, ada alasan mengapa situs SUPERMONEY88 ini sangat spesial. Kami memberikan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit yaitu dengan melakukan deposit pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dari situs game online lainnya. Ini membuat situs kami menjadi salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda bisa melakukan deposit pulsa menggunakan E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kami juga terkenal sebagai agen game online terpercaya. Kepercayaan Anda adalah prioritas kami, dan itulah yang membuat kami menjadi agen game online terbaik sepanjang masa.
Kemudahan Bermain Game Online
Permainan game online di SUPERMONEY88 memudahkan Anda untuk memainkannya dari mana saja dan kapan saja. Anda tidak perlu repot bepergian lagi, karena SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan beragam jenis game online. Kami juga memiliki jenis game online yang dipandu oleh host cantik, sehingga Anda tidak akan merasa bosan.
[url=https://diflucand.com/]diflucan over the counter nz[/url]
[url=https://accutaneo.com/]purchase accutane[/url]
[url=https://lasixtbs.com/]furosemide 4 mg[/url]
[url=http://xlyrica.online/]lyrica 75 mg capsule price[/url]
SUPERMONEY88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
SUPERMONEY88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di SUPERMONEY88.
Keunggulan SUPERMONEY88
SUPERMONEY88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Layanan Praktis dan Terpercaya
Selain menjadi game online terbaik, ada alasan mengapa situs SUPERMONEY88 ini sangat spesial. Kami memberikan layanan praktis untuk melakukan deposit yaitu dengan melakukan deposit pulsa XL ataupun Telkomsel dengan potongan terendah dari situs game online lainnya. Ini membuat situs kami menjadi salah satu situs game online pulsa terbesar di Indonesia. Anda bisa melakukan deposit pulsa menggunakan E-commerce resmi seperti OVO, Gopay, Dana, atau melalui minimarket seperti Indomaret dan Alfamart.
Kami juga terkenal sebagai agen game online terpercaya. Kepercayaan Anda adalah prioritas kami, dan itulah yang membuat kami menjadi agen game online terbaik sepanjang masa.
Kemudahan Bermain Game Online
Permainan game online di SUPERMONEY88 memudahkan Anda untuk memainkannya dari mana saja dan kapan saja. Anda tidak perlu repot bepergian lagi, karena SUPERMONEY88 menyediakan beragam jenis game online. Kami juga memiliki jenis game online yang dipandu oleh host cantik, sehingga Anda tidak akan merasa bosan.
[url=http://declomid.online/]clomid tablets for sale[/url]
pro88
PRO88: Situs Game Online Deposit Pulsa Terbaik di Indonesia
PRO88 adalah situs game online deposit pulsa terbaik tahun 2020 di Indonesia. Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap yang bisa Anda mainkan di situs game online kami. Hanya dengan mendaftar satu ID, Anda bisa memainkan seluruh permainan yang tersedia di PRO88.
Keunggulan PRO88
PRO88 juga merupakan situs agen game online berlisensi resmi dari PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), yang berarti situs ini sangat aman. Kami didukung dengan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia untuk menjaga keamanan database Anda. Selain itu, tampilan situs kami yang sangat modern membuat Anda nyaman mengakses situs kami.
Berbagai Macam Game Online
Kami menyediakan berbagai macam game online terbaik yang bisa Anda mainkan kapan saja dan di mana saja. Dengan satu ID, Anda bisa menikmati semua permainan yang tersedia, mulai dari permainan kartu, slot, hingga taruhan olahraga. PRO88 memastikan semua game yang kami sediakan adalah yang terbaik dan terlengkap di Indonesia.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan
Kami memahami betapa pentingnya keamanan dan kenyamanan bagi para pemain. Oleh karena itu, PRO88 menggunakan server hosting yang cepat dan sistem keamanan dengan metode enkripsi termutakhir di dunia. Ini memastikan bahwa data pribadi dan transaksi Anda selalu aman bersama kami. Tampilan situs yang modern juga dirancang untuk memberikan pengalaman bermain yang nyaman dan menyenangkan.
Kesimpulan
PRO88 adalah pilihan terbaik untuk Anda yang mencari situs game online deposit pulsa yang aman dan terpercaya. Dengan berbagai macam game online terbaik dan terlengkap, serta dukungan keamanan yang canggih, PRO88 siap memberikan pengalaman bermain game yang tak terlupakan. Daftar sekarang juga di PRO88 dan nikmati semua permainan yang tersedia hanya dengan satu ID.
Kunjungi kami di PRO88 dan mulailah petualangan game online Anda bersama kami!
[url=http://albuterolo.com/]ventolin tablet 4mg[/url]
[url=https://eflomax.online/]where can you buy flomax[/url]
Nice blog here! Also your site loads up fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as fast as yours lol
Your post was a revelation! The depth of analysis combined with your clear, accessible writing style made for a compelling read. It’s evident that you put your heart and soul into your writing, and it pays off magnificently. Thank you for sharing your knowledge with us.
Консультация по SEO продвижению.
Информация о том как взаимодействовать с низкочастотными запросами и как их подбирать
Стратегия по работе в конкурентной нише.
Имею регулярных работаю с 3 компаниями, есть что поделиться.
Ознакомьтесь мой досье, на 31 мая 2024г
число успешных проектов 2181 только здесь.
Консультация проходит в устной форме, без снимков с экрана и отчётов.
Длительность консультации указано 2 часа, но по реально всегда на доступен без твердой привязки к графику.
Как взаимодействовать с программным обеспечением это уже другая история, консультация по использованию ПО обсуждаем отдельно в другом разделе, узнаем что требуется при разговоре.
Всё без суеты на без напряжения не торопясь
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от телеграмм каналов для контакта.
общение только в устной форме, переписываться недостаточно времени.
Суббота и Вс выходные
[url=https://modafinilon.online/]modafinil online europe[/url]
sunmory33
https://superwoman.kyiv.ua вы на нашем надежном гиде в мире женской красоты и стиля жизни! У нас вы найдете актуальные статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье, а также советы по саморазвитию и карьерному росту. Присоединяйтесь к нам и обретайте новые знания и вдохновение каждый день!
[url=https://lasixav.online/]lasix medication over the counter[/url]
bocor88
разработка и продвижение сайтов [url=www.prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru/]www.prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve111.ru/[/url] .
курсовые на заказ https://kursovyematematika.ru
Сегодня, когда диплом – это начало удачной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании переоценить просто невозможно. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который собирается вступить в профессиональное сообщество или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
Предлагаем быстро получить этот необходимый документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом старого или нового образца, и это становится удачным решением для человека, который не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Каждый диплом изготавливается аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим деталям. В результате вы сможете получить 100% оригинальный документ.
Превосходство этого решения заключается не только в том, что вы быстро получите свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начав от выбора подходящего образца документа до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки по стране — все под абсолютным контролем опытных мастеров.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания готова предложить выгодное решение. Заказать диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и не теряя времени перейти к важным целям, будь то поступление в университет или начало карьеры.
http://diplomsagroups.com/kupit-diplom-v-gorode/voronezh.html
在線娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的迅速發展,在線娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多樣化的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的興奮和快感。本文將討論網上娛樂城的特點、優勢以及一些常有的遊戲。
什麼網上娛樂城?
線上娛樂城是一種通過互聯網提供博彩游戲的平台。玩家可以經由電腦、手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如撲克牌、輪盤、21點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專業的軟件公司開發,確保遊戲的公正和安全性。
線上娛樂城的利益
便利:玩家不需要離開家,就能享用賭錢的樂趣。這對於那些住在在偏遠實體賭場區域的人來說特別方便。
多樣化的遊戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多樣化的游戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新鮮。
好處和獎勵:許多在線娛樂城提供豐厚的獎勵計劃,包括註冊紅利、存款獎勵和忠誠計劃,吸引新玩家並激勵老玩家持續遊戲。
穩定性和隱私:合法的在線娛樂城使用先進的加密來保護玩家的私人信息和金融交易,確保遊戲過程的安全和公平。
常見的網上娛樂城游戲
撲克:德州撲克是最流行博彩游戲之一。線上娛樂城提供多樣撲克牌變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張撲克等。
輪盤:賭盤是一種傳統的賭博遊戲,玩家可以賭注在單數、數字組合上或顏色上,然後看小球落在哪個地方。
21點:又稱為二十一點,這是一種比拼玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡可能接近21點但不超過。
老虎機:吃角子老虎是最受歡迎且是最流行的賭博游戲之一,玩家只需旋轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出贏得的組合。
結尾
網上娛樂城為現代賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、刺激的且多元化的娛樂方式。不論是撲克牌愛好者還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的游戲。同時,隨著技術的的不斷發展,線上娛樂城的游戲體驗將變得越來越越來越逼真和有趣。然而,玩家在體驗游戲的同時,也應該自律,避免沉溺於博彩活動,保持健康的遊戲心態。
Консультация по сео стратегии продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными запросами запросами и как их определять
Тактика по работе в соперничающей нише.
Обладаю постоянных взаимодействую с тремя организациями, есть что рассказать.
Ознакомьтесь мой досье, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём завершённых задач 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация проходит устно, никаких снимков с экрана и отчетов.
Длительность консультации указано 2 ч, и реально всегда на связи без твердой привязки ко времени.
Как взаимодействовать с ПО это уже отдельная история, консультация по работе с софтом оговариваем отдельно в отдельном разделе, определяем что необходимо при общении.
Всё без суеты на расслабленно не спеша
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от Telegram канала для коммуникации.
разговор только устно, переписываться нету времени.
Сб и Воскресенье выходной
추자현 마약 연기
빠른 입출금 서비스 및 메이저업체의 안전
스포츠토토사이트 접속 시 가장 중요한 요소 중 하나는 빠른 입출금 프로세스입니다. 일반적으로 삼 분 이내에 충전하고, 열 분 내에 환전이 처리되어야 합니다. 대형 대형업체들은 넉넉한 스태프 채용을 통해 이와 같은 신속한 입출금 프로세스를 보장하며, 이를 통해 고객들에게 안전한 느낌을 제공합니다. 메이저사이트를 이용하면서 신속한 경험을 해보시기 바랍니다. 우리는 고객님이 보안성 있게 사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 지원하는 먹튀 해결 팀입니다.
보증금 걸고 배너 운영
먹튀해결사는 최대한 3000만 원에서 1억 원의 보증금을 예치하고 있는 사이트들의 배너를 운영하고 있습니다. 만일 먹튀 문제가 발생할 시, 배팅 룰에 어긋나지 않은 베팅 내역을 스크린샷을 찍어 먹튀 해결 전문가에게 연락 주시면, 사실 확인 후 보증금으로 즉시 손해 보상을 처리해드립니다. 피해가 발생하면 신속하게 스크린샷을 찍어 손해 내용을 저장해 두시고 보내주세요.
장기 운영 안전업체 확인
먹튀 해결 팀은 최대한 사 년 이상 먹튀 문제 없이 안전하게 운영한 업체만을 인증하여 광고 배너 입점을 받고 있습니다. 이 때문에 모두가 알만한 메이저사이트를 안전하게 사용할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다. 철저한 검증 절차를 통해 검증된 사이트를 놓치지 말고, 안전한 배팅을 즐겨보세요.
투명하고 공정한 먹튀 검증
먹튀해결사의 먹튀 검증은 투명성과 공평성을 근거로 합니다. 늘 고객들의 관점을 우선시하며, 사이트의 회유나 이익에 좌우되지 않고 한 건의 삭제 없이 진실만을 근거로 검증해오고 있습니다. 먹튀 사고를 당하고 후회하지 않도록, 바로 지금 시작해보세요.
먹튀검증사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 팀이 골라낸 안전 토토사이트 검증업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록된 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 문제가 발생 시 100% 보증을 제공해드립니다. 그러나, 제휴 기간이 만료된 업체에서 발생한 사고에 대해서는 책임을 지지 않습니다.
유일무이한 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 전문가는 청결한 베팅 문화를 만들기 위해 항상 애쓰고 있습니다. 저희는 추천하는 토토사이트에서 안전하게 베팅하시기 바랍니다. 회원님의 먹튀 신고는 먹튀 리스트에 등록 노출되어 그 해당 토토사이트에 심각한 영향을 미칩니다. 먹튀 리스트를 작성할 때 먹튀블러드 만의 검증 노하우를 충분히 활용하여 공평한 심사를 할 수 있게 하겠습니다.
안전한 베팅 문화를 만들기 위해 계속해서 노력하는 먹튀 해결 전문가와 함께 안전하게 즐겨보세요.
obviously like your website however you have to test the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very bothersome to inform the truth however I will certainly come again again.
Больше интересной информации о строительстве и ремонте можно прочитать на сайте https://stroyka-gid.ru. Только самые популярные статьи и обзоры процесса ремонта помещений и строительства зданий.
Консультация по сео продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными запросами запросами и как их подбирать
Тактика по действиям в соперничающей нише.
Имею постоянных клиентов работаю с несколькими компаниями, есть что поделиться.
Ознакомьтесь мой аккаунт, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём успешных проектов 2181 только в этом профиле.
Консультация только в устной форме, никаких снимков с экрана и отчетов.
Время консультации указано 2 часа, но по сути всегда на контакте без твердой привязки ко времени.
Как работать с ПО это уже отдельная история, консультация по работе с программами договариваемся отдельно в другом услуге, узнаем что требуется при общении.
Всё без суеты на без напряжения не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны контакты от Telegram чата для связи.
коммуникация только в устной форме, вести переписку недостаточно времени.
Сб и Вс выходной
[url=https://ciproo.online/]cipro prescription online[/url]
В нашем обществе, где диплом становится началом отличной карьеры в любом направлении, многие ищут максимально простой путь получения качественного образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа об образовании сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед людьми, стремящимися вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность приобрести диплом, и это становится удачным решением для всех, кто не смог закончить обучение или утратил документ. Любой диплом изготавливается с особой тщательностью, вниманием к мельчайшим деталям, чтобы в результате получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущество данного решения заключается не только в том, что вы сможете быстро получить свой диплом. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. Начиная от выбора нужного образца до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки в любое место России — все будет находиться под полным контролем качественных специалистов.
Таким образом, для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый и простой способ получить необходимый документ, наша компания предлагает выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого процесса обучения и сразу переходить к важным целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало удачной карьеры.
http://diplomsagroups.com/diplomy-po-specialnosti/diplom-yurista.html
order bisacodyl without prescription – where can i buy bisacodyl liv52 20mg us
[url=https://strattera.company/]200 mg strattera[/url]
buy rabeprazole generic – buy domperidone pills buy motilium 10mg online
persib
Motivasi dari Kutipan Taylor Swift
Taylor Swift, seorang vokalis dan komposer terkenal, tidak hanya terkenal berkat nada yang menawan dan nyanyian yang merdu, tetapi juga oleh karena syair-syair lagunya yang penuh makna. Dalam syair-syairnya, Swift sering menggambarkan beraneka ragam unsur kehidupan, mulai dari cinta hingga rintangan hidup. Berikut adalah sejumlah kutipan inspiratif dari karya-karya, dengan maknanya.
“Mungkin yang paling baik belum tiba.” – “All Too Well”
Arti: Bahkan di masa-masa sulit, selalu ada secercah harapan dan kemungkinan tentang hari yang lebih cerah.
Lirik ini dari lagu “All Too Well” mengingatkan kita bahwa meskipun kita mungkin menghadapi masa-masa sulit saat ini, selalu ada kemungkinan kalau hari esok akan membawa sesuatu yang lebih baik. Ini adalah pesan asa yang menguatkan, merangsang kita untuk tetap bertahan dan tidak mengalah, sebab yang terhebat mungkin belum datang.
“Aku akan bertahan karena aku tidak bisa menjalankan apapun tanpamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Mendapatkan cinta dan bantuan dari orang lain dapat menghadirkan kita kekuatan dan tekad untuk bertahan melalui tantangan.
oyo88
Ashley JKT48: Idola yang Berkilau Gemilang di Dunia Idola
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapa tokoh muda berbakat yang menyita perhatian banyak fans musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Beliau adalah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang terkenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Masuk dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan lekas menjadi salah satu anggota paling favorit.
Profil
Lahir di Jakarta pada tgl 13 Maret 2000, Ashley memiliki darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Beliau memulai karier di industri entertainment sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum akhirnya bergabung dengan JKT48. Kepribadiannya yang periang, suara yang bertenaga, dan kemahiran menari yang mengesankan membentuknya sebagai idola yang sangat dicintai.
Award dan Penghargaan
Ketenaran Ashley telah diakui melalui banyak award dan pencalonan. Pada tahun 2021, Ashley meraih penghargaan “Member Terpopuler JKT48” di event JKT48 Music Awards. Ashley juga dinobatkan sebagai “Idol Tercantik di Asia” oleh sebuah tabloid online pada masa 2020.
Fungsi dalam JKT48
Ashley memainkan peran krusial dalam grup JKT48. Ia adalah member Tim KIII dan berfungsi sebagai penari utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga merupakan anggota dari sub-unit “J3K” dengan Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karier Individu
Di luar kegiatannya dengan JKT48, Ashley juga mengembangkan perjalanan mandiri. Ashley telah merilis sejumlah single, diantaranya “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah bekerja sama bareng artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Hidup Pribadi
Selain bidang panggung, Ashley dikenal sebagai pribadi yang rendah hati dan ramah. Ia suka melewatkan masa bersama family dan sahabat-sahabatnya. Ashley juga memiliki hobi menggambar dan memotret.
проверка адреса криптокошелька 22
Верификация адреса криптовалюты
Анализ монет на платформе TRC20 и различных криптовалютных операций
На этом веб-сайте вы найдете подробные ревью различных ресурсов для анализа платежей и кошельков, в том числе anti-money laundering проверки для криптовалюты и прочих виртуальных валют. Вот основные функции, которые в наших описаниях:
Контроль криптовалюты на платформе TRC20
Определенные инструменты предоставляют полную верификацию платежей криптовалюты на блокчейне TRC20 блокчейна. Это дает возможность идентифицировать сомнительную операции и выполнять правовым правилам.
Анализ транзакций монет
В наших ревью описаны инструменты для комплексного анализа и мониторинга платежей монет, которые помогает обеспечивать прозрачность и защищенность операций.
антиотмывочного закона анализ криптовалюты
Определенные сервисы предоставляют антиотмывочного закона верификацию монет, позволяя идентифицировать и пресекать ситуации отмывания денег и валютных мошенничеств.
Контроль аккаунта монет
Наши ревью представляют сервисы, что обеспечивают верифицировать кошельки USDT на предмет блокировок и подозреваемых действий, гарантируя повышенный степень безопасности безопасности.
Контроль транзакции USDT на сети TRC20
Вы описаны ресурсы, поддерживающие анализ транзакций криптовалюты на платформе TRC20 сети, что обеспечивает удовлетворение всем необходимым требованиям положениям.
Контроль кошелька аккаунта USDT
В описаниях указаны инструменты для анализа адресов кошельков криптовалюты на наличие потенциальных проблем.
Проверка адреса токенов на сети TRC20
Наши обзоры охватывают сервисы, предоставляющие верификацию аккаунтов монет на платформе TRC20 платформы, что позволяет позволяет исключение финансовых преступлений и экономических преступлений.
Проверка монет на отсутствие подозрительных действий
Обозреваемые ресурсы обеспечивают проверять транзакции и кошельки на чистоту, обнаруживая сомнительную операции.
AML проверка криптовалюты на сети TRC20
В описаниях описаны инструменты, предлагающие антиотмывочного закона проверку для монет в блокчейн-сети TRC20, что помогает вашему делу выполнять глобальным положениям.
Проверка криптовалюты на блокчейне ERC20
Наши обзоры охватывают сервисы, предлагающие верификацию USDT на блокчейне ERC20 платформы, что позволяет проведение переводов и кошельков.
Проверка виртуального кошелька
Мы обозреваем инструменты, поддерживающие решения по верификации криптовалютных кошельков, охватывая отслеживание транзакций и обнаружение необычной действий.
Верификация кошелька криптокошелька
Наши описания охватывают сервисы, дающие возможность верифицировать адреса виртуальных кошельков для повышения дополнительного уровня безопасности.
Контроль криптовалютного кошелька на переводы
Вы найдете описаны ресурсы для верификации криптокошельков на операции, что позволяет гарантирует сохранять ясность платежей.
Контроль криптовалютного кошелька на отсутствие подозрительных действий
Наши обзоры представляют платформы, позволяющие проверять криптовалютные кошельки на чистоту, обнаруживая любые необычные действия.
Изучая данные обзоры, вы сможете надежные сервисы для анализа и мониторинга криптовалютных переводов, чтобы поддерживать повышенный уровень надежности и выполнять все законодательным требованиям.
We stumbled over here coming from a different page and thought I might check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to going over your web page again.
internet casinos
Digital Casinos: Advancement and Advantages for Contemporary Community
Overview
Internet casinos are virtual platforms that provide users the chance to engage in gambling activities such as card games, spin games, blackjack, and slots. Over the last several decades, they have become an integral part of digital leisure, offering various advantages and opportunities for players around the world.
Accessibility and Convenience
One of the primary advantages of online gambling sites is their accessibility. Users can enjoy their preferred activities from anywhere in the world using a computer, tablet, or mobile device. This conserves hours and funds that would otherwise be used going to traditional gambling halls. Additionally, 24/7 access to activities makes online gambling sites a easy option for individuals with busy lifestyles.
Variety of Games and Experience
Online casinos provide a vast range of games, allowing everyone to find something they enjoy. From classic card games and board activities to slots with diverse themes and progressive jackpots, the range of games ensures there is an option for every preference. The option to play at various skill levels also makes digital gambling sites an ideal place for both beginners and experienced gamblers.
Financial Advantages
The digital casino sector contributes greatly to the economy by generating jobs and generating revenue. It backs a diverse variety of careers, including programmers, customer support agents, and marketing professionals. The income produced by online casinos also contributes to tax revenues, which can be used to support public services and infrastructure initiatives.
Advancements in Technology
Digital gambling sites are at the cutting edge of tech innovation, continuously adopting new technologies to enhance the playing experience. High-quality graphics, live dealer activities, and VR casinos provide immersive and authentic playing entertainment. These innovations not only improve player experience but also expand the boundaries of what is possible in online leisure.
Responsible Gambling and Assistance
Many online casinos promote responsible gambling by offering resources and assistance to assist users control their gaming activities. Features such as fund restrictions, self-ban options, and access to assistance programs ensure that players can engage in betting in a secure and controlled setting. These steps demonstrate the industry’s commitment to encouraging safe gaming practices.
Social Interaction and Networking
Online casinos often provide interactive options that allow players to connect with each other, creating a sense of community. Group games, chat functions, and networking integration enable users to connect, exchange experiences, and form friendships. This social aspect improves the entire gaming experience and can be especially beneficial for those seeking social interaction.
Summary
Online casinos provide a wide variety of advantages, from accessibility and convenience to economic contributions and technological advancements. They offer varied betting choices, encourage responsible gambling, and promote social interaction. As the sector keeps to evolve, online casinos will probably stay a major and beneficial presence in the realm of digital leisure.
Free Slot Games: Entertainment and Benefits for All
No-Cost slot games have become a favored form of virtual entertainment, offering players the excitement of slot machines absent any economic investment.
The main goal of gratis slot games is to provide a fun and absorbing way for players to relish the rush of slot machines devoid of any financial liability. They are designed to mimic the impression of for-profit slots, enabling players to spin the reels, relish various themes, and obtain digital rewards.
Amusement: Free slot games are an fantastic resource of entertainment, delivering spans of excitement. They feature animated illustrations, compelling audio, and diverse ideas that accommodate a comprehensive variety of interests.
Proficiency Improvement: For novices, no-cost slot games grant a risk-free situation to familiarize the principles of slot machines. Players can get acquainted with multiple feature sets, paylines, and bonus rounds devoid of the apprehension of forfeiting money.
Stress Relief: Playing complimentary slot games can be a fantastic way to decompress. The easy gameplay and the chance for digital prizes make it an pleasurable pastime.
Community Engagement: Many free slot games integrate social functions such as tournaments and the capacity to interact with friends. These aspects inject a collective aspect to the player experience, inspiring players to challenge against each other.
Rewards of No-Cost Slot Games
1. Reachability and Comfort
Gratis slot games are conveniently approachable to anyone with an online connection. They can be accessed on multiple apparatuses including desktops, handhelds, and smartphones. This comfort enables players to savor their chosen games regardless of time and in any location.
2. Fiscal Unconcern
One of the primary rewards of free slot games is that they eliminate the economic dangers associated with wagering. Players can savor the thrill of spinning the reels and hitting big rewards absent investing any capital.
3. Variety of Games
Complimentary slot games are available in a extensive array of concepts and configurations, from traditional fruit slots to current slot machines with video with sophisticated storylines and graphics. This range secures that there is an alternative for everyone, regardless of their preferences.
4. Developing Intellectual Aptitudes
Playing gratis slot games can lead to develop thinking abilities such as anticipatory planning. The task to pursue payout lines, grasp game mechanics, and foresee outcomes can provide a cognitive exercise that is concurrently rewarding and beneficial.
5. Risk-Free Trial Phase for Paid-Participation
For those contemplating progressing to paid slots, no-cost slot games present a beneficial testing ground. Players can experiment with multiple games, develop approaches, and develop self-assurance prior to choosing to stake actual cash. This readiness can result in a more informed and rewarding paid gaming sensation.
Key Takeaways
No-Cost slot games deliver a abundance of advantages, from sheer fun to competency enhancement and social interaction. They offer a safe and non-monetary way to savor the excitement of slot machines, establishing them a worthwhile addition to the landscape of electronic amusement. Whether you’re seeking to unwind, sharpen your intellectual faculties, or just enjoy yourself, no-cost slot games are a fantastic possibility that continues to entertain players throughout.
Online Gaming Site For-Profit: Upsides for Customers
Introduction
Internet-based casinos delivering for-profit offerings have obtained significant popularity, offering users with the chance to receive economic winnings while enjoying their favorite gaming offerings from home. This text investigates the upsides of internet-based gambling platform actual currency experiences, highlighting their favorable consequence on the entertainment domain.
Simplicity and Approachability
Internet-based gambling platform paid offerings offer user-friendliness by giving participants to engage with a extensive array of activities from any setting with an online access. This removes the necessity to make trips to a physical gambling establishment, conserving expenses. Internet-based gambling platforms are likewise available 24/7, allowing players to play at their ease.
Variety of Games
Internet-based gambling platforms offer a more broad variety of experiences than traditional gaming venues, incorporating slot-related offerings, 21, spinning wheel, and table games. This breadth gives players to experiment with novel games and discover different favorites, improving their total interactive interaction.
Incentives and Special Offers
Internet-based gambling platforms present substantial perks and advantages to draw in and keep players. These rewards can involve new player bonuses, non-chargeable turns, and cashback discounts, providing additional value for participants. Loyalty initiatives in addition reward users for their persistent custom.
Proficiency Improvement
Engaging with paid experiences online can facilitate users refine skills such as critical analysis. Games like vingt-et-un and table games necessitate players to render decisions that can impact the end of the offering, helping them acquire decision-making skills.
Interpersonal Connections
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:08]
Online casinos grant opportunities for collaborative engagement through chat rooms, interactive platforms, and live dealer games. Users can communicate with one another, discuss strategies and strategies, and even form personal connections.
Monetary Upsides
The digital gaming sector generates positions and contributes to the fiscal landscape through fiscal revenues and licensing payments. This economic impact benefits a broad range of fields, from offering developers to user services agents.
Conclusion
Online casino for-profit offerings provide various rewards for participants, encompassing user-friendliness, breadth, rewards, capability building, shared experiences, and economic advantages. As the sector continues to progress, the widespread adoption of online casinos is projected to rise.
Wealth Gambling Platform: In a Place Where Pleasure Combines With Fortune
Prosperity Gambling Platform is a popular digital destination recognized for its comprehensive array of offerings and exciting incentives. Let’s explore the factors that explain why so numerous users savor playing at Luck Gaming Site and the extent to which it rewards them.
Entertainment Value
Luck Casino presents a breadth of activities, involving classic table games like vingt-et-un and spinning wheel, as together with innovative slot machines. This variety provides that there is an alternative for everyone, making each trip to Wealth Gaming Site satisfying and amusing.
Significant Rewards
One of the principal attractions of Luck Gaming Site is the prospect to earn significant rewards. With substantial top rewards and rewards, participants have the chance to achieve unexpected success with a single play or hand. Numerous players have acquired significant prizes, adding to the thrill of partaking in Luck Wagering Environment.
User-Friendliness and Availability
Luck Wagering Environment’s internet-based interface constitutes it as user-friendly for players to enjoy their most preferred activities from any place. Regardless of whether at home or in transit, participants can reach Wealth Gambling Platform from their laptop or mobile device. This accessibility guarantees that players can enjoy the anticipation of the casino whenever they choose, without the requirement to commute.
Variety of Games
Fortune Gambling Platform provides a extensive assortment of offerings, securing that there is a choice for every single style of player. Beginning with traditional wagering games to narrative-driven slot-based games, the range retains customers engaged and amused. This array as well allows players to investigate new activities and uncover novel favorites.
Promotional Benefits
Luck Wagering Environment acknowledges its customers with bonuses and benefits, incorporating sign-up bonuses and loyalty programs. These rewards not just bolster the leisure encounter but also increase the likelihoods of winning big. Customers are persistently driven to maintain participation, making Luck Wagering Environment further appealing.
Shared Experiences and Social Networking
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:30]
Wealth Casino provides a environment of collective engagement and group-based participation for customers. Via discussion forums and discussion boards, users can engage with one another, share strategies and approaches, and occasionally create friendships. This communal component brings another dimension of pleasure to the entertainment sensation.
Summary
Fortune Casino provides a comprehensive selection of rewards for users, incorporating amusement, the opportunity to achieve substantial winnings, user-friendliness, breadth, bonuses, and interpersonal connections. Regardless of whether seeking anticipation or hoping to strike it rich, Wealth Wagering Environment grants an captivating sensation for any partake in.
русское порно анал бесплатно [url=http://www.russkiy-anal-x.ru/]http://www.russkiy-anal-x.ru/[/url] .
free poker machine games
Gratis Poker Machine Experiences: A Pleasurable and Beneficial Sensation
Complimentary slot-based experiences have emerged as progressively sought-after among users desiring a thrilling and safe entertainment encounter. These experiences grant a extensive array of rewards, constituting them as a favored alternative for numerous. Let’s explore how free poker machine games can upside users and the factors that explain why they are so extensively enjoyed.
Fun Element
One of the main reasons people enjoy engaging with free poker machine experiences is for the amusement factor they provide. These activities are designed to be engaging and captivating, with lively visuals and absorbing sound effects that bolster the total interactive interaction. Whether you’re a casual user seeking to pass the time or a dedicated gaming aficionado aspiring to suspense, complimentary slot-based activities grant pleasure for everyone who.
Skill Development
Engaging with free poker machine offerings can in addition facilitate hone helpful faculties such as problem-solving. These experiences necessitate participants to render swift decisions reliant on the cards they are dealt, facilitating them improve their critical-thinking abilities and intellectual prowess. Moreover, customers can experiment with various tactics, honing their abilities without the potential for loss of parting with real money.
User-Friendliness and Availability
Another benefit of complimentary slot-based activities is their convenience and reachability. These experiences can be engaged with in the virtual sphere from the simplicity of your own residence, removing the need to journey to a traditional gambling establishment. They are likewise available around the clock, allowing users to experience them at whichever time that suits them. This simplicity renders complimentary slot-based experiences a popular choice for users with hectic schedules or those seeking a quick interactive resolution.
Communal Engagement
Several no-cost virtual wagering activities in addition offer communal aspects that allow participants to communicate with each other. This can feature communication channels, discussion boards, and competitive formats where participants can pit themselves against fellow users. These social interactions bring an extra aspect of pleasure to the gaming sensation, allowing users to engage with like-minded individuals who have in common their interests.
Anxiety Reduction and Mental Unwinding
Interacting with free poker machine offerings can as well be a wonderful way to relax and de-stress after a long duration. The straightforward activity and soothing audio can facilitate diminish stress and apprehension, granting a desired break from the pressures of normal experience. Moreover, the excitement of obtaining simulated payouts can elevate your frame of mind and render you rejuvenated.
Key Takeaways
Free poker machine offerings offer a wide array of benefits for participants, involving entertainment, skill development, user-friendliness, social interaction, and anxiety reduction and relaxation. Regardless of whether you’re seeking to sharpen your poker faculties or just enjoy yourself, no-cost virtual wagering activities offer a advantageous and pleasurable interaction for participants of any degrees.
online poker
Online Card Games: A Provider of Amusement and Skill Development
Online table games has emerged as a well-liked type of pleasure and a channel for proficiency improvement for customers worldwide. This piece analyzes the constructive facets of internet-based card games and in which manner it benefits people, emphasizing its widespread recognition and effect.
Fun Element
Digital table games grants a captivating and compelling gaming experience, spellbinding players with its calculated interactivity and variable results. The experience’s immersive character, combined with its communal aspects, delivers a singular kind of amusement that numerous find rewarding.
Capability Building
In addition to fun, digital table games as well functions as a medium for skill development. The game necessitates critical analysis, rapid responses, and the capacity to understand opponents, all of these contribute to intellectual maturation. Players can enhance their problem-solving abilities, interpersonal skills, and calculated approach aptitudes through consistent engagement.
Convenience and Accessibility
One of the principal advantages of online poker is its convenience and reachability. Players can savor the experience from the ease of their residences, at whichever period that fits them. This availability removes the necessity for travel to a traditional gaming venue, establishing it as a straightforward possibility for people with packed agendas.
Variety of Games and Stakes
Digital table games platforms present a extensive breadth of experiences and wagers to target players of any skill levels and desires. Regardless of whether you’re a learner wanting to learn the fundamentals or a veteran master desiring a trial, there is a activity for you. This breadth guarantees that participants can constantly uncover a experience that aligns with their proficiency and financial resources.
Communal Engagement
Internet-based card games in addition provides opportunities for communal engagement. A significant number of systems grant chat features and collaborative modes that enable customers to engage with like-minded players, communicate sensations, and build social relationships. This social factor injects substance to the gaming interaction, constituting it as more pleasurable.
Earnings Opportunities
For some, internet-based card games can in addition be a wellspring of profit potential. Proficient participants can obtain major earnings through consistent activity, rendering it a money-making undertaking for those who excel at the offering. Additionally, numerous virtual casino-style games events present considerable winnings, providing players with the possibility to earn significant rewards.
Recap
Digital table games offers a selection of benefits for participants, including amusement, competency enhancement, simplicity, shared experiences, and monetary gains. Its broad appeal continues to expand, with several users shifting to internet-based card games as a provider of pleasure and personal growth. Regardless of whether you’re aiming to hone your aptitudes or simply enjoy yourself, online poker is a multifaceted and beneficial hobby for customers of all perspectives.
курсовые работы на заказ https://zakazat-kontrolnuyu7.ru
이선균 마약
신속한 입출금 서비스 및 메이저업체의 안전
토토사이트 이용 시 매우 중요한 부분 중 하나는 신속한 환충 프로세스입니다. 일반적으로 세 분 이내에 입금, 십 분 이내에 환충이 완수되어야 합니다. 메이저 대형업체들은 넉넉한 인력 채용으로 이와 같은 빠릿한 환충 프로세스를 보증하며, 이 방법으로 고객들에게 안전감을 드립니다. 대형사이트를 이용하면서 스피드 있는 체험을 즐겨보세요. 우리 여러분들이 보안성 있게 사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 도와드리는 먹튀해결 전문가입니다.
보증금을 걸고 배너를 운영
먹튀해결사는 적어도 삼천만 원에서 억대의 보증 금액을 예치하고 있는 회사들의 배너를 운영 중입니다. 혹시 먹튀 사고가 발생할 경우, 베팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 배팅 내역을 스크린샷을 찍어 먹튀해결사에 연락 주시면, 사실 확인 뒤 보증 금액으로 즉시 피해 보전 처리합니다. 피해 발생 시 신속하게 캡처하여 피해 내용을 기록해두시고 보내주시기 바랍니다.
오랫동안 안전하게 운영된 업체 확인
먹튀 해결 팀은 최대한 사 년 이상 먹튀 이력 없이 무사히 운영하고 있는 사이트만을 인증하여 배너 등록을 허용합니다. 이 때문에 모두가 알만한 주요사이트를 안전하게 이용할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다. 철저한 검사 작업을 통해 검증된 사이트를 놓치지 않도록, 안심하고 도박을 체험해보세요.
투명하고 공정한 먹튀 검토
먹튀 해결 전문가의 먹튀 검증은 투명함과 공평성을 기반으로 합니다. 언제나 사용자들의 관점을 최우선으로 생각하며, 기업의 유혹이나 이익에 흔들리지 않고 하나의 삭제 없이 사실만을 근거로 검증해오고 있습니다. 먹튀 피해를 당하고 후회하지 않도록, 지금 시작해보세요.
먹튀검증사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 팀이 골라낸 안전 토토사이트 검증된 업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록되어 있는 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 사고 발생 시 100% 보장을 도와드립니다. 다만, 제휴 기간이 만료된 업체에서 발생한 사고에 대해서는 책임지지 않습니다.
탁월한 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀해결사는 청결한 도박 문화를 조성하기 위해 항상 애쓰고 있습니다. 저희가 소개하는 스포츠토토사이트에서 안전하게 배팅하세요. 회원님의 먹튀 신고는 먹튀 목록에 기재되어 그 해당 베팅 사이트에 치명적인 영향을 미칩니다. 먹튀 목록 작성 시 먹튀블러드의 검증 노하우를 충분히 활용하여 공정한 심사를 하도록 약속드립니다.
안전한 베팅 환경을 제공하기 위해 끊임없이 힘쓰는 먹튀해결사와 같이 안심하고 즐기시기 바랍니다.
решение задач на заказ https://resheniye-zadach7.ru заказать онлайн
[url=https://lyricawithoutprescription.com/]lyrica 25 mg capsule[/url]
jarisakti
Download Program 888 dan Peroleh Besar: Panduan Cepat
**Program 888 adalah pilihan unggulan untuk Para Pengguna yang mengharapkan pengalaman berjudi online yang menyenangkan dan berjaya. Bersama bonus harian dan fitur menarik, app ini menawarkan menawarkan aktivitas main optimal. Disini panduan singkat untuk menggunakan pelayanan Perangkat Lunak 888.
Unduh dan Awali Raih
Platform Terdapat:
App 888 dapat diunduh di Android, Sistem iOS, dan PC. Mulai main dengan praktis di gadget apa saja.
Bonus Sehari-hari dan Bonus
Keuntungan Buka Sehari-hari:
Masuk pada waktu untuk mengambil hadiah mencapai 100K pada waktu ketujuh.
Tuntaskan Tugas:
Peroleh opsi undi dengan menuntaskan tugas terkait. Satu aktivitas menyediakan Anda satu opsi undi untuk memenangkan imbalan hingga 888K.
Pengklaiman Manual:
Hadiah harus diambil sendiri di dalam program. Pastikan untuk mengambil hadiah saban waktu agar tidak batal.
Prosedur Undian
Kesempatan Undian:
Satu masa, Anda bisa meraih sebuah opsi lotere dengan menyelesaikan pekerjaan.
Jika opsi undi berakhir, tuntaskan lebih banyak aktivitas untuk meraih tambahan peluang.
Ambang Bonus:
Raih bonus jika jumlah pengeretan Pengguna lebih dari 100K dalam 1 hari.
Peraturan Penting
Pengambilan Imbalan:
Bonus harus diklaim manual dari aplikasi. Jika tidak, bonus akan otomatis diambil ke akun Anda Anda setelah sebuah periode.
Ketentuan Bertaruh:
Hadiah harus ada minimal satu bertaruh valid untuk digunakan.
Akhir
Aplikasi 888 menghadirkan pengalaman berjudi yang menggembirakan dengan imbalan signifikan. Pasang perangkat lunak saat ini dan nikmati keberhasilan tinggi setiap periode!
Untuk detail lebih terperinci tentang promosi, pengisian, dan agenda rujukan, lihat halaman utama program.
lucky jet на деньги [url=https://1win-luckyjet-ru.ru/]https://1win-luckyjet-ru.ru/[/url] .
[url=http://lyricawithoutprescription.com/]lyrica usa[/url]
купить диплом в ангарске
источник
Hi there! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I truly enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Thanks!
http://www.phonotope.net/topics/archives/000052.htmlВ
sdo.rea.ru/siteFDO/?executorID=ForumExecutor&mode=showThemes&&cursor=60В
lssrussia.ru/newslean/forum-v-ust-ilimske/В
vv.flybb.ru/topic1874.html?view=previousВ
eworlddxn.com/ar/product/122В
Все самое интересное из мира игр https://unionbattle.ru обзоры, статьи и ответы на вопросы
mponusa
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bersinar Gemilang di Langit Idol
Siapa Ashley JKT48?
Siapa tokoh belia berbakat yang menyita perhatian banyak sekali penyuka musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Beliau adalah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan nama bekennya, Ashley JKT48. Bergabung dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan lekas muncul sebagai salah satu personel paling terkenal.
Riwayat Hidup
Dilahirkan di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berdarah darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Beliau mengawali kariernya di industri entertainment sebagai model dan pemeran, sebelum kemudian bergabung dengan JKT48. Kepribadiannya yang gembira, nyanyiannya yang kuat, dan keterampilan menari yang mengesankan menjadikannya idola yang sangat dicintai.
Award dan Pengakuan
Kepopuleran Ashley telah dikenal melalui banyak penghargaan dan nominasi. Pada masa 2021, ia mendapat award “Anggota Paling Populer JKT48” di ajang JKT48 Music Awards. Ia juga dianugerahi sebagai “Idol Terindah di Asia” oleh sebuah media online pada tahun 2020.
Posisi dalam JKT48
Ashley mengisi fungsi penting dalam grup JKT48. Beliau adalah personel Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai penari utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga terlibat sebagai bagian dari unit sub “J3K” bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karier Individu
Di luar aktivitasnya bersama JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karier mandiri. Beliau telah mengeluarkan sejumlah single, termasuk “Myself” (2021) dan “Falling Down” (2022). Ashley juga telah berkolaborasi bareng artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Pribadi
Di luar dunia panggung, Ashley dikenal sebagai pribadi yang rendah hati dan friendly. Beliau menggemari menghabiskan waktu bareng family dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki hobi melukis dan memotret.
hongkong
Pasang Program 888 dan Raih Hadiah: Petunjuk Cepat
**Aplikasi 888 adalah opsi terbaik untuk Anda yang mencari aktivitas bermain daring yang seru dan bermanfaat. Dengan bonus sehari-hari dan opsi menarik, aplikasi ini menawarkan menyediakan pengalaman bermain terbaik. Inilah manual singkat untuk memanfaatkan penggunaan Perangkat Lunak 888.
Unduh dan Mulailah Menangkan
Platform Tersedia:
App 888 dapat diinstal di Sistem Android, iOS, dan Laptop. Mulai bermain dengan tanpa kesulitan di gadget apa saja.
Imbalan Harian dan Bonus
Imbalan Masuk Sehari-hari:
Login saban periode untuk meraih imbalan sebesar 100K pada hari ketujuh.
Tuntaskan Pekerjaan:
Peroleh opsi undian dengan menyelesaikan tugas terkait. Satu tugas menawarkan Anda satu kesempatan undian untuk mengklaim keuntungan sampai 888K.
Pengumpulan Manual:
Imbalan harus dikumpulkan mandiri di dalam aplikasi. Jangan lupa untuk mengambil keuntungan tiap waktu agar tidak batal.
Prosedur Pengeretan
Peluang Undi:
Masing-masing waktu, Anda bisa meraih sebuah kesempatan pengeretan dengan menyelesaikan misi.
Jika peluang lotere tidak ada lagi, rampungkan lebih banyak misi untuk meraih tambahan kesempatan.
Ambang Bonus:
Raih keuntungan jika keseluruhan undian Para Pengguna melampaui 100K dalam waktu satu hari.
Peraturan Pokok
Pengumpulan Hadiah:
Bonus harus dikumpulkan manual dari aplikasi. Jika tidak, imbalan akan otomatis diserahkan ke akun pengguna Anda setelah satu hari.
Syarat Taruhan:
Imbalan harus ada paling tidak satu betting berlaku untuk diklaim.
Penutup
Aplikasi 888 menawarkan keseruan berjudi yang menggembirakan dengan keuntungan besar. Unduh program sekarang juga dan nikmati kemenangan tinggi tiap waktu!
Untuk detail lebih terperinci tentang promo, pengisian, dan agenda undangan, lihat laman beranda program.
sultantoto
Inspirasi dari Petikan Taylor Swift
Taylor Swift, seorang vokalis dan komposer populer, tidak hanya dikenal karena melodi yang elok dan nyanyian yang merdu, tetapi juga karena syair-syair karyanya yang penuh makna. Dalam syair-syairnya, Swift sering menggambarkan berbagai faktor eksistensi, dimulai dari cinta sampai tantangan hidup. Berikut adalah beberapa kutipan menginspirasi dari lagu-lagunya, bersama maknanya.
“Mungkin yang terbaik belum datang.” – “All Too Well”
Arti: Bahkan di masa-masa sulit, selalu ada sedikit harapan dan potensi tentang masa depan yang lebih baik.
Lirik ini dari lagu “All Too Well” menyadarkan kita kalau meskipun kita mungkin menghadapi masa sulit pada saat ini, senantiasa ada kemungkinan bahwa masa depan bisa mendatangkan perubahan yang lebih baik. Ini adalah amanat harapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk terus bertahan dan tidak menyerah, sebab yang terbaik barangkali belum datang.
“Aku akan tetap bertahan lantaran aku tidak bisa menjalankan apa pun tanpamu.” – “You Belong with Me”
Arti: Menemukan cinta dan dukungan dari orang lain dapat menghadirkan kita tenaga dan niat untuk terus berjuang lewat kesulitan.
Exploring the Universe of Poker Game Free
Beginning
In the modern age, poker games have transformed into broadly accessible recreation possibilities. For those looking for an unpaid method to enjoy this card game, no-cost poker sites offer a thrilling venture. This article investigates the pros and factors why no-cost poker has become a popular selection for various players.
Perks of Complimentary Poker
Complimentary Fun
One of the very appealing attributes of complimentary poker is that it gives users with cost-free recreation. There is no demand to use funds to play the gameplay, making it reachable to everyone.
Skill Development
Playing poker game free allows users to refine their abilities without an monetary danger. It is a excellent opportunity for novices to understand the principles and tactics of poker games.
Social Interaction
Many complimentary poker websites provide possibilities for interactive interaction. Enthusiasts can engage with peers, talk about methods, and engage in warm tournaments.
Why Many Players Prefer Poker Game Free
Attainability
Complimentary poker are extensively available, allowing players from diverse backgrounds to experience the card game.
No Fiscal Risk
With free poker games, there is no financial hazard, making it a safe alternative for gamers who seek to experience this card game without using money.
Multiple Game Choices
Complimentary poker platforms offer a broad range of card games, guaranteeing that users can continually find an option that matches their preferences.
Ending
No-cost poker provides a entertaining and reachable method for users to engage in the game of poker. With no financial risk, chances for improving skills, and extensive game choices, it is no wonder that various gamers choose free poker games as their chosen betting choice.
Online casinos are steadily more in demand, providing different promotions to bring in new users. One of the most tempting propositions is the no deposit bonus, a offer that enables players to test their luck without any initial deposit. This write-up examines the merits of no upfront deposit bonuses and underscores how they can boost their efficiency.
What is a No Deposit Bonus?
A no upfront deposit bonus is a category of casino incentive where users receive bonus funds or complimentary spins without the need to deposit any of their own funds. This enables casino enthusiasts to try out the gaming site, test out different game options and potentially win real prizes, all without any monetary input.
Advantages of No Deposit Bonuses
Risk-Free Exploration
No upfront deposit bonuses give a cost-free option to discover internet casinos. Players can try different gaming activities, get to know the gaming environment, and analyze the overall user experience without using their own funds. This is especially advantageous for new players who may not be used to internet casinos.
Chance to Win Real Money
One of the most enticing features of no-deposit bonuses is the chance to earn real cash. While the amounts may be minor, any earnings earned from the bonus can typically be redeemed after meeting the casino’s staking criteria. This introduces an element of anticipation and offers a likely financial reward without any initial expenditure.
Learning Opportunity
Free bonuses provide a great opportunity to learn how multiple games function. Players can test out tactics, grasp the rules of the gaming activities, and grow more comfortable without fearing losing their own funds. This can be notably helpful for advanced gaming activities like strategy games.
Conclusion
No upfront deposit bonuses deliver several advantages for players, which include cost-free discovery, the possibility to get real rewards, and beneficial learning opportunities. As the sector continues to evolve, the demand of no upfront deposit bonuses is set to expand.
casino online
Exploring the Domain of Online Casinos
Start
Currently, online casinos have transformed the way people play gambling. With advanced innovations, users can get to their beloved casino games from the ease of their living spaces. This article examines the perks of virtual casinos and as to why they are attracting popularity.
Pros of Internet Casinos
Convenience
One of the major advantages of internet casinos is comfort. Users can play whenever they want and wherever they are they prefer, doing away with the demand to go to a traditional betting place.
Diverse Game Selection
Virtual casinos provide a broad variety of casino games, including vintage slots and board games to live dealer games and new slot games. This variety assures that there is something for every kind of gambler.
Perks and Specials
Among the most attractive features of internet casinos is the selection of promotions and deals available to enthusiasts. These can include welcome bonuses, complimentary spins, refund incentives, and player clubs.
Security and Reliability
Renowned internet casinos ensure user safety and security with cutting-edge cybersecurity techniques. This secures private credentials and financial exchanges.
Motives Behind the Popularity of Internet Casinos
Accessibility
Internet casinos are extensively reachable, enabling players from numerous locations to enjoy casino games.
신속한 환충 서비스와 더불어 대형업체의 보안성
토토사이트 접속 시 가장 중요한 요소는 빠릿한 환충 절차입니다. 대개 세 분 내에 입금, 열 분 안에 환충이 완수되어야 합니다. 메이저 대형업체들은 넉넉한 직원 채용으로 이 같은 신속한 입출금 처리를 보장하며, 이 방법으로 고객들에게 안전한 느낌을 드립니다. 대형사이트를 사용하면서 빠른 경험을 해보시기 바랍니다. 우리는 고객님이 안심하고 토토사이트를 접속할 수 있도록 도와드리는 먹튀해결사입니다.
보증금 걸고 배너 운영
먹튀 해결 팀은 최소 3000만 원에서 1억 원의 보증 금액을 예치하고 있는 사이트들의 배너 광고를 운영하고 있습니다. 만약 먹튀 사고가 발생할 경우, 배팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 베팅 내역을 캡처해서 먹튀 해결 전문가에게 문의하시면, 사실 확인 후 보증 자금으로 즉시 피해 보전 처리합니다. 피해가 생기면 신속하게 캡처하여 피해 상황을 기록해두시고 제출해 주세요.
오랫동안 안전하게 운영된 업체 확인
먹튀 해결 전문가는 최대한 4년 이상 먹튀 이력 없이 안정적으로 운영하고 있는 사이트들을 검증하여 배너 등록을 허가합니다. 이 때문에 누구나 잘 알려진 대형사이트를 안전하게 접속할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다. 정확한 검증 절차를 통해 인증된 사이트를 놓치지 마시고, 안심하고 배팅을 즐겨보세요.
투명하고 공정한 먹튀 검증
먹튀해결사의 먹튀 검토는 투명함과 공평성을 바탕으로 실시합니다. 항상 사용자들의 관점을 우선시하며, 업체의 유혹이나 이익에 좌우되지 않고 1건의 삭제 없이 사실만을 바탕으로 검증해오고 있습니다. 먹튀 사고를 당하고 후회하지 않도록, 지금 시작하세요.
먹튀 검증 사이트 목록
먹튀 해결 팀이 선별한 안전 토토사이트 검증된 업체 목록 입니다. 지금 등록된 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 사고 발생 시 100% 보증을 해드립니다. 하지만, 제휴 기간이 만료된 업체에서 발생한 피해에 대해서는 책임이 없습니다.
독보적인 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 팀은 청결한 베팅 환경을 형성하기 위해 항상 노력합니다. 우리가 추천하는 베팅사이트에서 안심하고 베팅하세요. 사용자의 먹튀 제보는 먹튀 목록에 등록되어 해당되는 베팅 사이트에 중대한 영향을 미칩니다. 먹튀 목록 작성 시 먹튀블러드 만의 검토 경험을 최대로 사용하여 공평한 심사를 할 수 있도록 하겠습니다.
안전한 도박 환경을 제공하기 위해 끊임없이 힘쓰는 먹튀 해결 팀과 같이 안심하고 경험해보세요.
sweepstakes casino
Examining Contest Gaming Hubs: A Captivating and Accessible Betting Option
Prelude
Promotion gambling platforms are growing into a well-liked alternative for players looking for an engaging and legitimate approach to enjoy internet-based betting. Differing from classic digital casinos, contest gambling platforms function under different lawful models, enabling them to deliver activities and gifts without adhering to the equivalent laws. This article analyzes the concept of sweepstakes gambling platforms, their benefits, and why they are drawing a growing figure of gamers.
What is a Sweepstakes Casino?
A sweepstakes betting site operates by providing players with online money, which can be applied to participate in activities. Gamers can win more digital coins or real gifts, for example funds. The main distinction from traditional betting sites is that players do not acquire coins straightforwardly but obtain it through marketing efforts, such as acquiring a goods or taking part in a no-cost entry sweepstakes. This model permits lottery betting sites to work legitimately in many areas where classic internet-based wagering is limited.
Discovering Free-of-Charge Casino Games
Introduction
Today, complimentary casino games have evolved into a preferred option for gamers who wish to engage in casino activities free from spending cash. This text examines the pros of complimentary casino games and the reasons they are drawing interest.
Pros of Complimentary Casino Games
No-Risk Gaming
One of the major advantages of complimentary casino games is the ability to gamble without monetary loss. Enthusiasts can enjoy their preferred games devoid of the stress of misplacing cash.
Skill Enhancement
No-cost casino games supply an ideal arena for gamblers to sharpen their abilities. Whether learning techniques in poker, users can train minus financial consequences.
Diverse Game Selection
Complimentary casino games provide a broad range of casino games, such options as vintage slot games, board games, and real-time games. This variety guarantees that there is a game for all types of players.
Motives Behind the Popularity of Complimentary Casino Games
Reachability
Free-of-charge casino games are commonly attainable, facilitating enthusiasts from different locations to enjoy betting.
Free from Financial Burden
Unlike money-based casino games, free casino games do not require a financial outlay. This permits enthusiasts to engage in gaming without concerns about wasting cash.
Test Before Betting
No-cost casino games give gamblers the possibility to test games in advance of committing hard-earned finances. This aids users make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Free-of-charge casino games gives a entertaining and secure method to engage in gaming. With no financial commitment, diverse game options, and abilities for skill enhancement, it is understandable that various gamblers like free casino games for their gambling needs.
Examining Money Slots
Overview
Gambling slots have become a popular option for players desiring the excitement of winning actual currency. This write-up delves into the advantages of money slots and the motivations they are gaining a growing number of users.
Advantages of Cash Slots
Tangible Earnings
The most draw of cash slots is the opportunity to secure real money. As opposed to no-cost slots, real money slots provide gamblers the adrenaline of prospective economic gains.
Diverse Game Options
Real money slots offer a wide array of types, attributes, and reward systems. This makes sure that there is an activity for everyone, ranging from vintage three-reel classic slots to contemporary slot games with numerous betting lines and special bonuses.
Exciting Bonuses and Promotions
Many internet casinos offer exciting bonuses for cash slot players. These can comprise initial offers, free spins, cashback offers, and loyalty programs. Such promotions boost the general gambling journey and supply additional opportunities to gain money.
Why Enthusiasts Enjoy Gambling Slots
The Thrill of Winning Real Money
Gambling slots provide an exhilarating adventure, as enthusiasts anticipate the potential of winning actual cash. This characteristic contributes another layer of thrill to the gaming activity.
Immediate Rewards
Gambling slots provide users the satisfaction of quick payouts. Winning cash promptly increases the betting activity, rendering it more fulfilling.
Extensive Game Variety
Alongside cash slots, users can experience a diverse selection of games, guaranteeing that there is always an activity exciting to experience.
Summary
Cash slots offers a adrenaline-filled and gratifying gaming adventure. With the potential to earn tangible money, a wide selection of games, and exciting offers, it’s no wonder that various users choose real money slots for their casino requirements.
[url=http://acyclovirmc.online/]zovirax pharmacy[/url]
buy cotrimoxazole 960mg sale – buy tobra generic buy generic tobra
play slots for real money
In the present-day virtual age, the domain of wagering activities has gone through a exceptional change, with online gaming venues establishing themselves as the freshest domain of amusement and anticipation.
Among the the top captivating components as part of this lively realm are the ever-in-demand virtual slot games, welcoming users to begin a journey of captivating engagement and the chance to win monetary prizes.
Internet-based slot machines have transformed into a embodiment of excitement and anticipation for customers encompassing the world, offering an unmatched level of convenience and approachability.
Through just a several selections, you can immerse yourself in a brilliant collection of slot motifs, all precisely designed to stimulate your awareness and keep you on the edge of your chair.
A primary the primary appeals of betting on slot machines for cash rewards on digital platforms is the chance to feel the anticipation of conceivably transformative winnings. The anticipation of witnessing the elements rotate, the features align, and the grand prize entice can be genuinely thrilling.
Internet-based gaming venues have flawlessly embedded state-of-the-art frameworks to present a leisure sensation that is both aesthetically enthralling and beneficial.
Apart from the appeal of conceivable winnings, virtual slot games likewise present a extent of flexibility and power that is unsurpassed in the typical casino scenario. You can tailor your wagers to suit your monetary constraints, adjusting your wagers to discover the optimal balance that aligns with your individual desires and comfort with uncertainty. This amount of customization equips customers to strengthen their monetary funds and amplify their enjoyment, entirely from the simplicity of their individual dwellings.
телефон такси эконом стоимость такси в новочеркасске
как пожаловаться на мошенников [url=https://pozhalovatsya-na-moshennikov.ru/]как пожаловаться на мошенников[/url] .
http://bamcreativestudio.com.au
Hi! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the outstanding work!
110.77.137.121/iwebboard/index.php?p=view_topic&id=1В
cospack.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=106В
sharypovo.today/news/society/page/9/В
verbanent.hu/elfelejtett-jelszoВ
mse-online.ru/novosti/vybor-luchshej-shkoly-dlya-vashego-rebenka.htmlВ
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be exciting to read content from other authors and use a little something from other web sites.
cialis 5mg vs 20mg
Hey! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the great work!
prikol100500.ru/kupit-diplom-s-besplatnoy-dostavkoy-po-vsey-rossiiВ
staceylcrow.com/2013/jess-kenny-redlands-ca/В
bestcoolfun.ru/page/32В
americanautotitleloan.com/lake-wylie-sc-title-loansВ
http://www.andorracf.com/datosprimerequipo.php?ids=PlantillaВ
[url=http://mcadvair.online/]advair pill[/url]
That is very fascinating, You’re an overly professional blogger. I have joined your rss feed and look forward to in search of extra of your magnificent post. Additionally, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks
ultras.lv/topic1669.html?view=printВ
kronverskiy.ru/topic2171.html?view=printВ
bbs.17dra.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=225766В
http://www.hot166.com/blogs/2763/Why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-decreasing-all-the-timeВ
beta.getonvibe.net/blogs/246/Why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-constantly-declining-nowadaysВ
[url=https://lasixor.online/]no script generic lasix[/url]
http://lkp-it.net
Hi, every time i used to check website posts here in the early hours in the dawn, as i love to gain knowledge of more and more.
qvmagazine.com/resposible-gambling/В
umorforme.ru/prodazha-diplomov-lyubogo-uchebnogo-zavedeniya-rossiiВ
forum.meha.biz/topic/1071/В
probki.kirov.ru/content/reshenie-1442012?page=19В
http://www.successwebtech.com/blog/digital-marketing/best-digital-marketing-company-in-delhiВ
[url=https://sildenafilps.online/]how to buy viagra usa[/url]
Regards for this howling post, I am glad I found this website on yahoo.
[url=https://metforminn.online/]how to buy glucophage[/url]
[url=https://modafinilon.online/]modafinil prices online[/url]
Советы по сео стратегии продвижению.
Информация о том как управлять с низкочастотными запросами ключевыми словами и как их подбирать
Стратегия по действиям в конкурентной нише.
Обладаю регулярных сотрудничаю с несколькими организациями, есть что рассказать.
Посмотрите мой досье, на 31 мая 2024г
количество выполненных работ 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация только в устной форме, без снимков с экрана и отчетов.
Продолжительность консультации указано 2 ч, но по факту всегда на доступен без жёсткой привязки ко времени.
Как взаимодействовать с программным обеспечением это уже отдельная история, консультация по работе с программами оговариваем отдельно в другом разделе, определяем что необходимо при разговоре.
Всё спокойно на расслабленно не спеша
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от телеграмм чата для контакта.
разговор только устно, общаться письменно недостаточно времени.
Суббота и воскресенья нерабочие дни
vong lo?i euro 2024
http://silentcomputers.ru
buy fulvicin 250 mg online – dipyridamole canada buy gemfibrozil medication
В современном мире, где аттестат – это начало отличной карьеры в любой области, многие пытаются найти максимально простой путь получения образования. Факт наличия официального документа сложно переоценить. Ведь диплом открывает дверь перед каждым человеком, который желает начать профессиональную деятельность или продолжить обучение в ВУЗе.
В данном контексте наша компания предлагает максимально быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы имеете возможность купить аттестат, и это будет отличным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. Все аттестаты производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием к мельчайшим нюансам, чтобы в итоге получился 100% оригинальный документ.
Преимущество этого решения состоит не только в том, что можно оперативно получить аттестат. Весь процесс организован комфортно и легко, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца аттестата до точного заполнения персональной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все будет находиться под абсолютным контролем наших специалистов.
Всем, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести аттестат – значит избежать длительного обучения и не теряя времени переходить к достижению собственных целей: к поступлению в ВУЗ или к началу успешной карьеры.
http://tlsp.paris/mentions-legales/
Euro
[url=https://amoxicillinbact.com/]amoxicillin 250 mg pills[/url]
Euro 2024
https://aisory.tech – платформа для создания AI Telegram-ботов. Наделяйте своих ботов способностями к естественному диалогу, генерации уникального контента и решению аналитических задач. Простой конструктор платформы делает создание умных чат-ботов доступным для любой компании.
Whats Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other customers like its aided me. Great job.
http://e-art.com.ua
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
lefolyotakaritas.hu/nyomvonal-meghatarozas/В
microstockhowto.com/tag/community/В
http://www.agrolib.ru/В
regullife.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&show_all=yes&page=40В
dip-vuz.ru/kupit-diplom-v-tyumeni/index.htmlВ
Great post.
tadalafil bulk powder
АудиоКниги в течение онлайн на AudioBook26.ru — это еще цифра ресурс начиная с. ant. до сильнее 10 000 аудиокниг, которые хоть слушать бесплатно и без рекламы
https://audiobook26.ru
tadalafil 7mg
Идеальная коляска Cybex для вашего малыша, лучшие предложения.
Коляска Cybex: комфорт и безопасность в одном, для самых взыскательных.
Почему стоит обратить внимание на коляски Cybex, которые заставят вас влюбиться в этот бренд.
Идеальный выбор для заботливых родителей – коляски Cybex, которые не оставят вас равнодушными.
Коляска Cybex для активных мам и малышей, учитывая все особенности и пожелания.
Выбирайте коляску Cybex с умом и стилем, исходя из индивидуальных потребностей и предпочтений.
Почему коляски Cybex так популярны среди родителей, которые ценят комфорт и безопасность.
Топ-модели колясок Cybex на любой вкус и цвет, которые порадуют вас своим разнообразием и качеством.
Ключевые моменты, на которые стоит обратить внимание при выборе коляски Cybex, для вашего малыша.
Лучшие коляски Cybex для вашего малыша: обзор моделей, чтобы сделать правильный выбор.
Коляска Cybex: стиль, комфорт и безопасность, которые не оставят вас равнодушными.
Лучшие модели колясок Cybex для вашей семьи, которые порадуют вас своим качеством и функционалом.
Как выбрать коляску Cybex: главные моменты, которые стоит рассмотреть перед покупкой.
Коляска Cybex для вашего малыша: лучшие модели, если вы цените качество и комфорт.
Выбор коляски Cybex для вашего малыша: как не ошибиться, которые ценят надежность и стиль.
Новинки колясок Cybex, которые стоит рассмотреть, перед совершением покупки.
Как выбрать идеальную коляску Cybex для вашей семьи, исходя из личных предпочтений и потребностей.
Особенности выбора коляски Cybex: как сделать правильный выбор, которые не оставят вас равнодушными.
коляска cybex balios s [url=https://kolyaskicybex.ru/]коляска cybex balios s[/url] .
Самые популярные коляски Tutis, для требовательных родителей, как избежать ошибок при выборе, универсальный вариант, правила использования коляски, аксессуары, которые сделают вашу жизнь проще, секреты успешного выбора, Секреты долговечности и красоты вашей коляски Tutis, Tutis: безопасность вашего малыша превыше всего, правила использования коляски, полезные советы для удобства, подготовка к разным временам года, рекомендации стилистов, секреты качественного производства, Почему Tutis – выбор стильных родителей, Почему Tutis – надежный партнер для вашей семьи?, преимущества использования коляски Tutis
коляска тутис 3 в 1 цена [url=https://kolyaskatutis.ru/]https://kolyaskatutis.ru/[/url] .
vardenafil uses
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing. The clearness on your publish is simply nice and i can think you are a professional in this subject. Well together with your permission allow me to seize your RSS feed to stay up to date with coming near near post. Thank you a million and please keep up the rewarding work.
live draw hk tercepat
You got a very fantastic website, Gladiolus I found it through yahoo.
vardenafil vs tadalafil
娛樂城官網
娛樂城官網
[url=https://modafinile.com/]buy provigil online australia[/url]
Amazing! Its genuinely amazing article, I have got much clear idea on the topic of from this piece of writing.
arusak-attestats24.com
Hi, everything is going perfectly here and ofcourse every one is sharing information, that’s actually excellent, keep up writing.
purchase tadalafil
Thank you for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your efforts and I am waiting for your next post thank you once again.
suster4d
Slotเว็บตรง – ร่วมสนุกในการเล่นได้ทุกอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เน็ต
ในยุคนี้ การเล่นเกมสล็อตมีความสะดวกสบายมากยิ่งขึ้น คุณไม่จำเป็นเดินทางไปยังบ่อนการพนันที่ไหน ๆ เพียงแค่มีเครื่องมือที่ใช้งานได้เชื่อมต่อกับอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็มีโอกาสสนุกกับการเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ได้จากทุกที่
การพัฒนาเทคโนโลยีของ PG Slot
ที่ PG Slot เราได้ปรับปรุงโซลูชั่นสำหรับการจัดการเกมคาสิโนออนไลน์เพื่อตอบสนองความต้องการของผู้เล่นให้มากที่สุด คุณไม่จำเป็นติดตั้งแอปหรือนำมาใช้งานแอปพลิเคชันใด ๆ ให้ยุ่งยากหรือกินพื้นที่ในเครื่องมือของคุณ การดูแลเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ของเราดำเนินการผ่านเว็บตรงที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี HTML 5 ที่ทันยุค
ปั่นสล็อตได้ทุกเครื่องมือ
คุณสามารถเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ได้อย่างสะดวกเพียงเยี่ยมชมในเว็บไซต์ของเรา เว็บตรงสล็อตออนไลน์ของเรารองรับทุกระบบและทุกเครื่องทั้ง Android และ iOS ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้สมาร์ทโฟน โน้ตบุ๊ก หรือแท็บเล็ตรุ่นไหน ก็สามารถมั่นใจได้ว่าคุณจะปั่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้อย่างไม่ติดขัด ไม่มีอุปสรรคหรือกระตุกใด ๆ
เล่นสล็อตฟรี
เว็บตรงของเรามีบริการเพียงแค่คุณเข้ามาในเว็บไซต์ของ PG Slot ก็มีโอกาสทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรีได้ทันที ไม่ต้องเสียค่าใช้จ่ายใด ๆ นี่เป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นและศึกษาเกมเกี่ยวกับเกมก่อนที่จะเล่นจริงด้วยเงินจริง
การเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์กับ PG Slot ทำให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นเกมคาสิโนได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าคุณจะอยู่ที่ไหน เพียงแค่มีอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่เข้าถึงอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็อาจสนุกกับการเล่นสล็อตได้อย่างไม่มีขีดจำกัด!
I needed to post you one very little word in order to say thank you again relating to the gorgeous opinions you have featured in this article. It has been quite remarkably open-handed of people like you to grant freely what most people might have sold for an e-book to help with making some bucks on their own, principally since you could possibly have done it if you considered necessary. Those principles likewise acted like the great way to recognize that someone else have a similar eagerness similar to my very own to grasp very much more with reference to this problem. Certainly there are some more pleasurable sessions ahead for many who read carefully your site. denticore reviews
XRumer – это самое популярное и еще лучшее программное обеспечение для создания ссылок и продвижения сайтов. Он используется для автоматического прогона веб- сайтов помощью разные соц сети, форумы, блоги также другие интернет-ресурсы.
http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/
Купить Лицензированный Хрумер
[url=http://www.botmasterru.com/product33230/][img]https://xrumer.cc/i/x.png[/img][/url]
infinix zero 30 5g
[url=https://abamoxicillin.com/]order amoxicillin from canada[/url]
купить диплом о среднем специальном [url=https://www.russa24-diploms-srednee.com]https://www.russa24-diploms-srednee.com[/url] .
A beloved National Park Service ranger died when he tripped, fell and struck his head on a rock during an annual astronomy festival in southwestern Utah, park officials said over the weekend.
[url=https://web-kraken13.at]kraken14.at[/url]
Tom Lorig was 78 when he died after the incident at Bryce Canyon National Park late Friday.
kraken13.at
https://kraken13.at-kraken16.at
He was known for his extensive work as a ranger and volunteer at 14 National Park Service sites, including Yosemite National Park, Carlsbad Caverns National Park and Dinosaur National Monument, the park service said in a statement Saturday.
“Tom Lorig served Bryce Canyon, the National Park Service, and the public as an interpretive park ranger, forging connections between the world and these special places that he loved,” Bryce Canyon Superintendent Jim Ireland said in the statement.
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。
RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
缺點
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
取款方式
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
電競遊戲 — 熊貓體育
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚
online viagra pharmacy reviews
[url=https://accutanemix.online/]accutane canada pharmacy[/url]
gates of olympus играть [url=http://gates-of-olympus-ru.ru/]gates of olympus играть[/url] .
Подарок для конкурента
https://xrumer.ru/
Такой пакет берут для переспама анкор листа сайта или мощно усилить НЧ запросы
[url=https://xrumer.ru/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
carefirst rx pharmacy
В нашем обществе, где аттестат является началом успешной карьеры в любой сфере, многие пытаются найти максимально быстрый путь получения качественного образования. Факт наличия официального документа об образовании трудно переоценить. Ведь именно он открывает двери перед каждым человеком, который стремится вступить в сообщество профессиональных специалистов или продолжить обучение в высшем учебном заведении.
В данном контексте мы предлагаем быстро получить любой необходимый документ. Вы сможете приобрести аттестат, и это является удачным решением для человека, который не смог завершить обучение, утратил документ или желает исправить свои оценки. Все аттестаты изготавливаются аккуратно, с максимальным вниманием к мельчайшим элементам. В итоге вы получите полностью оригинальный документ.
Плюсы данного решения заключаются не только в том, что можно оперативно получить аттестат. Процесс организовывается комфортно, с профессиональной поддержкой. От выбора подходящего образца до правильного заполнения личной информации и доставки в любое место страны — все находится под абсолютным контролем качественных специалистов.
В результате, для всех, кто хочет найти быстрый способ получения требуемого документа, наша компания предлагает отличное решение. Приобрести аттестат – значит избежать длительного процесса обучения и сразу переходить к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или старт карьеры.
https://hoisuhoc.vn/review-chi-tiet-kem-chong-nang-kpem-aktnb/
mexican pharmacy viagra
pharmacy that sells phentermine
https://seotrendist.bligblogging.com/27875769/Технические-особенности-студии-xrumer-art
https://seovisivize.bloguetechno.com/Преимущества-сотрудничества-с-xrumer-art-62841222
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was searching for!
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after reading through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely glad I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
geinoutime.com
Fang Jifan과 Zhou La는 우연히 우회하여 Meridian Gate에서 궁전으로 돌진했습니다.
ventolin inhaler inhouse pharmacy
sirkuit4d
monograph oral – order generic pletal 100 mg cheap cilostazol
2024娛樂城推薦,經過玩家實測結果出爐Top5!
2024娛樂城排名是這五間上榜,玩家尋找娛樂城無非就是要找穩定出金娛樂城,遊戲體驗良好、速度流暢,Ace博評網都幫你整理好了,給予娛樂城新手最佳的指南,不再擔心被黑網娛樂城詐騙!
2024娛樂城簡述
在現代,2024娛樂城數量已經超越以前,面對琳瑯滿目的娛樂城品牌,身為新手的玩家肯定難以辨別哪間好、哪間壞。
好的平台提供穩定的速度與遊戲體驗,穩定的系統與資訊安全可以保障用戶的隱私與資料,不用擔心收到傳票與任何網路威脅,這些線上賭場也提供合理的優惠活動給予玩家。
壞的娛樂城除了會騙取你的金錢之外,也會打著不實的廣告、優惠滿滿,想領卻是一場空!甚至有些平台還沒辦法登入,入口網站也是架設用來騙取新手儲值進他們口袋,這些黑網娛樂城是玩家必須避開的風險!
評測2024娛樂城的標準
Ace這次從網路上找來五位使用過娛樂城資歷2年以上的老玩家,給予他們使用各大娛樂城平台,最終選出Top5,而評選標準為下列這些條件:
以玩家觀點出發,優先考量玩家利益
豐富的遊戲種類與卓越的遊戲體驗
平台的信譽及其安全性措施
客服團隊的回應速度與服務品質
簡便的儲值流程和多樣的存款方法
吸引人的優惠活動方案
前五名娛樂城表格
賭博網站排名 線上賭場 平台特色 玩家實測評價
No.1 富遊娛樂城 遊戲選擇豐富,老玩家優惠多 正面好評
No.2 bet365娛樂城 知名大廠牌,運彩盤口選擇多 介面流暢
No.3 亞博娛樂城 多語言支持,介面簡潔順暢 賽事豐富
No.4 PM娛樂城 撲克牌遊戲豐富,選擇多元 直播順暢
No.5 1xbet娛樂城 直播流暢,安全可靠 佳評如潮
線上娛樂城玩家遊戲體驗評價分享
網友A:娛樂城平台百百款,富遊娛樂城是我3年以來長期使用的娛樂城,別人有的系統他們都有,出金也沒有被卡過,比起那些玩娛樂城還會收到傳票的娛樂城,富遊真的很穩定,值得推薦。
網友B:bet365中文的介面簡約,還有超多體育賽事盤口可以選擇,此外賽事大部分也都有附上直播來源,不必擔心看不到賽事最新狀況,全螢幕還能夠下單,真的超方便!
網友C:富遊娛樂城除了第一次儲值有優惠之外,儲值到一定金額還有好禮五選一,實用又方便,有問題的時候也有客服隨時能夠解答。
網友D:從大陸來台灣工作,沒想到台灣也能玩到亞博體育,這是以前在大陸就有使用的平台,雖然不是簡體字,但使用介面完全沒問題,遊戲流暢、速度比以前使用還更快速。
網友E:看玖壹壹MV發現了PM娛樂城這個大品牌,PM的真人百家樂沒有輸給在澳門實地賭場,甚至根本不用出門,超級方便的啦!
https://stixandstonz.ca/situs-slot-gacor
В нашем обществе, где диплом является началом отличной карьеры в любой области, многие ищут максимально быстрый и простой путь получения образования. Необходимость наличия официального документа переоценить невозможно. Ведь именно диплом открывает дверь перед всеми, кто стремится начать трудовую деятельность или продолжить обучение в каком-либо ВУЗе.
Предлагаем максимально быстро получить этот важный документ. Вы можете приобрести диплом нового или старого образца, и это будет выгодным решением для всех, кто не смог завершить образование или потерял документ. дипломы производятся с особой аккуратностью, вниманием ко всем элементам, чтобы в итоге получился полностью оригинальный документ.
Преимущества такого решения состоят не только в том, что можно оперативно получить диплом. Весь процесс организовывается удобно, с нашей поддержкой. Начав от выбора требуемого образца документа до консультации по заполнению персональных данных и доставки по стране — все находится под абсолютным контролем квалифицированных мастеров.
Таким образом, для тех, кто ищет быстрый способ получения необходимого документа, наша компания может предложить выгодное решение. Купить диплом – это значит избежать долгого обучения и сразу перейти к своим целям, будь то поступление в ВУЗ или начало карьеры.
http://www.seoyour.ru
viagra cost pharmacy
онлайн казино Dragon Money драгон мани казино вход
Daddy Casino – Официальный телеграм канал со слотами от Дэдди Casino [url=https://t.me/daddycasinorussia]daddy casino[/url] . Актуальное, рабочее зеркало официального сайта Дэдди Казино. Регистрируйся в Казино Daddy, получай бонус используя промокод, не забудь скачать
daddy casino регистрация
https://t.me/daddycasinorussia
Что такое прогон по профилям?
На форумах при каждом прогоне регистрируется новый юзер, в профайле которого в поле Вебсайт или Домашняя страница стоит ваша ссылка. Также в некоторых форумах есть возможность в профиль вставить подпись, туда можно вставить ссылку с анкором. Все это можно варьировать. В профилях ссылки живут довольно долго, т.к. нет спама в чистом виде, и профили не мозолят глаза ни читателям форума, ни модераторам. Прогон производится последней версией хрумера с сервера с максимально возможной скоростью и производительностью.
ПОДРОБНЕЕ
НОВЫЙ [url=https://xrumer.ru/]ОТЛИЧНЫЙ VPN[/url] ДЛЯ XRUMERA!
За последние недели состоялась серия важных обновлений комплекса: XAuth, Captchas Benchmark, XRumer, XEvil 6.0 [Beta]. В XEvil 6.0 [Beta] обновлен механизм обработки hCaptcha и многое другое, в XAuth повышена стабильность работы, в XRumer повышена эффективность, устранён ряд погрешностей и обновлены прилагаемые базы.
https://xrumer.ru/
buy feldene sale – piroxicam 20 mg sale buy exelon pills
娛樂城
2024娛樂城介紹
台灣2024娛樂城越開越多間,新開的線上賭場層出不窮,每間都以獨家的娛樂城優惠和體驗金來吸引玩家,致力於提供一流的賭博遊戲體驗。以下來介紹這幾間娛樂城網友對他們的真實評價,看看哪些娛樂城上榜了吧!
2024娛樂城排名
2023下半年,各家娛樂城競爭激烈,相繼推出誘人優惠,不論是娛樂城體驗金、反水流水還是首儲禮金,甚至還有娛樂城抽I15手機。以下就是2024年網友推薦的娛樂城排名:
NO.1 富遊娛樂城
NO.2 Bet365台灣
NO.3 DG娛樂城
NO.4 九州娛樂城
NO.5 亞博娛樂城
2024娛樂城推薦
根據2024娛樂城排名,以下將富遊娛樂城、BET365、亞博娛樂城、九州娛樂城、王者娛樂城推薦給大家,包含首儲贈點、免費體驗金、存提款速度、流水等等…
娛樂城遊戲種類
線上娛樂城憑藉其廣泛的遊戲種類,成功滿足了各式各樣玩家的喜好和需求。這些娛樂城遊戲不僅多元化且各具特色,能夠為玩家提供無與倫比的娛樂體驗。下面是一些最受歡迎的娛樂城遊戲類型:
電子老虎機
魔龍傳奇、雷神之鎚、戰神呂布、聚寶財神、鼠來寶、皇家777
真人百家樂
真人視訊百家樂、牛牛、龍虎、炸金花、骰寶、輪盤
電子棋牌
德州撲克、兩人麻將、21點、十三支、妞妞、三公、鬥地主、大老二、牌九
體育下注
世界盃足球賽、NBA、WBC世棒賽、英超、英雄聯盟LOL、特戰英豪
線上彩票
大樂透、539、美國天天樂、香港六合彩、北京賽車
捕魚機遊戲
三仙捕魚、福娃捕魚、招財貓釣魚、西遊降魔、吃我一砲、賓果捕魚
2024娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城/線上賭場(現金網)是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,而且是現金網,大家也許會好奇為什麼不直接叫做線上賭場或是線上博弈就好了。
其實這是有原因的,線上賭場這種東西,架站在台灣是違法的,在早期經營線上博弈被抓的風險非常高所以換了一個打模糊仗的代稱「娛樂城」來規避警方的耳目,畢竟以前沒有Google這種東西,這樣的代稱還是多少有些作用的。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種賭博平台,允許玩家在沒有預先充值的情況下參與遊戲。這種模式類似於信用卡,通常以周結或月結的方式結算遊戲費用。因此,如果玩家無法有效管理自己的投注額,可能會在月底面臨巨大的支付壓力。
娛樂城不出金怎麼辦?
釐清原因,如未違反娛樂城機制,可能是遇上黑網娛樂城,請盡快通報165反詐騙。
игровой автомат sweet bonanza [url=http://sweet-bonanza-ru.ru]http://sweet-bonanza-ru.ru[/url] .
misoprostol pharmacy cost
online pharmacy in usa
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
Интернет-казино [url=https://t.me/daddycasinorussia]дэдди казино[/url] — сайт или специальная программа, которые позволяют играть в азартные игры в интернете. Сайты интернет-казино могут специализироваться на различных азартных играх: игровых автоматах, рулетке, лотереях, викторинах, покере или других карточных и настольных играх. Википедия
daddy казино зеркало
https://t.me/daddycasinorussia
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。
娛樂城
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 – Casino, Gambling、中國 – 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 – オンラインカジノ、越南 – Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。
https://kupit-kvartiruspb.ru в новостройках Санкт-Петербурга. Цены и фотографии квартир от застройщика в готовых и строящихся ЖК. Подбор жилья, ипотечные программы, сопровождение сделок и выгодные предложения.
квартиры с отделкой от застройщика https://kvartiru-kupit78.ru
A person necessarily lend a hand to make significantly articles I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and to this point? I amazed with the research you made to create this actual submit incredible. Fantastic activity!
https://erokomiksi6.com/?keyword=wd138
[url=http://prednisonecsr.online/]purchase prednisone for dogs online without a prescription[/url]
Каталог эротических рассказов https://vicmin.ru подарит тебе возможность уйти от рутины и погрузиться в мир секса и безудержного наслаждения. Обширная коллекция рассказов для взрослых разбудит твое воображение и принесет немыслимое удовольствие.
I needed to compose you a little bit of observation to be able to thank you very much once again on the beautiful views you have documented on this site. It is certainly extremely open-handed of you to make easily what exactly numerous people would’ve offered for sale as an e-book to make some profit on their own, notably considering the fact that you could possibly have tried it in case you decided. The guidelines additionally acted as a good way to understand that the rest have the same dreams much like my very own to figure out lots more related to this problem. I am sure there are many more pleasant periods up front for individuals who scan your blog post. lottery defeater
Новостройки в Екатеринбурге, купить квартиру в новостройке https://kupit-kvartiruekb.ru от застройщика. Строительство жилой и коммерческой недвижимости. Высокое качество, прозрачность на всех этапах строительства и сделки.
купить диплом о высшем в ижевске https://diplom-izhevsk.ru
crazy monkey на деньги [url=www.crazy-monkey-ru.ru/]www.crazy-monkey-ru.ru/[/url] .
Cериал Голяк https://golyak-serial-online.ru смотреть онлайн в хорошем качестве и с лучшей озвучкой на любых устройствах. Все сезоны истории мелкого преступника Винни и его друзей в английском городке!
https://gaonrentcar.com/?keyword=data-macau-5d
Каждый год в середине сентября проходит Тюменский инновационный форум «[u][b]НЕФТЬГАЗТЭК[/b][/u]».
Форум посвящен развитию способов инновационного роста секторов [b]топливно-энергетического комплекса[/b], обсуждению а также поиску решений, образованию наилучших условий для развития инновационных проектов. Ежегодный тюменский форум представляетсобой влиятельной дискуссионной площадкой по развитию нефтегазовой отрасли в Российской Федерации, содержит большой статус и своевременность, созвучен корпоративной стратегии развития инновационного курса в [u][b]Российской Федерации[/b][/u]
-https://neftgaztek.ru/
สล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรง: ความบันเทิงที่ท่านไม่ควรพลาด
การเล่นสล็อตในยุคนี้ได้รับความสนใจเพิ่มมากขึ้น เนื่องจากความสะดวกสบายที่นักเดิมพันสามารถใช้งานได้จากทุกหนทุกแห่งได้ตลอดเวลา โดยไม่ต้องเสียเวลาในการเดินทางถึงบ่อน ในเนื้อหานี้ เราจะกล่าวถึง “สล็อตแมชชีน” และความเพลิดเพลินที่คุณสามารถพบได้ในเกมสล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรง
ความง่ายดายในการเล่นเกมสล็อต
หนึ่งในเหตุผลสล็อตเว็บตรงเป็นที่ยอดนิยมอย่างแพร่หลาย คือความสะดวกที่นักเดิมพันมี คุณจะเล่นได้ทุกที่ได้ตลอดเวลา ไม่ว่าจะเป็นในบ้าน ที่ทำงาน หรือแม้กระทั่งในการเดินทาง สิ่งที่คุณควรมีคือเครื่องมือที่ต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นมือถือ แท็บเล็ท หรือคอมพิวเตอร์
เทคโนโลยีกับสล็อตออนไลน์เว็บตรง
การเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ในยุคนี้ไม่เพียงแต่สะดวก แต่ยังมาพร้อมกับเทคโนโลยีใหม่ล่าสุดอีกด้วย สล็อตที่เว็บตรงใช้เทคโนโลยีที่ทันสมัย HTML5 ซึ่งทำให้คุณไม่ต้องกังวลเกี่ยวกับเกี่ยวกับการติดตั้งโปรแกรมหรือแอพพลิเคชั่น แค่เปิดเบราว์เซอร์บนอุปกรณ์ของคุณและเข้าไปที่เว็บไซต์ คุณก็สามารถเริ่มเล่นได้ทันที
ความหลากหลายของเกมของเกมสล็อต
สล็อตเว็บตรงมาพร้อมกับตัวเลือกหลากหลายของเกมที่ท่านสามารถเลือก ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมสล็อตแบบคลาสสิกหรือเกมที่มีฟีเจอร์เด็ดและโบนัสหลากหลาย ท่านจะเห็นว่ามีเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากมาย ซึ่งทำให้ไม่เคยเบื่อกับการเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์
รองรับทุกเครื่องมือ
ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือระบบ Androidหรือ iOS คุณก็สามารถเล่นสล็อตได้ไม่มีสะดุด เว็บไซต์ของเราสนับสนุนOSและทุกเครื่อง ไม่ว่าจะเป็นโทรศัพท์มือถือรุ่นล่าสุดหรือรุ่นก่อน หรือถึงแม้จะเป็นแทปเล็ตและแล็ปท็อป ท่านก็สามารถเล่นเกมสล็อตได้อย่างไม่มีปัญหา
สล็อตทดลองฟรี
สำหรับผู้ที่ยังใหม่กับการเล่นสล็อต หรือยังไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับเกมที่ชอบ PG Slot ยังมีฟีเจอร์สล็อตทดลองฟรี คุณเริ่มเล่นได้ทันทีทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงินลงทุน การทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อตนี้จะช่วยให้ท่านเรียนรู้วิธีการเล่นและรู้จักเกมได้โดยไม่ต้องเสียค่าใช้จ่าย
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษ
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตเว็บตรงกับ PG Slot คือมีโปรโมชันและโบนัสมากมายสำหรับผู้เล่น ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็นสมาชิกเพิ่งสมัครหรือผู้เล่นเก่า ผู้เล่นสามารถใช้โปรโมชันและโบนัสต่าง ๆ ได้อย่างสม่ำเสมอ ซึ่งจะเพิ่มโอกาสชนะและเพิ่มความสนุกสนานในการเล่น
สรุป
การเล่นสล็อตที่ PG Slot เป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า ท่านจะได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกจากการเล่นเกม นอกจากนี้ยังมีโอกาสชนะรางวัลและโบนัสเพียบ ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะใช้มือถือ แท็บเล็ตหรือโน้ตบุ๊กยี่ห้อไหน ก็สามารถเล่นได้ทันที อย่ารอช้า สมัครสมาชิกและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ PG Slot ทันที
pg slot
สล็อตตรงจากเว็บ — ใช้ได้กับ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเลต คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว ฯลฯ เพื่อเล่น
ระบบสล็อตเว็บโดยตรง ของ PG ได้รับการพัฒนาและอัปเดต เพื่อให้ สามารถใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง ครบถ้วน ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือ คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว รุ่นใด
ที่ พีจีสล็อต เราเข้าใจถึงความต้องการ ของลูกค้า ในเรื่อง การใช้งานง่าย และ การเข้าถึงเกมออนไลน์อย่างรวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีที่ล้ำสมัย ปัจจุบันนี้ มาพัฒนาเว็บไซต์ของเรากันเถอะ คุณจึงไม่ต้อง ดาวน์โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดเบราว์เซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณใช้อยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บของเรา คุณสามารถ สนุกกับสล็อตได้ทันที
การใช้งานกับอุปกรณ์หลากหลาย
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ ระบบ แอนดรอยด์ หรือ iOS ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตได้อย่างราบรื่น ระบบของเรา ได้รับการออกแบบให้รองรับ ระบบปฏิบัติการทั้งหมด ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ มี มือถือ รุ่นใหม่หรือรุ่นเก่า หรือ แม้แต่แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้ ไม่มีปัญหา ความเข้ากันได้
เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
ข้อดีของการเล่น PG Slot ก็คือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ ที่บ้าน ที่ทำงาน หรือแม้แต่ สถานที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ การเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เล่นเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง ห่วงเรื่องการดาวน์โหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ ใช้พื้นที่ในอุปกรณ์
ลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีนฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่นที่ใหม่ ได้ลองและรู้จักเกมสล็อตของเรา PG Slot ยังมีบริการสล็อตฟรี คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงิน การ ทดลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีนฟรีนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเรียนรู้วิธีเล่นและเข้าใจเกมก่อนตัดสินใจเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
บริการและการรักษาความปลอดภัย
PG Slot มุ่งมั่นที่จะให้บริการที่ดีที่สุดแก่ลูกค้า เรามี ทีมงานมืออาชีพพร้อมให้บริการและช่วยเหลือคุณตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง นอกจากนี้เรายังมี ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลและการเงินของคุณจะปลอดภัย
โปรโมชันและโบนัส
อีกข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot คือ มี โปรโมชันและโบนัสพิเศษสำหรับสมาชิก ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชันและโบนัสได้ สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและเพิ่มความเพลิดเพลินในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
geinoutime.com
이 상태에서 Yang Yiqing은 거의 내각에 들어서기 직전입니다.
สำหรับ ไซต์ PG Slots ในขณะที่ มี ข้อได้เปรียบ หลายประการ เมื่อเทียบกับ คาสิโนแบบ ทั่วไป, โดยมาก ใน ยุคสมัยใหม่. คุณสมบัติสำคัญ เหล่านี้ ได้แก่:
ความสะดวก: ผู้เล่น สามารถเข้าเล่น สล็อตออนไลน์ได้ ทุกเวลา จาก ทุกที่, ทำให้ ผู้เล่นสามารถ เข้าร่วม ได้ ทุกสถานที่ ไม่จำเป็นต้อง เสียเวลา ไปคาสิโนแบบ เดิม ๆ
เกมมากมายแตกต่าง: สล็อตออนไลน์ ให้ ตัวเกม ที่ หลากหลาย, เช่น สล็อตประเภทคลาสสิค หรือ รูปแบบเกม ที่มี ความสามารถ และค่าตอบแทน พิเศษ, ไม่ก่อให้เกิด ความเบื่อหน่าย ในเกม
แคมเปญส่งเสริมการขาย และค่าตอบแทน: สล็อตออนไลน์ มักจะ มี โปรโมชั่น และค่าตอบแทน เพื่อปรับปรุง ความเป็นไปได้ ในการ รับรางวัล และ เพิ่ม ความเพลิดเพลิน ให้กับเกม
ความเชื่อถือได้ และ ความน่าเชื่อถือ: สล็อตออนไลน์ แทบจะ ใช้ การป้องกัน ที่ ดี, และ เป็นที่น่าเชื่อถือ ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนตัว และ การทำธุรกรรม จะมี ปกป้อง
ความช่วยเหลือ: PG Slots มี บุคลากร ที่มีประสบการณ์ ที่ตั้งใจ สนับสนุน ตลอดเวลาไม่หยุด
การเล่นบนมือถือ: สล็อต PG ให้บริการ การเล่นบนอุปกรณ์พกพา, ช่วยให้ ผู้เล่นสามารถเข้าร่วม ได้ทุกที่
เล่นฟรี: เกี่ยวกับ ผู้เล่นเริ่มต้น, PG ยังเสนอ ทดลองเล่นโดยไม่เสียค่าใช้จ่าย เช่นกัน, เพื่อให้ ผู้เล่น ทดลอง การเล่น และทำความเข้าใจ เกมก่อน เล่นด้วยเงินจริง
สล็อต PG มีคุณลักษณะ ข้อดี เป็นจำนวนมาก ที่ ก่อให้เกิด ให้ได้รับความสำคัญ ในปัจจุบันนี้, ปรับปรุง การ ความสนุกสนาน ให้กับเกมด้วย.
ทดลองลองใช้เล่นสล็อต และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร!
สำหรับนักพนันที่กำลังค้นหาความบันเทิงและโอกาสในการชนะรางวัลมหาศาล สล็อตออนไลน์เป็นอีกหนึ่งตัวเลือกที่คุ้มค่าศึกษา.ด้วยความจำนวนมากของเกมสล็อตที่น่าตื่นเต้น ผู้เล่นสามารถปฏิบัติและค้นหาเกมที่เหมาะกับตัวเองได้อย่างง่ายดาย.
ไม่ว่าคุณจะถูกใจเกมสล็อตคลาสสิกหรือต้องการความท้าทาย, ทางเลือกมากมายรอล้ำหน้าให้คุณสัมผัส. จากสล็อตที่มีหัวข้อมากมาย ไปจนถึงเกมที่มีลักษณะพิเศษและโบนัส, ผู้เล่นจะได้พบกับการทดลองเล่นที่น่าตื่นเต้นและน่าติดตาม.
ด้วยการทดสอบสล็อตฟรี, คุณสามารถศึกษาวิธีการเล่นและค้นค้นพบกลยุทธ์ที่ถูกใจก่อนลงทุนด้วยเงินจริง. นี่คือโอกาสที่ดีที่จะเรียนรู้กับเกมและเพิ่มโอกาสในการแสดงรางวัลใหญ่.
อย่าขยายเวลา, เข้าไปกับการลองเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์วันนี้ และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร! เพลิดเพลินกับความน่าสนใจ, ความสนุกสนาน และโอกาสทองชนะรางวัล. ทำก้าวแรกเดินทางสู่ความสำเร็จลุล่วงของคุณในวงการสล็อตออนไลน์แล้ววันนี้!
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
ลองใช้ เข้าร่วม สล็อต PG ไปพร้อมกับ เข้าถึง ไปสู่ โลก แห่ง ความเพลิดเพลิน ที่ ไร้ขอบเขต
ของ ผู้เล่นพนัน ที่ ต้องการ ค้นหา ประสบการณ์ เกมที่แปลกใหม่, สล็อต PG เป็น ตัวเลือก ที่ ดึงดูดความสนใจ มาก. ด้วย ความหลากหลายของ ของ เกมสล็อต ที่ น่าทึ่ง และ น่าค้นหา, นักพนัน จะสามารถ ตรวจสอบ และ ลอง รูปแบบเกม ที่ ถูกใจ ความชอบการเล่น ของตนเอง.
ไม่ว่า ผู้เล่น จะตามหา ความเพลิดเพลิน แบบทั่วไป หรือ การท้าทาย ที่ไม่เคยพบเจอ, สล็อต PG จะมี ให้เลือกจำนวนมาก. ตั้งแต่ สล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม ที่ คุ้นเคย ไปจนถึง รูปแบบเกม ที่ มี คุณสมบัติพิเศษ และ โบนัสล้นหลาม, ผู้เล่น จะสามารถ สัมผัส บรรยากาศ ที่ ตื่นเต้น และ เพลิดเพลิน
เนื่องจาก การทดสอบเล่น สล็อต PG ฟรี, ผู้เล่น จะสามารถ ทำความเข้าใจ ขั้นตอนการเล่น และ ลอง กลวิธี ต่างๆ ก่อนที่จะ เริ่มพนัน ด้วยเงินทุน. ถึงกระนั้น คือ ทางเลือก ที่ดีเยี่ยม ที่จะ เตรียมความพร้อม และ ยกระดับ โอกาส ในการ ได้รับรางวัล รางวัลใหญ่.
อย่าเนิ่นช้า, เข้าสู่ ในการ การเล่นทดลอง สล็อต PG เดี๋ยวนี้ และ ทดสอบ การเล่น ที่ ไร้ขอบเขต! พบเจอ ความตื่นเต้น, ความเพลิดเพลินใจ และ ความเป็นไปได้ ในการ ชนะรางวัล มากมาย. เริ่มลงมือ เดินทาง สู่ ความเจริญรุ่งเรือง ของคุณในวงการ สล็อตออนไลน์ ตั้งแต่วันนี้!
Драгон Мани Казино https://krpb.ru – ваше место для азартных приключений! Наслаждайтесь широким выбором игр, щедрыми бонусами и захватывающими турнирами. Безопасность и честная игра гарантированы. Присоединяйтесь к нам и испытайте удачу в самом захватывающем онлайн-казино!
metronidazole online pharmacy
Famous French footballer Kylian Mbappe https://kylianmbappe.prostoprosport-ar.com has become a global ambassador for Dior. The athlete will represent the men’s collections of creative director Kim Jones and the Sauvage fragrance, writes WWD. Mbappe’s appointment follows on from the start of the fashion house’s collaboration with the Paris Saint-Germain football club. Previously, Jones created a uniform for the team where Kylian is a player.
pharmacy first fluconazole
lamotrigine online pharmacy
seroquel pharmacy price
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ซื้อฟรีสปิน
สำรวจเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อการหมุนฟรี
ในเวลานี้ การเล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้รับการยอมรับอย่างมาก โดยเฉพาะเกมสล็อตจากค่าย PG Slot ที่มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษมากมายให้นักเล่นได้เพลิดเพลิน หนึ่งในคุณสมบัติที่น่าสนใจและทำให้การหมุนสนุกยิ่งขึ้นคือ “การซื้อฟรีสปิน” ซึ่งเป็นการเพิ่มช่องทางในการชนะและเพิ่มความเร้าใจในการเล่น
การซื้อฟรีสปินคืออะไร?
การซื้อฟรีสปินคือการที่ผู้เล่นสามารถซื้อโอกาสในการหมุนวงล้อสล็อตโดยไม่ต้องรอให้เกิดไอคอนฟรีสปินบนวงล้อ ซึ่งเป็นการเพิ่มช่องทางในการได้รับรางวัลพิเศษพิเศษต่างๆ ภายในเกม เช่น โบนัส แจ็คพอต และอื่นๆ ยิ่งไปกว่านั้น การซื้อฟรีสปินยังช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพิ่มจำนวนเงินที่ได้ได้อย่างรวดเร็วและมีประสิทธิภาพ
ผลดีของการลองเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อการหมุนฟรี
เพิ่มโอกาสชนะ: การซื้อตัวเลือกการหมุนฟรีช่วยให้ผู้ใช้งานมีโอกาสในการได้รับของขวัญมากขึ้น เพราะว่ามีการหมุนวงล้อฟรีเพิ่มเติม ซึ่งอาจนำพาไปถึงการได้รับแจ็คพอตหรือรางวัลโบนัสที่สูงขึ้นอื่นๆ
ประหยัดเวลาในการเล่น: การซื้อฟรีสปินช่วยประหยัดเวลาทำงานในการเล่น เพราะว่าไม่ต้องรอให้เกิดสัญลักษณ์ฟรีสปินบนวงล้อ นักพนันสามารถเข้าสู่รอบฟรีสปินได้ทันที
ลองเล่นฟรี: สำหรับผู้เล่นที่ยังไม่แน่ใจเกี่ยวกับเกม PG Slot ยังมีตัวเลือกทดลองเล่นฟรีผู้เล่นได้ทดสอบเล่นและเรียนรู้เกมก่อนที่จะเลือกที่จะซื้อฟรีสปินด้วยเงินจริง
เพิ่มความสนุก: การซื้อตัวเลือกฟรีสปินช่วยเพิ่มความสนุกในการเล่น จากที่ผู้ใช้งานสามารถเข้าสู่รอบโบนัสและคุณลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษอื่นๆ ได้อย่างสะดวก
วิธีการทำการซื้อฟรีสปินในสล็อต PG
เลือกเกมที่ต้องการเล่นจากผู้ผลิต PG Slot
คลิกที่ปุ่มคำสั่ง “ซื้อฟรีสปิน” ที่แสดงขึ้นบนหน้าจอการเล่น
ระบุจำนวนฟรีสปินที่ต้องการใช้และยืนยันการซื้อ
เริ่มต้นการหมุนวงล้อและเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่น
บทสรุป
การสำรวจเล่นสล็อต PGและการซื้อตัวเลือกฟรีสปินเป็นวิธีที่ดีเยี่ยมในการเพิ่มช่องทางในการชนะและเพิ่มความรื่นรมย์ในการเล่น ด้วยคุณสมบัติพิเศษนี้ ผู้ใช้งานสามารถเข้าสู่รอบโบนัสและลักษณะพิเศษพิเศษต่างๆ ได้อย่างเร็วและมีประสิทธิผล ไม่ว่าคุณคือผู้เล่นใหม่เอี่ยมหรือผู้เล่นที่มีความสามารถ การทดลองเล่นสล็อต PGและการซื้อตัวเลือกหมุนฟรีจะช่วยให้คุณมีประสบการณ์ในการเล่นที่น่าตื่นตาตื่นใจและสนุกสนานมากยิ่งขึ้น
ทดสอบเล่นสล็อต PG ซื้อหมุนฟรี แล้วคุณจะพบกับความสนุกสนานและความเป็นไปได้ในการชนะที่ไม่มีที่สิ้นสุด
Подарок для конкурента
https://xrumer.ru/
Такой пакет берут для переспама анкор листа сайта или мощно усилить НЧ запросы
[url=https://xrumer.ru/]Подарок для конкурента[/url]
Скачать свежие новинки песен https://muzfo.net 2024 года ежедневно. Наслаждайтесь комфортным прослушиванием, скачивайте музыку за пару кликов на сайте.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg เว็บ ตรง
ประสบการณ์การสำรวจเล่นเกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนแพลตฟอร์มเสี่ยงโชคไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์: เข้าสู่โลกแห่งความสนุกสนานที่ไม่มีข้อจำกัด
เพื่อนักเสี่ยงโชคที่กำลังมองหาการพบเจอเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร และปรารถนาเจอแหล่งวางเดิมพันที่เชื่อถือได้, การลองเกมสล็อต PG บนเว็บตรงนับว่าตัวเลือกที่น่าประทับใจอย่างมาก. เนื่องจากมีความหลากหลายมากมายของเกมสล็อตต่างๆที่มีให้คัดสรรมากมาย, ผู้เล่นจะได้เผชิญกับโลกแห่งความตื่นเต้นเร้าใจและความสนุกเพลิดเพลินที่ไม่มีข้อจำกัด.
แพลตฟอร์มวางเดิมพันไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์นี้ มอบประสบการณ์การเล่นที่มั่นคง มั่นคง และตรงตามความต้องการของนักเสี่ยงโชคได้เป็นอย่างดี. ไม่ว่าคุณจะท่านจะหลงใหลเกมสล็อตแมชชีนที่คุ้นเคยที่เป็นที่รู้จัก หรืออยากประสบการณ์เกมแปลกใหม่ที่มีคุณลักษณะเฉพาะตัวและรางวัลพิเศษล้นหลาม, เว็บตรงนี้ก็มีให้เลือกอย่างหลากหลายชนิด.
อันเนื่องมาจากระบบการทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อต PG ไม่มีค่าใช้จ่าย, ผู้เล่นจะได้โอกาสเรียนรู้ขั้นตอนเล่นและทดลองเทคนิคต่างๆนาๆ ก่อนที่จะเริ่มใช้เงินลงทุนด้วยเงินจริง. สิ่งนี้นับว่าเป็นโอกาสอันดีที่สุดที่จะเสริมความพร้อมเพรียงและพัฒนาโอกาสในการชิงรางวัลมหาศาลใหญ่.
ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะท่านจะมุ่งหวังความสนุกสนานที่เคยชิน หรือความท้าทายแปลกใหม่, สล็อต PG บนเว็บเดิมพันตรงก็มีให้เลือกอย่างหลากหลายชนิด. ผู้เล่นจะได้ประสบกับการทดลองเล่นการเล่นที่น่ารื่นเริง เร้าใจ และสนุกสนานไปกับจังหวะในการชิงโบนัสมหาศาล.
อย่ารอ, ร่วมสำรวจเกมสล็อตแมชชีน PG บนเว็บเสี่ยงโชคตรงนี้เวลานี้ และค้นพบโลกแห่งความสนุกสนานที่น่าเชื่อถือ น่าสนใจ และพร้อมด้วยความเพลิดเพลินรอคอยคุณ. ประสบความเร้าใจ, ความสนุกเพลิดเพลิน และจังหวะในการได้รางวัลมหาศาลมหาศาล. เริ่มเดินทางสู่ความสำเร็จในวงการเกมออนไลน์เวลานี้!
สล็อตเว็บโดยตรง — สามารถใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ต คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว ฯลฯ สำหรับการเล่น
ระบบสล็อตเว็บโดยตรง ของ PG Slot ได้รับการพัฒนาและปรับปรุง เพื่อให้ รองรับการใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง ครบถ้วน ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ต หรือ คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว แบบไหน
ที่ พีจีสล็อต เราเข้าใจว่าผู้เล่นต้องการ ของลูกค้า ในเรื่อง ความสะดวก และ การเข้าถึงเกมออนไลน์อย่างรวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีที่ทันสมัยที่สุด ปัจจุบันนี้ มาพัฒนาเว็บไซต์ของเรากันเถอะ คุณจึงไม่ต้อง โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดบราวเซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ คุณใช้อยู่ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บของเรา คุณสามารถ สนุกกับสล็อตได้ทันที
การสนับสนุนหลายอุปกรณ์
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ ระบบ แอนดรอยด์ หรือ ไอโอเอส ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตออนไลน์ได้ไม่มีสะดุด ระบบของเรา ออกแบบมาเพื่อรองรับ ระบบปฏิบัติการทั้งหมด ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ ใช้ มือถือ ใหม่หรือเก่า หรือ แม้แต่แท็บเล็ตหรือแล็ปท็อป ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้ดี ไม่มีปัญหา ความเข้ากันได้
เล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot นั่นคือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ อยู่ที่บ้าน ออฟฟิศ หรือแม้แต่ สถานที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ อินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง กังวลเรื่องการโหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ เปลืองพื้นที่อุปกรณ์
ลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีนฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้ใช้ใหม่ ได้ลองเล่นและสัมผัสเกมสล็อตของเรา PG Slot ยังมีบริการสล็อตฟรี คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องสมัครสมาชิกหรือฝากเงิน การ เล่นฟรีนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจวิธีเล่นและรู้จักเกมก่อนลงเดิมพันจริง
บริการและการรักษาความปลอดภัย
PG Slot ตั้งใจให้บริการที่ดีที่สุดกับลูกค้า เรามี ทีมงานพร้อมบริการคุณตลอดเวลา นอกจากนี้เรายังมี ระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลและธุรกรรมทางการเงินของคุณจะได้รับการปกป้องอย่างดีที่สุด
โปรโมชั่นและของรางวัลพิเศษ
การเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ยังมีข้อดี ก็คือ มี โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสพิเศษมากมายสำหรับผู้เข้าร่วม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือสมาชิกเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชันและโบนัสได้เรื่อย ๆ สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและเพิ่มความเพลิดเพลินในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
best online pharmacies no prescription
navarro pharmacy
slot demo gratis
[url=http://peregonavtofgtd.kiev.ua]http://peregonavtofgtd.kiev.ua[/url]
Быстро, эффективно и надежно переместить Ваш ярис изо Украины в течение Европу, или изо Европы в течение Украину вместе всего нашей командой. Оформление доказательств да экспортирование изготовляются на оклеветанные сроки.
peregonavtofgtd kiev ua
купить диплом фармацевта [url=http://www.ukr-diplom.ru]http://www.ukr-diplom.ru[/url] .
Агентство по продвижению телеграм-каналов https://883666b.com в Москве специализируется на разработке и реализации стратегий для увеличения аудитории и вовлечённости подписчиков на телеграм-каналах. Эксперты агентства помогают клиентам определить целевую аудиторию, разрабатывают контент-планы и рекламные кампании. Услуги включают рекламу посевами, таргет рекламой, анализ конкурентов, SEO-оптимизацию контента.
интернет эквайринг https://internet-ekvajring.kz – безопасные и эффективные платежные решения для вашего бизнеса.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ไม่ เด้ง
ทดลองทดสอบเล่นสล็อต และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร!
สำหรับนักพนันที่กำลังต้องการความบันเทิงและโอกาสในการแสวงหารางวัลมหาศาล สล็อตออนไลน์เป็นอีกหนึ่งโอกาสที่คุ้มค่าพิจารณา.ด้วยความมากมายของเกมสล็อตที่น่าตื่นเต้น ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นและค้นหาเกมที่ชื่นชอบได้อย่างง่ายดาย.
ไม่ว่าคุณจะถูกใจเกมสล็อตคลาสสิกหรือต้องการความแปลกใหม่, โอกาสรอกลับมาให้คุณสัมผัส. จากสล็อตที่มีหัวข้อมากมาย ไปจนถึงเกมที่มีรูปแบบพิเศษและเงินรางวัล, ผู้เล่นจะได้พบกับการทดลองเล่นที่น่าตื่นเต้นและน่าติดตาม.
ด้วยการลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี, คุณสามารถทำความคุ้นเคยวิธีการเล่นและค้นหากลยุทธ์ที่เหมาะสมก่อนเริ่มลงเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง. นี่คือโอกาสดีที่จะศึกษากับเกมและปรับปรุงโอกาสในการคว้ารางวัลใหญ่.
อย่ารอช้า, เข้าไปกับการทดสอบสล็อตออนไลน์วันนี้ และค้นพบประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่ไม่เหมือนใคร! เพลิดเพลินกับความท้าทาย, ความสนุกสนาน และโอกาสชนะรางวัล. เริ่มต้นเดินทางสู่ความเฟื่องฟูของคุณในวงการสล็อตออนไลน์แล้ววันนี้!
[url=https://tretinoineff.com/]tretinoin 0.05 otc[/url]
I precisely wished to thank you so much once more. I do not know the things I would’ve handled in the absence of the type of pointers discussed by you regarding my situation. It truly was the scary matter for me personally, however , spending time with this professional way you resolved it took me to leap with delight. Now i’m happier for the guidance and pray you are aware of a powerful job your are providing teaching the others with the aid of your web blog. I am sure you have never got to know all of us.
cabergoline online pharmacy
הימורי ספורט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד הענפים המתפתחים ביותר בהימור ברשת. שחקנים מסוגלים להמר על תוצאותיהם של אירועים ספורט מוכרים למשל כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האופציות להתערבות הן מרובות, כולל תוצאתו ההתמודדות, כמות השערים, מספר הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקים נפוצים במיוחד עליהם אפשרי להתערב:
כדורגל: ליגת האלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדור סל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
משחק הטניס: ווימבלדון, US Open, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר באינטרנט – הימור ברשת
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימורים המוכרים ביותר כיום. שחקנים מסוגלים להתמודד נגד יריבים מרחבי העולם בסוגי וריאציות משחק , כגון Texas Hold’em, Omaha, סטאד ועוד. ניתן למצוא תחרויות ומשחקי קש במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות הימור מגוונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של וריאציות פוקר
טורנירים שבועיים וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחק מהיר ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות בלעדיות
בטיחות ואבטחה והוגנות
בעת הבחירה פלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק בטוחה והגיונית. אתרים אלו עושים שימוש בטכנולוגיית הצפנה מתקדמות להבטחה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסיים, וגם בתוכנות גנרטור מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות המשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, חשוב לשחק גם באופן אחראית תוך הגדרת מגבלות אישיות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. מרבית האתרים מאפשרים גם לשחקנים להגדיר מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחקו בתבונה ואל תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם למשחקי קזינו אונליין, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
ההימורים ברשת מציעים עולם שלם הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, מתחיל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור גם אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו לשחק תמיד בצורה אחראית תמיד ואחראי – ההימורים ברשת אמורים להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא גם ליצור בעיות פיננסיות או חברתיים.
купить аккаунт телеграмм пустой [url=https://www.kupit-akkaunt-telegramm11.ru]https://www.kupit-akkaunt-telegramm11.ru[/url] .
viagra online pharmacy no prescription
פוקר באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורט נהיו לאחד הענפים המתפתחים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. שחקנים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאות של אירועים ספורט נפוצים לדוגמה כדור רגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האופציות להימור הן מרובות, כולל תוצאתו ההתמודדות, כמות הגולים, מספר הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקים נפוצים עליהם אפשרי להמר:
כדור רגל: ליגת האלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות אזוריות
כדורסל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
טניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה”ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר באינטרנט – הימור באינטרנט
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור הנפוצים ביותר כיום. שחקנים מסוגלים להתחרות מול יריבים מרחבי העולם במגוון סוגי של המשחק , למשל טקסס הולדם, אומהה, סטאד ועוד. אפשר למצוא תחרויות ומשחקי במבחר דרגות ואפשרויות שונות. אתרי הפוקר הטובים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של וריאציות פוקר
טורנירים שבועיות וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP VIP עם הטבות
בטיחות ואבטחה והוגנות
בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים באינטרנט, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק מאובטחת והגיונית. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיות הצפנה מתקדמת להבטחה על מידע אישי ופיננסיים, וגם בתוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, הכרחי לשחק באופן אחראית תוך קביעת מגבלות אישיות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. רוב אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים גם למשתתפים להגדיר מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחק בתבונה ואל תרדפו אחרי הפסד.
המדריך המלא לקזינו ברשת, הימורי ספורט ופוקר ברשת
ההימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, מתחיל מקזינו באינטרנט וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בעת בחירת בפלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. זכרו לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים באינטרנט אמורים להיות מבדרים ולא לגרום בעיות כלכליות או חברתיות.
Секрет современного дизайна плинтус теневой для вашего офиса
скрытый теневой плинтус [url=https://msk-alyuminievyj-tenevoj-plintus.ru/]скрытый теневой плинтус[/url] .
Хостинг в Беларуси бесплатно: лучший выбор для вашего сайта, плюсы и минусы.
Сравниваем лучшие предложения хостинга в Беларуси, советы и рекомендации.
Выбор профессионалов: топ-3 хостинга в Беларуси бесплатно, оценка и обзор.
Простой гайд: как перенести свой сайт на бесплатный хостинг в Беларуси, техническая документация.
Безопасность сайта: SSL на хостинге в Беларуси бесплатно, плюсы и минусы.
Простая инструкция: создание сайта на бесплатном хостинге в Беларуси, гайд для начинающих.
Децентрализованный хостинг в Беларуси: перспективы и возможности, прогноз и анализ.
Виртуальный хостинг бесплатно [url=https://gerber-host.ru/]https://gerber-host.ru/[/url] .
https://knight-kun.com/?keyword=bensu4d
купить диплом в самаре [url=school5-priozersk.ru]купить диплом в самаре[/url] .
купить квартиру недорого https://nedvizhimost47.ru
הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימור ספורטיביים נהיו לאחד הענפים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. שחקנים יכולים להמר על תוצאת של אירועים ספורטיביים נפוצים לדוגמה כדור רגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להימור הן מרובות, וביניהן תוצאת ההתמודדות, מספר השערים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. הבא דוגמאות של למשחקי נפוצים עליהם ניתן להמר:
כדורגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות אזוריות
כדורסל: ליגת NBA, ליגת יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה”ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר ברשת ברשת – הימורים ברשת
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימור הנפוצים ביותר בימינו. שחקנים מסוגלים להתמודד מול מתחרים מכל רחבי העולם בסוגי וריאציות משחק , כגון Texas Hold’em, Omaha, Stud ועוד. אפשר למצוא תחרויות ומשחקי במגוון רמות ואפשרויות מגוונות. אתרי הפוקר הטובים מציעים גם:
מגוון רחב של וריאציות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני עם הטבות בלעדיות
בטיחות ואבטחה והגינות
בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים ברשת, חשוב לבחור אתרים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבת משחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמת להבטחה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסי, וגם בתוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקים.
בנוסף, חשוב לשחק גם בצורה אחראי תוך קביעת מגבלות אישיות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. רוב אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים לשחקנים לקבוע מגבלות להפסדים ופעילות, וגם לנצל כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחק בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם לקזינו באינטרנט, הימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
הימורים באינטרנט מציעים עולם שלם של של הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם בהימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בזמן הבחירה פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור גם אתרים מפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק בטוחה והוגנת. זכרו לשחק בצורה אחראית תמיד – משחקי ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא גם לגרום לבעיות כלכליות או גם חברתיים.
Предлагаем для вас пройти консультацию (аудит) по усилению продаж равным образом прибыли в вашем бизнесе. Формат аудита: индивидуальная встреча или онлайн конференция по скайпу. Делая очевидные, но простые действия, результат от ВАШЕГО коммерциала можно превознести в много раз. В нашем арсенале более 100 проверенных фактических методологий подъема продаж а также прибыли. В зависимости от вашего коммерциала расчитаем для вас наиболее сильные и сможем шаг за шагом претворять в жизнь.
http://r-diplom.ru/
купить квартиру в новостройке от застройщика https://novostroyka47.ru
купить диплом о среднем специальном [url=https://school-10-lik.ru]https://school-10-lik.ru[/url] .
анальный секс с разговорами на русском [url=www.safavia.ru]анальный секс с разговорами на русском[/url] .
[url=http://valtrexv.online/]paypal buy valtrex online canada[/url]
Hey I am so excited I found your web site, I really found you by error, while I was researching on Askjeeve for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say cheers for a remarkable post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the moment but I have saved it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the fantastic work.
financetimenews.ru/page/14/
poznanie.gtaserv.ru/viewtopic.php?f=9&p=1937
old.kakdelat.ru/company/personal/user/1695/blog/8780/
kembekeltetes.hu/egyutt-nem-mukodo-vallalkozasok/ajanlast-nem-teljesito-vallalkozasok/
jeepgarage.ru/forum/topic.php?forum=24&topic=633
купить диплом фельдшера [url=www.school-10-lik.ru]www.school-10-lik.ru[/url] .
Ежегодно в течение сентября проходит Тюменский инновационный форум «НЕФТЬГАЗТЭК».
Форум посвящен развитию мнтодов инновационного развития секторов топливно-энергетического комплекса, обсуждению а также определению ответов, созданию наилучших условий для развития инновационных проектов. Ежегодный тюменский форум является влиятельной дискуссионной площадкой по продвижению нефтегазовой ветви в России, содержит большой авторитет и актуальность, созвучен общей стратегии формирования инноваторского курса в Российской Федерации
https://neftgaztek.ru/
Highly energetic blog, I enjoyed that a lot. Will there be a part 2?
купить диплом автомеханика [url=https://www.school5-priozersk.ru]https://www.school5-priozersk.ru[/url] .
you are in reality a excellent webmaster. The website loading velocity is incredible. It sort of feels that you’re doing any unique trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have performed a magnificent task on this subject!
clickandconnectclubs.com/index.php?do=/public/blog/view/id_119636/title_-2024/
linkheed.com/blogs/920/Why-is-the-demand-and-popularity-of-universities-declining-now
mybuildhouse.ru/page/13/
http://www.autodijagnostika.biz/carforum/showthread.php?1865-Launch-Diagun-2&p=47411&viewfull=1
sanatoriy-yuscki18.ru/pacient/reviews.php?strIMessage=%D1%EF%E0%F1%E8%E1%EE+%C2%E0%EC+%E7%E0+%EE%F2%E7%FB%E2%21&PAGEN_1=11
жиросжигатель купить [url=https://www.ozon.ru/product/nexis-effektivnye-tabletki-dlya-pohudeniya-zhiroszhigatel-dlya-zhenshchin-60-kapsul-kurs-na-mesyats-1564574748//]https://www.ozon.ru/product/nexis-effektivnye-tabletki-dlya-pohudeniya-zhiroszhigatel-dlya-zhenshchin-60-kapsul-kurs-na-mesyats-1564574748//[/url] .
[url=https://strattera.company/]strattera 40 mg pills generic[/url]
[url=https://bellingham-judefr.biz]bellingham-judefr.biz[/url]
Be Superb Online Casinos in the Magic 2023. Leading online casino aggregator.
bellingham
Проведение независимой строительной экспертизы — сложный процесс, требующий глубоких знаний. Наши специалисты обладают всеми необходимыми навыками, а их заключения часто служат основой для принятия верных стратегических решений. Строительно-техническая экспертиза https://stroytehexp.ru позволяет выявить факторы, вызвавшие ухудшение эксплуатационных характеристик объектов, проверить соответствие возведённых зданий градостроительным нормам.
Hi there friends, its great piece of writing concerning educationand fully explained, keep it up all the time.
The story of Mbappe’s asma-online.org rise to fame is as remarkable as his on-field feats. Mbappe’s journey from local pitches to global arenas was meteoric. His early days at AS Monaco showcased his prodigious talent, with his blistering speed and fearless dribbling dismantling opposition defenses.
Информационный ресурс https://ardma.ru, посвящен бизнесу, финансам, инвестициям и криптовалютам. Сайт предлагает экспертные статьи, аналитические отчеты, стратегии и советы для предпринимателей и инвесторов. Здесь можно найти новости и обзоры о бизнесе, маркетинге, трейдинге, а также практические рекомендации по различным видам заработка и управлению финансами.
[url=https://lasixor.com/]furosemide 80 mg daily[/url]
купить диплом специалиста [url=https://diplomvash.ru/]diplomvash.ru[/url] .
Широчайший ассортимент военных товаров|Оружие и снаряжение для настоящих мужчин|Здесь найдете все для военного дела|Армейские товары по выгодным ценам|Выбор настоящих военных победителей|Профессиональное снаряжение для военных|Военная экипировка от лучших брендов|Только качественные товары для военных задач|Оружие и снаряжение для любых задач|Снаряжение от лучших производителей|Снаряжение для профессионалов военного дела|Оружие и снаряжение для истинных воинов|Выбирайте только профессиональное снаряжение|Оружие и экипировка для настоящих героев|Специализированный магазин для военных операций|Выбор настоящих защитников|Армейский магазин с широким выбором экипировки|Оружие и снаряжение для успешных миссий|Качественные товары для военных целей|Выбирайте только надежные военные товары
військовий інтернет магазин [url=https://magazinvoentorg.kiev.ua/]військовий інтернет магазин[/url] .
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful article. Thank you for supplying this info.
stlouisbluesclub.com/read-blog/327_why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-decreasing-nowadays.html?mode=day
pialci.ru/index.php?links_exchange=yes&page=322&show_all=yes
щербиновскийрайон.рф/users/160?page=4
moskva-medcentr.ru/index.html
skazka.g-talk.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1679&p=1705
https://medium.com/@momejar21741/pg-59490dd058fd
สล็อตเว็บโดยตรง — สามารถใช้ สมาร์ทโฟน แท็บเล็ต คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว ฯลฯ ในการเล่น
ระบบสล็อตเว็บโดยตรง ของ PG Slot ได้รับการพัฒนาและปรับแต่ง เพื่อให้ สามารถใช้งาน บนอุปกรณ์ที่หลากหลายได้อย่าง ครบถ้วน ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้ โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือ คอมฯ รุ่นใด
ที่ พีจีสล็อต เราเข้าใจถึงสิ่งที่ผู้เล่นต้องการ ของผู้เล่น ในเรื่อง ความสะดวกสบาย และ การเข้าถึงเกมคาสิโนที่รวดเร็ว เราจึง ใช้ HTML 5 ซึ่งเป็น เทคโนโลยีที่ล้ำสมัย ปัจจุบันนี้ มาใช้พัฒนาเว็บไซต์ คุณจึงไม่ต้อง ดาวน์โหลดแอป หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมเพิ่มเติม เพียง เปิดเบราว์เซอร์ บนอุปกรณ์ที่ มีอยู่ของคุณ และเยี่ยมชม เว็บของเรา คุณสามารถ เพลิดเพลินกับสล็อตแมชชีนได้ทันที
การรองรับอุปกรณ์หลายชนิด
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้ มือถือ ระบบ Android หรือ ไอโอเอส ก็สามารถ เล่นสล็อตได้อย่างราบรื่น ระบบของเรา ออกแบบมาให้รองรับ ทุกระบบปฏิบัติการ ไม่สำคัญว่าคุณ ใช้ โทรศัพท์ ใหม่หรือเก่า หรือ แท็บเล็ตหรือโน้ตบุ๊ก ทุกอย่างก็สามารถ ใช้งานได้ดี ไม่มีปัญหา เรื่องความเข้ากันได้
สามารถเล่นได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา
หนึ่งในข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot นั่นคือ คุณสามารถ เล่นได้ทุกเวลา ไม่ว่าจะ เป็นที่บ้าน ที่ทำงาน หรือแม้แต่ สถานที่สาธารณะ สิ่งที่คุณต้องมีคือ อินเทอร์เน็ต คุณสามารถ เริ่มเกมได้ทันที และคุณไม่ต้อง ห่วงเรื่องการดาวน์โหลด หรือติดตั้งโปรแกรมที่ ใช้พื้นที่ในอุปกรณ์
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
เพื่อให้ ผู้ใช้ใหม่ มีโอกาสลองและสัมผัสประสบการณ์สล็อตแมชชีนของเรา PG Slot ยังเสนอบริการสล็อตทดลองฟรีอีกด้วย คุณสามารถ เริ่มเล่นได้ทันทีโดยไม่ต้องลงทะเบียนหรือฝากเงิน การ ทดลองเล่นสล็อตแมชชีนฟรีนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเรียนรู้วิธีเล่นและเข้าใจเกมก่อนตัดสินใจเดิมพันด้วยเงินจริง
บริการและการรักษาความปลอดภัย
PG Slot มุ่งมั่นในการบริการลูกค้าที่ดีที่สุด เรามี ทีมงานมืออาชีพพร้อมให้บริการและช่วยเหลือคุณตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง นอกจากนี้เรายังมี การรักษาความปลอดภัยที่ทันสมัย ด้วยวิธีนี้ คุณจึงมั่นใจได้ว่า ข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลและธุรกรรมทางการเงินของคุณจะได้รับการปกป้องอย่างดีที่สุด
โปรโมชั่นและของรางวัลพิเศษ
อีกข้อดีของการเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot ก็คือ มี โปรโมชันและโบนัสมากมาย ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น สมาชิกใหม่หรือเก่า คุณสามารถ รับโปรโมชันและโบนัสได้ สิ่งนี้จะ เพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและเพิ่มความเพลิดเพลินในเกม
สรุปการเล่นสล็อตเว็บที่ PG Slot ถือเป็นการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่า คุณจะไม่เพียงได้รับความสุขและความสะดวกสบายจากเกมเท่านั้น แต่คุณยังมีโอกาสลุ้นรับรางวัลและโบนัสมากมายอีกด้วย ไม่สำคัญว่าจะใช้โทรศัพท์มือถือ แท็บเล็ต หรือคอมพิวเตอร์รุ่นใด สามารถมาร่วมสนุกกับเราได้เลยตอนนี้ อย่ารอช้า ลงทะเบียนและเริ่มเล่นสล็อตกับ PG Slot วันนี้!
Первый партнер охраны труда
[url=https://www.ppot.ru/]Аудит системы охраны труда[/url] – экспертный центр по аудиту и подготовке специалистов в области охраны труда и пожарной безопасности. Наша компания предоставляет широкий спектр услуг по обеспечению безопасности производственных процессов для индивидуальных предпринимателей и организаций различных секторов промышленности в Москве, Московской области и других регионах России.
Соблюдение правил безопасности труда – законодательное требование, за нарушение которого на организацию может быть наложен штраф или приостановлена деятельность предприятия на срок до 90 суток.
Мы помогаем решать вопросы обеспечения безопасности и организации труда на предприятии, разрабатываем и актуализируем документы по охране труда, проводим комплексное обследование охраны труда на соответствие государственным нормативным требованиям. Проводим обучение сотрудников по охране труда и пожарной безопасности, проверяем СУОТ и оцениваем профессиональные риски.
Виктория Набойченко сделала для нашего канала заявление,
[url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0smZ5_QOcU]Новости Гермес[/url]
касающееся своего бывшего супруга – главного свидетеля обвинения по так называемому уголовному делу “Лайф-из-Гуд”-“Гермес”-“Бест Вей”
?? Забирай 100,000 Рублей + 400 Фриспинов в виде Welcome бонуса, на официальном сайте 7К Казино ??
?????? Официальное зеркало ??????
[url=https://t.me/s/casino_7k_official]7k казино регистрация [/url]
НОВЫЕ ПРОМОКОДЫ ОТ НАШЕГО ТЕЛЕГРАМ КАНАЛА 7К КАЗИНО! МОЩНЫЙ СТАРТ НАШИМ ИГРОКАМ. ???? ЖЕЛАЕМ КРУТЫХ ЗАНОСОВ ??
Joker7070 – бонус 170%+ 70 FS в Joker Stoker
777WIN – бонус 100%+ 30 FS в Hot Triple Sevens
HOT100 – бонус 100 FS в Indiana’sQuest
?? Добавляйте промокод в разделе бонусов на официальном сайте 7К Казино.
?? Важно! Для новых игроков после регистрации 7K Casino приготовил Welcome бонус до 100,000 Рублей + 400 Фриспинов! Успейте активировать ???
?? Подробная информация на официальном сайте 7К в разделе бонусов! Каждый промокод можете использовать по очереди.
7к казино актуальное зеркало на сегодня
https://t.me/s/casino_7k_official
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is fantastic, as well as the content!
rising.chew.jp/END/inside/dbbs/dicebbs.cgi?mode=resmsg&no=7866
newspromworld.ru/page/2
shop005.getmall.kr/board/board.php?pagetype=view&num=245&board=customerqna&block=0&gotopage=1&search=&s_check=
museums.artyx.ru/books/c0003_1.shtml
http://www.moj.webservis.ru/forums/search.php?action=members&p=150&s=d&order=ASC%D0%92%C2%A0
Заявление Виктории Набойченко – бывшей супруги главного свидетеля обвинения Евгения Набойченко
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0smZ5_QOcU
Здравствуйте, меня зовут Виктория Набойченко.
Я являюсь бывшей супругой Набойченко Евгения Витальевича, с которым состояла в официальном браке с 2017 по 2022 год. Из средств массовой информации мне стало известно о фактах уголовного преследования лиц из окружения Романа Василенко, который является президентом международной бизнес-карты на территории России, Казахстана и Киргизии. На протяжении 20 лет Евгений Набойченко и Роман Василенко дружили, вместе путешествовали, проводили время, ездили на рыбалку. Роман очень доверял Евгению, делился с ним своими идеями, планами на коммерческую деятельность и реализацию новых проектов. Мне известно, что Роман предложил Евгению разработать фирменный логотип и сайт компании Life is Good, а впоследствии возглавить IT-отдел ЖК. Евгений с радостью согласился на предложение Романа и возглавил IT-отдел. Роман достойно оплачивал работу Евгения, гонорар которого вырос со 100,000 рублей до 500,000 рублей в месяц, что было связано с ростом и развитием кооператива Best. Роман всегда был щедр к Евгению и ценил его работу, за что ежегодно премировал.
Тот успех, которого достиг Роман за эти годы, очень задевал Евгения как мужчину. В ходе совместной жизни Евгений делился со мной, что мечтает однажды превзойти Романа в бизнесе, а его проект стать круче Илона Маска. Примерно с июня 2021 года Евгений стал нервным и злился на Романа, рассказывая мне, что Роман не хочет заплатить ему 170,000 евро. Я не вдавалась в подробности их взаимоотношений. Чуть позже я узнала о письмах Евгения к Роману, в которых он требовал от него указанную сумму и угрожал увечьями и убийством Роману и всем членам его семьи, в том числе и детям. Данные угрозы он отправлял голосовыми сообщениями и в электронных письмах. Мне известно, что Роман не реагировал на угрозы Евгения, что очень злило его, потому что он ждал от него указанную сумму. В моём присутствии Евгений постоянно по нескольку раз переслушивал свои голосовые сообщения, которые с угрозами отправлял в адрес Романа Василенко. Он получал от этого огромное удовольствие, с ухмылкой хвастаясь, что Роман обязательно заплатит.
[url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0smZ5_QOcU]Best Way[/url]
17 февраля 2022 года в 7:00 по МСК в нашем доме в посёлке в Краснодарском крае произошел обыск. В доме находилась только я и дети, а Евгений в это время находился в Краснодаре на съёмной квартире, куда заблаговременно уехал, предупредив меня за 3 дня о предстоящем обыске в доме. Как будто его друзья из правоохранительных органов Петербурга предупредили его. На мои вопросы о том, что происходит, он отвечал, что это формальность и что мне не о чем беспокоиться. Позже мне стало известно, что подобные обыски проходили и у других сотрудников кооператива в Санкт-Петербурге, Краснодаре, Анапе и других городах. В обыске нашего дома принимали участие шесть оперативных работников ОББ города Санкт-Петербурга, фамилии которых указаны в протоколе обыска, копия которого имеется в моём распоряжении. В ходе обыска оперативные работники оскорбляли Евгения и Романа, называя их преступниками и мошенниками, а также иными оскорбительными словами. При обыске был изъят планшет Евгения, оперативные работники перевернули весь дом и напугали детей, а также пообещали, что задержат Евгения в тот же день.
17 февраля 2022 года Евгений был задержан сотрудниками оперативных служб в городе Краснодар и примерно через 3 дня был доставлен в Санкт-Петербург, где был допрошен в УП по рекомендации сотрудников полиции. Допрос происходил без участия его личного адвоката Ирины Черняховской, от услуг которой он отказался в тот же момент. Мне позвонила Ирина в бешенстве и недоумении, крича о том, что Евгений её опозорил перед сотрудниками полиции, отказавшись от её услуг в грубой форме. Впоследствии мне стало известно от Евгения, что он лично получил покровительство начальника ОББ города Санкт-Петербурга в своей безнаказанности по факту проводимого расследования. Об этом он похвастался мне в личном разговоре, будучи окрылённый поддержкой начальника ОББ, который с ним разговаривал на доверительной ноте.
Евгений мне рассказал, что получит от органов абсолютную неприкосновенность и поддержку за информацию, которая интересовала оперативных работников, за что Евгению также была предоставлена госохрана. В период с февраля по середину апреля Евгений находился в Питере под госзащитой и плотно взаимодействовал с правоохранительными органами. Он предоставлял им всю информацию, в том числе полный доступ к системе базы данных Best Way и Life is Good. Евгений инициативно предлагал органам заблокировать доступ к личным кабинетам пайщиков и членов ЖК БСТ, чем полностью парализовал хозяйственную деятельность кооператива, создавая напряжённость и негативные отзывы. Также Евгений активно призывал граждан к написанию заявлений в отношении Романа Василенко с целью возврата пайщиками своих денежных средств, делал он это через каналы Telegram и YouTube. Евгений был единственным, кто имел и имеет доступ к базам данных и ключам. Желая намеренно создать проблемы Роману, он отказывается восстанавливать работу системы Best Way при наличии такой возможности.
Миссия Евгения – это привлечение Романа Василенко к уголовной ответственности, что спровоцирует крах компании и полное прекращение её деятельности, а это в свою очередь 30,000 пайщиков, которые могут стать потерпевшими по уголовному делу. Всё это мне известно из личного общения с Евгением, когда я приезжала к нему в Санкт-Петербург на несколько дней. Мне также достоверно известно, что в настоящее время нет реальных заявлений от недовольных пайщиков, так как в Романа Василенко все верят. Самое главное, что у Евгения есть возможность в любой момент через свой личный ноутбук восстановить работу ЖК Best Way и вернуть доступ к личным кабинетам пайщиков. Однако он этого не делает, преследуя свои личные цели.
купить диплом в томске [url=https://vm-tver.ru]https://vm-tver.ru[/url] .
игра лаки джет на деньги [url=1win-luckyjet-game.ru]1win-luckyjet-game.ru[/url] .
Amazing! Its genuinely amazing post, I have got much clear idea about from this paragraph.
ukrevent.ru/page/12/
http://www.knx-fr.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=9935
51.15.223.140/forum/member.php?tab=visitor_messaging&u=76509&page=6
batdongsanmiennam.vn/mnre-tich-cuc-day-manh-kenh-ban-hang-truc-tuyen/
volteis.com/fr/canal-volteis/actualites/131-nouveau-distributeur-pour-la-guadeloupe-st-barth-et-st-martin
[url=http://sildenafilps.online/]price for sildenafil 20 mg[/url]
[url=https://doxycyclineo.online/]doxycycline minocycline[/url]
вскрыть замок цена [url=https://vskrytie-zamkov-moskva113.ru]https://vskrytie-zamkov-moskva113.ru[/url] .
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
– 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
– 體育博彩
– 彩票遊戲
– 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
– 全天候24小時提供服務
– 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
– 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
– 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
– 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
– 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
– 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
– 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
– 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
– 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
– 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
– 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。
piracetam 800 mg sale – sinemet 10mg cost sinemet 20mg us
寶島娛樂城儲值
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
188.17.148.172/forum/profile.php?action=show&member=7512
artem-energo.ru/forums.php?m=posts&q=17775
http://www.thusc.org/home.php?layout=365424
forumaniga.me/member/414-uf_23829059/visitormessage/13030-%D0%BF%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B5-%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%89%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D0%BE%D1%82-uf_23829059
shoelovershub.com/read-blog/475_why-is-the-popularity-of-universities-declining-in-our-time.html?mode=day
[url=https://lyricamd.com/]how much is lyrica 75 mg[/url]
создание и продвижение сайтов в москве цена [url=http://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru]http://prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve117.ru[/url] .
волчонок серия смотреть онлайн https://volchonok-tv.ru
Как получить лицензию на недвижимость|Ключевая информация о лицензии на недвижимость|Как начать карьеру в недвижимости с лицензией|Успешные стратегии получения лицензии на недвижимость|Разберитесь в процессе получения лицензии на недвижимость|Полезные советы по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Лицензия на недвижимость: важные аспекты|Шаг за шагом к лицензии на недвижимость|Три шага к успешной лицензии на недвижимость|Лицензия на недвижимость для начинающих: советы и рекомендации|Процесс получения лицензии на недвижимость: как это работает|Полезные советы по получению лицензии на недвижимость|Получите лицензию на недвижимость и станьте профессионалом|Лицензия на недвижимость: ключ к успешной карьере|Как получить лицензию на недвижимость легко и быстро|Эффективные стратегии для успешного получения лицензии на недвижимость|Секреты получения лицензии на недвижимость от экспертов|Как быстро и легко получить лицензию на недвижимость|Ключевые моменты получения лицензии на недвижимость|Легко получите лицензию на недвижимость с этими советами|Как стать агентом по недвижимости с лицензией|Основные шаги к профессиональной лицензии на недвижимость|Получение лицензии на недвижимость для начинающих: советы от экспертов|Процесс получения лицензии на недвижимость: ключевые моменты|Три шага к профессиональной лицензии на недвижимость|Лицензия на недвижимость: важные аспекты для успешного получения
How to get your real estate license in Virginia [url=https://realestatelicensehefrsgl.com/states/virginia-real-estate-license/]How to get your real estate license in Virginia[/url] .
Ежегодно в течение сентября организовывается Тюменский инновационный форум «НЕФТЬГАЗТЭК».
Форум посвящен определению механизмов инновационного роста секторов топливно-энергетического комплекса, обсуждению а также изысканию ответов, образованию благоприятных условий для развития инноваторских проектов. Ежегодный тюменский форум является авторитетной дискуссионной площадкой по увеличению роста нефтегазовой ветви в России, имеет высокий статус и своевременность, созвучен корпоративной стратегии формирования инновационного курса в России
https://neftgaztek.ru/
buy generic hydrea – purchase ethionamide without prescription robaxin 500mg tablet
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last few posts have been kinda boring?K I miss your tremendous writings. Past several posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
[url=http://diflucanr.com/]diflucan pill canada[/url]
перевозка мебели [url=www.gruzchikiminsk.ru]www.gruzchikiminsk.ru[/url] .
[url=https://advaird.online/]advair cost in canada[/url]
Understanding NanoDefense Pro: What is it? NanoDefense Pro is a specialized formula designed to improve nail and foot health naturally.
I like the valuable information you supply in your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and test again here frequently. I am quite certain I will be told lots of new stuff right here! Good luck for the following!
After looking at a few of the blog articles on your web page, I truly like your way of blogging. I saved it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back soon. Take a look at my web site as well and let me know what you think.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Virgil van Dijk https://virgilvandijk.prostoprosport-br.com Futebolista holandes, zagueiro central, capitao do clube ingles Liverpool e capitao do a selecao holandesa.
It’s going to be finish of mine day, but before finish I am reading this enormous piece of writing to increase my experience.
Victor James Osimhen https://victor-osimhen.prostoprosport-br.com e um futebolista nigeriano que atua como atacante. O clube italiano Napoli e a selecao nigeriana.
Следственная группа по делу «Бест Вей»: следователи или оборотни в погонах?
[url=https://vestnik-jurnal.com/novosti/item/100193-voennyh-unizhayut-tylovye-krysy-opg-kolokolceva]Бест Вей[/url]
Следственная группа по делу кооператива «Бест Вей» во главе со следователями ГСУ ГУ МВД по Санкт-Петербургу и Ленобласти майором юстиции Екатериной Сапетовой и подполковником юстиции Константином Иудичевым играет собственную партию либо для того, чтобы выслужиться перед непосредственным начальством, либо из-за прямой заинтересованности в уничтожении кооператива со стороны конкурентов и/или банков.
Следствие по делу кооператива «Бест Вей» вступило в активную фазу ровно год назад. За это время арестованы четверо технических сотрудников, и уже год они томятся в СИЗО, пятеро граждан объявлены в розыск.
Офис кооператива буквально разгромлен двумя обысками, документация изъята, и следствие запрещает ее копировать, счета и недвижимость арестованы. Под арестом — активы на более чем 15 млрд рублей, хотя ущерб для так называемых потерпевших, пул которых следователи год собирали под разными предлогами, не превышает 115 млн рублей. Это спустя почти полтора года с момента возбуждения уголовного дела, не считая периода длительного проведения оперативно-разыскных мероприятий. Гора родила мышь.
При этом значительная часть этих потерпевших, например, бывшие пайщики, которые внесли невозвратный вступительный взнос, но затем не смогли копить на квартиру и сами вышли из кооператива, а теперь по наущению следствия подали заявление о том, что кооператив им не вернул то, что и не должен был вернуть. Потерпевших 100 с лишним человек, притом что в кооперативе — более 19 тыс. пайщиков, то есть капля в море, да и эти 100 не имеют юридически обоснованных претензий к кооперативу. Среди представленных следствием потерпевших есть и конкуренты — бывшие пайщики, которые еще несколько лет назад вышли из «Бест Вей» и создали «альтернативный» кооператив «Вера».
Следователи обосновывают арест счетов тем, что «деньги могут украсть», хотя они же сами как минимум участвуют во вполне криминальном использовании чужих денег, уже год не давая пайщикам ни приобрести квартиру за счет средств, которые они скопили на счете в кооперативе, ни забрать деньги, при этом предоставляя возможность банкам. Следователи уже год дают возможность банкам пользоваться счетами почти на 4 млрд рублей, притом постоянно пополняющимися, так как большинство пайщиков продолжает вносить паевые и членские взносы.
Парадокс в том, что новая история обиженных дольщиков (в данном случае пайщиков) всероссийского масштаба возникла не из-за того, что у организации не оказалось средств для выполнения обязательств, а из-за того, что следственная группа лишила ее возможности пользования средствами и прямо блокирует выполнение обязательств перед пайщиками.
Адвокатам кооператива несколько раз удавалось добиться снятия арестов с активов кооператива, однако следователи и банки просто игнорируют решения судов. Потом, пользуясь высоким статусом следователей главка, заходят с новым ходатайством об аресте через кабинет судьи и без участия представителей кооператива, и активы снова арестовываются — до следующей успешной апелляции адвокатов, после которой в дело вступают банки, по договоренности со следствием блокирующие счета в рамках процедур комплаенс, игнорируя решения судов.
Должностное преступление
Действия следственной группы не могут квалифицироваться иначе, как должностное преступление, так как в них прослеживается заинтересованность в уничтожении кооператива. Фактически они сами организуют преступление, которое якобы расследуют, целенаправленно разрушают кооператив, а не спасают пайщиков, не нуждающихся в их спасении и 15 февраля проводящих всероссийскую акцию в защиту своего кооператива от следственной группы.
Адвокаты подавали в Следственный комитет заявление о преступлении, но оно было положено под сукно.
К службе не годны
Отдельная тема — вопиющая профнепригодность следственной группы. Иудичев в своих ответах на запросы ничтоже сумняшеся пишет, что Центральный банк признал кооператив финансовой пирамидой, хотя ЦБ, во-первых, не суд, чтобы делать такие «признания», во-вторых, такого признания просто не было: утверждение не соответствует действительности.
ЦБ внес кооператив в так называемый предупредительный список, являющийся инструментом информирования потребителей финансовых услуг об организациях, работа с которыми чревата для граждан рисками, и решение о включении в этот список состоялось после возбуждения уголовного дела, скорее всего, как раз на основе информации о его возбуждении.
Любимая тема следственной группы — якобы незаконность переименования кооператива из жилищного в потребительский: они не могут даже прочитать Жилищный кодекс, где черным по белому написано, что жилищный кооператив — один из видов жилищного. И подобных примеров некомпетентности и выдумок в деятельности следователей масса.
В итоге мы имеем шитое белыми нитками дело, наносящее колоссальный ущерб тысячам пайщиков кооператива, среди которых преобладают малообеспеченные люди.
Возникают вопросы: не пора ли министру Колокольцеву разобраться со своими сотрудниками, не пора ли главе Следкома Бастрыкину обратить внимание на должностные преступления в «соседнем» ведомстве?
[url=https://doxycyclinepr.com/]buy doxycycline no prescription[/url]
Toni Kroos https://toni-kroos.prostoprosport-cz.org je nemecky fotbalista, ktery hraje jako stredni zaloznik za Real Madrid a nemecky narodni tym. Mistr sveta 2014. Prvni nemecky hrac v historii, ktery sestkrat vyhral Ligu mistru UEFA.
Разбираю ситуацию вокруг “кооператива” Life is Good
[url=https://newscryptocoin.com/news/chto-delat-postradavshim-ot-deyatelnosti-life-is-good-bestway-i-hermes-kotorye-osnoval-beglyj-roman-vasilenko/]смотреть жесткое порно[/url]
Я решил написать этот пост, чтоб пройтись по доводам тех, кто привлекает новых “пайщиков” в структуры г-на Василенко (на деле – оплачивающих существование пирамиды Life is Good). Понятно, что, в этом сообществе крутятся сотни тех, кто занимается привлечением и теперь ЦБ с прокуратурой их оставят не только без заработка, но, возможно, придется отвечать за свои действия в суде. А деньги уже, наверняка, потрачены. Также есть люди, которые уже живут в квартире от LIG или выплатили некую сумму, они верят до конца и отказываются принимать ситуацию, в которой надо признать, что они могут остаться и без денег, и без квартиры. В любом случае, даже если кто-то живет в квартире от LIG, она ему не принадлежит и, в отличие от банковского залога, урегулировать вопрос не получится (их просто выселят через суд при банкротстве LIG, хотя ситуация скандальная и возможно государство что-то предпримет, чтоб сгладить проблему).Теперь по сути, что такое LIG.
Компания LIG – «Лайф-из-гуд» заявляет два основных направления деятельности: инвестиционные счета «Виста» в компании Hermes Management Ltd. и жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей» — альтернатива ипотеке.
Если верить консультантам «Лайф-из-гуд», доходность счетов «Виста» в компании «Гермес-менеджмент» последние годы держится в районе 20% годовых в долларах. Это довольно много (Уоррен Баффет позавидовал бы такой доходности), при этом непонятно, за счет чего достигается такая доходность.
Деятельность «Гермес-менеджмента» непрозрачна, на сайте не видно полноценных отчетов, нет сведений о структуре компании и ее руководстве.
«Гермес-менеджмент» привлекает российских клиентов через компанию «Лайф-из-гуд», но у него нет лицензии Центрального банка России на брокерскую деятельность или доверительное управление.
«Гермес-менеджмент» зарегистрирован в Белизе, офшорной зоне в Центральной Америке. Там же расположен офис компании. Еще в документах упоминается компания Hermes M в Шотландии. В случае проблем придется разбираться с зарубежной компанией, что делает задачу бесперспективной. Более того, учитывая реалии мошеннических схем, бывшие пайщики столкнутся еще и с лже-юристами, обещающими вернуть им вложенные деньги и конечно, останутся в крайне бедственном положении, с кредитами, без жилья и перспектив (у кого-то могут опуститься руки со всеми вытекающими).
Компания платит за привлечение новых клиентов, открывающих инвестиционные счета «Виста» (по сути – ничем не обеспеченные цифры на сайте. Заведение средств происходит через перевод средств на счета частных лиц(!), выполняющих роль консультантов LIG (а это сразу нарушает законы РФ и привлекает внимание регулятора), вывод – через перепродажу воздуха других буратинам. После внесения LIG в черный список, чаты структуры полны объявлений о продажи токенов Виста, но покупателей почти нет)) и вступающих в жилищный кооператив «Бест-вей». Система комиссионных выглядит такой разветвленной и продуманной, что становится понятно, что именно в ней суть компании, а не в инвестициях или альтернативе ипотеке.
Сам по себе сетевой маркетинг — вполне законный способ привлечения новых клиентов. Но когда он выглядит как основной вид деятельности, а клиентам при этом рассказывают про инвестиции, пассивный доход и успех в жизни, это наводит на очевидные выводы.
Суть предложения «Гермеса» такая: инвесторы открывают счет и перечисляют компании доллары или евро, а взамен получают пассивный доход. Минимальная сумма инвестиционного контракта — 10 тысяч долларов или евро. При этом первый взнос может быть 1130 долларов или 1100 евро, а оставшуюся сумму можно довнести позже.
Чтобы открыть счет «Виста», надо заполнить регистрационную форму на сайте «Лайф-из-гуд». При регистрации сайт просит поставить галочку «Я ознакомился и принимаю условия указанные в публичной оферте» (пунктуация сохранена).
По ссылке открывается не оферта, а договор об оказании услуг. В договоре не указаны название и реквизиты компании, с которой заключается договор. Кроме того, речь в нем идет не об управлении активами, а только об «образовательных и консультационных услугах об инвестиционных механизмах и способах управления капиталом». Это не похоже на обещанный пассивный доход от слова совсем. Таким образом, зазывалы в пирамиду пытаются уйти от ответственности.
[url=https://roman-vasilenko-wanted.com/]гей член[/url]
Чтобы открыть счет и пользоваться им, придется заплатить различные комиссии. Все они прописаны в договоре:
Комиссия за открытие счета: 100 евро или 130 долларов.
Ажио, или входная комиссия: 7% от суммы лицевого счета. На сайте есть пример расчета: при вложении 100 000 $ ажио составит 7000 $.
Комиссия за управление счетом: 1% в год от размера счета, взимается каждый месяц по 1/12.
Комиссия с прибыли: 20% от ежемесячной прибыли, «полученной от инвестиционных продуктов сторонних партнерских компаний или физических лиц, в результате рекомендаций и деятельности Исполнителя».
Итак, LIG состоит из двух основных компаний: Гермес, которая предлагает участникам инвестиционный доход (с идеей полученную прибыль направить на квартиру) и Бест-Вэй, являющаяся ЖНК. Что это такое?
Это Жилищный накопительный кооператив (общепринятое сокращение — ЖНК) — вид потребительского кооператива, сочетающий в себе качества финансового и жилищно-строительного кооператива. ЖНК работают в соответствии с № 215-ФЗ «О жилищных накопительных кооперативах». Целью деятельности жилищных накопительных кооперативов является удовлетворения потребностей членов кооператива в жилых помещениях путём объединения членами кооператива паевых взносов. Жилищный накопительный кооператив имеет право:
– привлекать и использовать денежные средства граждан на приобретение жилых помещений;
– вкладывать имеющиеся у него денежные средства в строительство жилых помещений (в том числе в многоквартирных домах), а также участвовать в строительстве жилых помещений в качестве застройщика или участника долевого строительства;
– приобретать жилые помещения;
– привлекать заёмные денежные средства, общая величина не должна превышать сорок процентов стоимости имущества кооператива.
Членами жилищного накопительного кооператива могут быть только граждане РФ. Жилищный накопительный кооператив создаётся по инициативе не менее чем пятидесяти человек и не более чем пяти тысяч человек. Контроль за деятельностью кооператива по привлечению и использованию денежных средств граждан на приобретение жилых помещений, а также за соблюдением кооперативом требований действующего законодательства Российской Федерации осуществляет Центральный банк Российской Федерации.
Уже отсюда понятно, что заявления заинтересованных лиц из структур LIG о том, что ЦБ не в праве вмешиваться в деятельность собственно LIG лишены оснований. Может и вмешался.
Если говорить о цифрах, то на 13 декабря 2021 года в LIG было свыше 19 000 пайщиков изо всех уголков РФ. LIG выкупил и передал в безвозмездное пользование пайщикам примерно 2 500 объектов недвижимости, из них по 247 пайщики полностью выплатили пай, оформив недвижимость в собственность. Интересная статистика – 19 000 вступили, заплатив членский взнос в 160 000 рублей, но лишь 8 часть из них накопила необходимые 35% для получения недвижимости при том, что фактически недвижимость их собственностью не является. Заявления о том, что получившие недвижимость прописаны в квартирах – это пережитки советского прошлого и, вероятно, сознательное введение остальных в заблуждение. В современной РФ не существует института прописки, есть регистрация, постоянная и временная. Есть найм жилья и есть собственность. Допускаю, что какая-то часть людей все еще проживает в государственных квартирах и не оформила их в собственность, но это – давно не норма, как это было в СССР (где собственность как раз была редким явлением).
По сути кооператив — посредник между покупателем и продавцом жилья, а это увеличивает риски. Приходится полагаться на то, что кооператив соблюдает закон и что он не закроется до того, как вы оформите квартиру на себя.
Даже если все по закону, риск потерять деньги остается. Если кооператив по каким-то причинам перестанет работать, его собственность распродадут. Сначала он рассчитается с кредиторами и только затем вернет деньги пайщикам — пропорционально их паевым взносам. Хватит ли у кооператива денег, чтобы вернуть все паевые взносы, неизвестно.
[url=http://rettretinoin.online/]buy retin a cream[/url]
эскорт услуги от индивидуалок москвы https://prostitutki-213.ru. Вызвать проститутку на любой вкус по низким ценам. Каталог шлюх Москвы
спортивная площадка купить [url=http://ploshadka-sport.ru/]спортивная площадка купить[/url] .
Веб-студия SUHOV-IT ru в Москве – комплексный интернет-маркетинг “под ключ” и еще разработка сайтов и использований
https://suhov-it.ru/
[url=https://mcadvair.online/]price of advair without insurance[/url]
ремонт стиральных машин адреса [url=centr-remonta-stiralnyh-mashin.ru]ремонт стиральных машин адреса[/url] .
flexeril canada – buy primaquine without prescription enalapril over the counter
KMSpico: What is it?
[url=https://kmspico.ws]скачать kmspico[/url]
Operating systems and Office suites are among the primary Microsoft software items that still need to be paid for. Some consumers may find alternate activation methods due to the perceived expensive cost of these items. There may be restrictions, unforeseen interruptions, and persistent activation prompts if these items are installed without being properly activated.
Our KMSpico app was created as a solution to this issue. By using this program, customers may access all of the functionality of Microsoft products and simplify the activation procedure.
KMSPico is a universal activator designed to optimize the process of generating and registering license codes for Windows and Office. Functionally, it is similar to key generators, but with the additional possibility of automatic integration of codes directly into the system. It is worth paying attention to the versatility of the tool, which distinguishes it from similar activators.
The above discussion primarily focused on the core KMS activator, the Pico app. Understanding what the program is, we can briefly mention KMSAuto, a tool with a simpler interface.
By using the KMSPico tool, you can setup Windows&Office for lifetime activation. This is an essential tool for anybody looking to reveal improved features and go beyond limitations. Although it is possible to buy a Windows or Office key.
KMSPico 11 (last update 2024) allows you to activate Windows 11/10/8 (8.1)/7 and Office 2021/2019/2016/2013/2010 for FREE.
KMSpico Download | Official KMS Website New July 2024
[url=https://kmspico.io/]ez активатор[/url]
Are you looking for the best tool to activate your Windows & Office? Then you should download and install KMSpico, as it is one of the best tools everyone should have. In this article, I will tell you everything about this fantastic tool, even though I will also tell you if this is safe to use.
In this case, don’t forget to read this article until the end, so you don’t miss any critical information. This guide is for both beginners and experts as I came up with some of the rumours spreading throughout the internet.
Perhaps before we move towards downloading or installing a section, we must first understand this tool. You should check out the guide below on this tool and how it works; if you already know about it, you can move to another section.
What is KMSPico?
KMPico is a tool that is used to activate or get a license for Microsft Windows as well as for MS Office. It was developed by one of the most famous developers named, Team Daz. However, it is entirely free to use. There is no need to purchase it or spend money downloading it. This works on the principle of Microsft’s feature named Key Management Server, a.k.a KMS (KMSPico named derived from it).
The feature is used for vast companies with many machines in their place. In this way, it is hard to buy a Windows License for each device,, which is why KMS introduced. Now a company has to buy a KMS server for them and use it when they can get a license for all their machines.
However, this tool also works on it, and similarly, it creates a server on your machine and makes it look like a part of that server. One thing different is that this tool only keeps the product activated for 180 days. This is why it keeps running on your machine, renews the license keys after 180 days, and makes it a permanent activation.
KMSAuto Net
Microsoft Toolkit
Windows Loader
Windows 10 Activator
Features
We already know what this tool means, so let’s talk about some of the features you are getting along with KMSPico. Reading this will surely help you understand whether you are downloading the correct file.
Ok, so here are some of the features that KMSPico provides:
Activate Windows & Office
We have already talked about this earlier, as using this tool, you will get the installation key for both Microsoft Products. Whether it is Windows or Office, you can get a license in no time; however, this supports various versions.
Supports Multi-Arch
Since this supports both products, it doesn’t mean you have to download separate versions for each arch. One version is enough, and you can get the license for both x32-bit or even the x64-bit.
It Is Free To Use
Undoubtedly, everything developed by Team Daz costs nothing to us. Similarly, using this tool won’t cost you either, as it is entirely free. Other than this, it doesn’t come with any ads, so using it won’t be any trouble.
Permanent License
Due to the KMS server, this tool installs on our PC, we will get the license key for the rest of our lives. This is because the license automatically renews after a few days. To keep it permanent, you must connect your machine to the internet once 180 days.
Virus Free
Now comes the main feature of this tool that makes it famous among others. KMSPico is 100% pure and clean from such viruses or trojans. The Virus Total scans it before uploading to ensure it doesn’t harm our visitors.
[url=http://acutanep.online/]how to get accutane prescription[/url]
ondansetron 4mg brand – buy procyclidine without prescription buy requip pills
[url=https://dexamethasoneff.com/]dexamethasone 4 mg tablet buy online[/url]
[url=https://xlyrica.com/]lyrica 300 mg price uk[/url]
Game World online https://games-online-eg.com the latest online gaming news, game reviews, gameplay, ideas, gaming tactics and tips. The most popular and amazing games and get ready to become the leader in the online gaming world!
The Dota 2 website https://dota2-kz.kz provides the most complete information about the latest game updates, tournaments and upcoming events. We are here for every winning tactic, secret and important guide.
Студия Подкастов в Москве, Запись подкастов в Москве.
http://video-podcast.ru/
mexico pharmacy: mexican mail order pharmacies – mexico drug stores pharmacies
Аренда телесуфлеров в Москве, Аренда и обслуживание телесуфлеров в Москвеhttps://xn--e1aaawb5aeenk.xn--p1ai/
mexican pharmaceuticals online
https://cmqpharma.online/# buying prescription drugs in mexico
buying from online mexican pharmacy
The Dota 2 website https://dota2-ar.com provides the most detailed information about the latest game updates, tournaments and upcoming events. We have all the winning tactics, secrets and important guides.
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов 31 августа 2022 года внесены следующие организации, обладающие признаками финансовой пирамиды или признаками мошенничества.
[url=https://forum-kpfu.ru/100624/novosti-vasilenko-roman-poslednie-novosti/]красивый анальный секс[/url]
Etihad Rail (etihadrail-ae.com)
Club Unite To Live, Life Is Good, Unite To Live (uniteto.live). Новый домен пирамиды находящегося в розыске Романа Василенко.
TopBoom, «платформа хедж-фонда, специализирующегося на сделках с обратным исходом спортивного события» (topboom.vip, t.me/TopBoom001)
Change Team, мошенники указывают реквизиты чужого юрлица ООО «АТТИС ГРУПП» (ОРГН 1207700314128, ИНН 9702022065), телеграм-канал «Change Team: Главный Канал» (change-team.ru). Фальшивый обменник раньше назывался C Exchange.
Ещё лохотроны:
Scam! Чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов и отзывы
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов включены организации, имеющие признаки финансовой пирамиды по классификации Центрального банка; организации, обладающие признаками матричной пирамиды (массовый привод друзей, «столы»); сборы денег с пенсионеров и прочих незащищённых слоёв населения; хайпы; организации, имеющие негативные отзывы; структуры, оказывающие финансовые услуги без лицензии и прочие лохотроны за исключением псевдоброкеров, кооперативов (с ними тоже не рекомендуем связываться) и некоторых других категорий.
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов 31 августа 2022 года внесены следующие организации, обладающие признаками финансовой пирамиды или признаками мошенничества.
[url=https://consultant-uniteto.live/]первый анальный секс[/url]
Etihad Rail (etihadrail-ae.com)
Club Unite To Live, Life Is Good, Unite To Live (uniteto.live). Новый домен пирамиды находящегося в розыске Романа Василенко.
TopBoom, «платформа хедж-фонда, специализирующегося на сделках с обратным исходом спортивного события» (topboom.vip, t.me/TopBoom001)
Change Team, мошенники указывают реквизиты чужого юрлица ООО «АТТИС ГРУПП» (ОРГН 1207700314128, ИНН 9702022065), телеграм-канал «Change Team: Главный Канал» (change-team.ru). Фальшивый обменник раньше назывался C Exchange.
Ещё лохотроны:
Scam! Чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов и отзывы
В чёрный список пирамид и лохотронов включены организации, имеющие признаки финансовой пирамиды по классификации Центрального банка; организации, обладающие признаками матричной пирамиды (массовый привод друзей, «столы»); сборы денег с пенсионеров и прочих незащищённых слоёв населения; хайпы; организации, имеющие негативные отзывы; структуры, оказывающие финансовые услуги без лицензии и прочие лохотроны за исключением псевдоброкеров, кооперативов (с ними тоже не рекомендуем связываться) и некоторых других категорий.
[url=https://bacclofen.online/]baclofen cream uk[/url]
ascorbic acid pills – kaletra generic buy compro pills for sale
Автомойка под ключ – это ваш легкий старт в автосервисном бизнесе. Не требуется прежний опыт – мы сопровождаем вас на каждом шагу.
AML проверка
AML-проверка: Посредством чего избежать ограничение средств на платформах обмена криптовалют
Зачем нужна AML-проверка?
Проверка по борьбе с отмыванием денег (Борьба с отмыванием денег) – представляет собой набор мер, предназначенных в целях противодействия легализации ресурсов. Эта проверка дает возможность оберегать криптовалютные фонды владельцев а также предотвращать применение систем нелегальных действий. Антиотмывочные меры необходима в целях обеспечения защищенности Ваших средств наряду с соблюдением нормативных стандартов.
Главные подходы оценки
Криптобиржи и другие платежные услуги применяют несколько важнейших способов в рамках проверки пользователей:
Идентификация личности: Эта методика включает базовые процедуры по идентификации документов пользователя, такие как валидация документов и адреса. “Знай своего клиента” помогает убедиться, что пользователь выступает в качестве доверенным.
Противодействие финансированию терроризма: Сфокусирована в интересах предотвращения поддержки экстремистских групп. Система мониторит вызывающие вопросы действия при необходимости приостанавливает кошельки с целью проведения внутренней аудита.
Выгоды проверки по борьбе с отмыванием денег
AML-проверка обеспечивает платформам обмена криптовалют:
Выполнять глобальные вместе с национальными правовые требования.
Сохранять владельцев криминальной активности.
Наращивать показатель репутации со стороны клиентов и регуляторов.
Как защитить себя в ходе транзакций на криптовалютном рынке
Для того чтобы уменьшить опасности замораживания активов, выполняйте этому списку указаниям:
Обращайтесь к заслуживающие доверие сервисы: Обращайтесь исключительно к сервисам положительной востребованностью и высоким уровнем надежности.
Исследуйте участников: Прибегайте к услуги по противодействию отмыванию в интересах проверки виртуальных счетов получателей предварительно перед совершением операций.
Периодически обновляйте криптоадреса: Данное действие позволит предотвратить потенциальных опасений, в ситуации когда Ваши партнеры контрагенты будут внесены под подозрение.
Обеспечивайте свидетельства операций: Когда потребуется ситуации окажетесь способны доказать чистоту получаемых ресурсов.
Резюме
AML-проверка – является ключевой инструмент с целью обеспечения безопасности действий
с криптовалютой. Эта практика способствует минимизировать сокрытие средств, обеспечение незаконных инициатив и другие нелегальные мероприятия. Выполняя требованиям в интересах безопасности в совокупности с выбором надежные биржи, будете в состоянии минимизировать опасности замораживания ресурсов и наслаждаться надежной деятельностью в криптосфере.
[url=https://flomaxms.online/]flomax for kidney stones[/url]
wow raid carry [url=https://kreativwerkstatt-esens.de/]wow raid carry[/url] .
What’s up, its nice article regarding media print, we all be familiar with media is a enormous source of data.
order durex gel – how to order durex condoms zovirax over the counter
[url=https://lyricamd.online/]lyrica price[/url]
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I wanted to thanks for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
Об агентстве недвижимости СЦН
Агентство недвижимости Саровский Центр Недвижимости (СЦН) занимает лидирующие позиции среди профессиональных компаний в городе Саров. Мы оказываем квалифицированную поддержку клиентам, желающим приобрести, реализовать или обменять квартиру, или другие объекты недвижимости, а также осуществить разнообразные сделки в этой сфере. Наше агентство заключает официальные договоры, и оказываем услуги по прейскуранту.
[url=https://сцн.рф]страхование ипотеки саров[/url]
Опытные риэлторы в нашей команде обладают значительным опытом в области недвижимости и помогут вам найти идеальное жилье на вторичном рынке Сарова, а также подобрать вторичку и новостройки по всей России. Мы работаем с крупным всероссийским агентством недвижимости, что позволяет нам оказывать высококачественные услуги на рынке недвижимости как в пределах России, так и за рубежом.
Наше агентство предлагает выгодные условия по страхованию ипотеки, а также специальные скидки при оформлении ипотеки для партнеров банка. Мы установили партнерские отношения с известными крупными страховыми компаниями и банками, что обеспечивает нашим клиентам надежность и прозрачность процесса сделки. Юрист с двадцатилетним стажем, Антон Марсов, обеспечивает правовую защиту интересов наших клиентов на каждом этапе взаимодействия.
Мы также предлагаем услуги по ремонту и отделке квартир, а наш дизайнер интерьеров поможет воплотить в жизнь ваши дизайнерские идеи. Если вы ищете квартиру в Сарове для инвестиций, мы найдем для вас оптимальное решение. Мы также готовы рассмотреть сотрудничество с инвесторами для совместных проектов в сфере недвижимости. Наша профессиональная бригада ремонтников гарантирует высокое качество выполнения работ.
Не стесняйтесь обращаться к нам, если вам необходима помощь в приобретении или реализации недвижимости в Сарове. СЦН – ваш партнер по всем вопросам недвижимости в городе и за его пределами.
страхование ипотеки саров
https://сцн.рф
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。
lets hack 1win [url=https://1win.tr-kazakhstan.kz]https://1win.tr-kazakhstan.kz/[/url] куда вводить промокод в 1win https://www.1win.tr-kazakhstan.kz
I do consider all of the ideas you have offered to your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Nonetheless, the posts are very short for novices. May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
I’m still learning from you, while I’m improving myself. I absolutely liked reading everything that is posted on your website.Keep the posts coming. I liked it!
Звон Колокольцева
[url=https://compromat.group/main/investigations/130259-zvon-kolokolceva.html]Бест Вей[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
Министр, управляемый мафией
Итак, Колокольцев публично солгал Совету Федерации, выдумав пирамиду, выдумав многомиллиардный ущерб и десятки тысяч пострадавших, он – некомпетентный руководитель, абсолютно ведомый своей камарильей, стремящейся создавать громкие пиар-истории на пустом месте и с коррупционной выгодой для себя. Он вызвал социальный протест десятков тысяч пайщиков кооператива «Бест Вей» и клиентов компании «Гермес» и членов их семей – в большинстве своем представителей социально незащищенных слоев населения, на годы лишенных возможности пользоваться своими деньгами и приобрести недвижимость, на которую они собрали средства, – в том числе десятков участников СВО. Министр вредит в тылу тем, кто защищает страну на фронте.
Глава МВД находится под влиянием или даже контролем давно ставшей притчей во языцех питерской полицейской мафии. Ликвидация этой мафии, как и ликвидация преступной, коррупционной, вредящей социально-политической стабильности системы управления МВД, со стороны Колокольцева является важнейшей государственной задачей.
Звон Колокольцева
[url=https://compromat.group/main/investigations/130259-zvon-kolokolceva.html]Лайф-из-Гуд[/url]
Поздравляем вас, гражданин министр, соврамши!
Выступая прошлой осенью в Совете Федерации, министр внутренних дел Владимир Колокольцев рассказывал, о так называемом уголовном деле «Лайф-из-Гуд» – «Гермес» – «Бест Вей», обещал миллиарды рублей ущерба и десятки тысяч потерпевших. Пресс-служба МВД под руководством его боевой подруги Ирины Волк заявила о том, что вскрыта деятельность крупнейшей в истории России финансовой пирамиды.
Однако в уголовном деле, расследованном или, вернее сказать, изготовленном ГСУ питерского главка МВД, которое в феврале начал рассматривать Приморский районный суд Санкт-Петербурга, 282 млн рублей ущерба и 221 лицо, признанное следствием потерпевшим: никаких миллиардов и десятков тысяч потерпевших.
Министр и его Волк публично солгали – на основе информации, переданной замначальника ГСУ руководителем следственной группы полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, фактически даже руководившей СГ его заместительницей майором, а затем подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой по материалам, состряпанным опером УЭБиПК питерского главка МВД майором полиции А.Ю. Машевским, при попустительстве (или соучастии?) начальника ГСУ Негрозова и замначальника Следственного департамента федерального министерства Вохмянина. Полковник и подполковник с примерно пятого-шестого уровня иерархии МВД виляет генералом полиции Российской Федерации, постоянным членом Совета безопасности России – это позор для государства.
Так называемые потерпевшие и реально пострадавшие
Большинство «потерпевших» на суде заявляют суммы около 1–2 млн рублей, при этом в ходе судебного следствия выясняется, что они, как правило, получали немалый доход, причем, они еще и налоговые/валютные преступники, так как этот доход не декларировали. Среди «потерпевших» есть граждане, заявляющие смехотворные суммы в 50–70 тыс., то есть количество потерпевших специально накручивалось следствием. И даже с этим накручиванием удалось набрать так мало – учитывая, что у «Гермеса», по данным самого же следствия, более 200 тыс. клиентов в России, а в кооперативе «Бест Вей» – около 20 тыс. пайщиков.
То есть большинство и клиентов «Гермеса», и пайщиков кооператива не считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности этих организаций.
Судя по тысячам обращений во все инстанции, нескольким волнам митингов, прокатившихся по России, они считают себя потерпевшими от деятельности органов внутренних дел.
Ведь именно завербованный питерским УЭБиПК сисадмин российской платежной системы «Гермеса» Набойченко заблокирован и разгромил в феврале 2022 года эту платежную систему, повесив на сайте дисклеймер: «Обращайтесь в правоохранительные органы», что на месяцы прекратило вывод средств. Именно действия правоохранительных органов в отношении компании до и после затруднили вывод средств. Дело в том, что для вывода средств многими использовался механизм p2p, позволяющий не платить комиссию, то есть для вывода средств нужно, чтобы кто-то вносил средства (что, понятно, резко сократилось из-за уголовного дела) и происходил обмен. Однако этот способ не единственный, вывод средств так или иначе осуществляется.
Тысячи пайщиков кооператива тем более не считают себя потерпевшими от его деятельности – потому что именно правоохранительные органы воспрепятствовали приобретению недвижимости с помощью кооператива, а она из-за более чем двухлетнего ареста его счетов, на которых около 4 млрд рублей, не может быть приобретена по прежней цене.
Именно правоохранительные органы прямо запрещают выплаты пайщикам кооператива, решившим забрать свой пай, – даже по исполнительным листам судов. И клиентам «Гермеса», и пайщикам кооператива правоохранительными органами нанесен колоссальный ущерб – и материальный, и моральный, который они намерены взыскать с государства.
«Следователи»-преступники должны сидеть в тюрьме
Весьма скромный результат следствия МВД был достигнут откровенно преступным путем.
1. Некоторые из преступлений следствия были фактически признаны судами. 1 декабря прошлого года Приморский районный суд города Санкт-Петербурга признал незаконным, нарушающим УПК фактический отказ кооперативу в ознакомлении с материалами уголовного дела.При рассмотрении дела в суде выяснилось, что следственная группа ГСУ питерского главка МВД, формально руководимая замначальника ГСУ полковником юстиции А.Н. Винокуровым, а фактически – подполковником юстиции Е.А. Сапетовой, подделала документы. Автор подделки – Сапетова – еще в феврале была уволена из ГСУ «по собственному желанию».
Уличенная адвокатами кооператива в нарушении УПК, следственная группа составила письмо об удовлетворении ходатайства задним числом и попыталась представить дело так, что кооператив не получил письмо по своей вине. Ложь была выявлена в том числе и с помощью системы электронного документооборота питерского главка МВД.
2. Подделка документов была вынужденным преступлением для сокрытия более серьезного: незаконного содержания под стражей. Следственная группа грубо нарушила права гражданских истцов и ответчиков, потому что без этого нарушения она не успела за 30 суток до истечения предельного срока содержания четверых обвиняемых под стражей начать ознакомление обвиняемых с материалами дела –а это было единственное основание продления им срока содержания под стражей свыше предельного.
Следственная группа из-за спешки даже толком не смогла завершить следственные действия, незаконно вела параллельное расследование по «резервному» делу, но позднее, отбросив стыд, из-за отсутствия материала для составления «нужного» обвинительного заключения, незаконно продолжила расследование «основного» дела, в том числе проводила следственные действия, которые, согласно УПК, невозможны после начала ознакомления обвиняемых с материалами дела. Все эти ухищрения были необходимы для того, чтобы ни в коем случае не выпускать обвиняемых и продолжать держать их в заложниках.
3. Де-факто происходит уголовное наказание неосужденных людей – четверо подсудимых уже второй год сидят в тюрьме. При этом наказываются явно ни в чем неповинные люди – технические сотрудники «Лайф-из-Гуд»: даже если предположить, что действительно работала пирамида – что опровергается показаниями свидетелей самого обвинения, которые сообщают суду, что компания «Гермес» хорошо работала, они были довольны получаемым доходом, и проблемы начались после того, как российская платежная система компании была обрушена завербованным полицией петербургским сисадмином компании Набойченко. Все подсудимые – технические сотрудники компании «Лайф-из-Гуд» и ни к каким управленческим решениям отношения никогда не имели. Их взяли в заложники для того, чтобы они дали показания на руководство компании.
4. Еще одно преступление – заведомо подложное постановление руководителя следственной группы А.Н. Винокурова о привлечении кооператива «Бест Вей» в качестве гражданского ответчика на 16 млрд рублей, тогда как сумма ущерба в уголовном деле –282 млн, и в деле нет ни одного искового заявления – даже на 100 рублей.
5. Следствие стимулировало двух особенно активных так называемых потерпевших написать заявления о моральном ущербе на миллиард (!) рублей каждое – исключительно для ложного обоснования ареста активов кооператива, но понятно, что это ничтожные документы, так как моральный ущерб во всех случаях, не связанных с причинением смерти, присуждается российскими судами в размере не более десятков тысяч рублей.
6. Ни один из «потерпевших» не доказал обоснованность своих претензий в гражданском суде. При этом арестованы активы кооператива почти на 4 млрд рублей и активы частных лиц на такую же сумму. Это не что иное, как попытка захвата активов при участии органов внутренних дел некой заинтересованной группой клиентов «Гермеса» – необязательно из числа «потерпевших», то есть коррупционное преступление, которое упорно игнорирует ГУСБ МВД.
Механизм для такого захвата есть – это передача средств под управление Федерального общественно-государственного фонда по защите прав вкладчиков и акционеров. Понятно, почему не ограничиваются активами подсудимых и обвиняемых: этого недостаточно для удовлетворения аппетитов тех, кто стоит за заказным уголовным делом. И понятно, почему одно юридическое лицо – кооператив «Бест Вей» – незаконно пытаются привлечь к ответственности за другое – компанию «Гермес»: активы «Гермеса» – за рубежом.
7. Следствие, а теперь и прокуратура совершают еще одно преступление: незаконно удерживает средства пайщиков кооператива, отказываясь их вернуть, то есть совершают хищение.
Министр, управляемый мафией
Итак, Колокольцев публично солгал Совету Федерации, выдумав пирамиду, выдумав многомиллиардный ущерб и десятки тысяч пострадавших, он – некомпетентный руководитель, абсолютно ведомый своей камарильей, стремящейся создавать громкие пиар-истории на пустом месте и с коррупционной выгодой для себя. Он вызвал социальный протест десятков тысяч пайщиков кооператива «Бест Вей» и клиентов компании «Гермес» и членов их семей – в большинстве своем представителей социально незащищенных слоев населения, на годы лишенных возможности пользоваться своими деньгами и приобрести недвижимость, на которую они собрали средства, – в том числе десятков участников СВО. Министр вредит в тылу тем, кто защищает страну на фронте.
Глава МВД находится под влиянием или даже контролем давно ставшей притчей во языцех питерской полицейской мафии. Ликвидация этой мафии, как и ликвидация преступной, коррупционной, вредящей социально-политической стабильности системы управления МВД, со стороны Колокольцева является важнейшей государственной задачей.
外送茶
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。
ProNerve 6 nerve relief formula stands out due to its advanced formula combining natural ingredients that have been specifically put together for the exceptional health advantages it offers.
[url=https://pin-up-casino-no.biz]pin up no[/url]
Plasser innsatsen din hos pin up online – direkte palitelig bookmaker
pinup casino
[url=https://pin-up-casino-sv.biz]Pin up[/url]
Placera ditt spel hos pin up online – mest prestigeious bookmaker
Pinup
[url=https://pin-up-casino-ar.biz]Pinup casino[/url]
Place your bet at pinup online – direct prestigious bookmaker
Pinup
[url=https://pin-up-casino-no.biz]pin up no[/url]
Plasser innsatsen din hos pinup online – mest elite bookmaker
pin up no
[url=https://pin-up-casino-sv.biz]online casino[/url]
Placera ditt spel hos pinup online – akta elite bookmaker
Pin up casino
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Опытная Замена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Перемещение Домов
Фирма Gerakl24 специализируется на выполнении всесторонних работ по реставрации фундамента, венцов, настилов и передвижению зданий в месте Красноярске и за пределами города. Наша команда опытных специалистов обеспечивает высокое качество выполнения различных типов ремонтных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасные, из кирпича или бетонные конструкции строения.
Достоинства сотрудничества с Gerakl24
Квалификация и стаж:
Каждая задача проводятся только высококвалифицированными экспертами, имеющими многолетний опыт в области строительства и реставрации домов. Наши специалисты эксперты в своей области и реализуют задачи с безупречной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы осуществляем полный спектр услуг по реставрации и восстановлению зданий:
Замена фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что гарантирует долговечность вашего дома и избежать проблем, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Замена венцов: реставрация нижних венцов из дерева, которые обычно подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: установка новых полов, что кардинально улучшает визуальное восприятие и функциональные характеристики.
Перемещение зданий: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на другие участки, что обеспечивает сохранение строения и избежать дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Деревянные дома: восстановление и укрепление деревянных конструкций, защита от гниения и вредителей.
Дома с каркасом: укрепление каркасов и смена поврежденных частей.
Кирпичные строения: восстановление кирпичной кладки и укрепление конструкций.
Бетонные строения: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы работаем с только проверенные материалы и современное оборудование, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все наши проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Персонализированный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем персонализированные решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Наша цель – чтобы итог нашей работы полностью соответствовал вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы найдете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по восстановлению и ремонту вашего здания. Мы обещаем выполнение всех задач в сроки, установленные договором и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и ответить на все ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить ваш проект и узнать больше о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Gerakl24 – ваш партнер по реставрации и ремонту домов в Красноярске и окрестностях.
minoxidil price – buy dutas pills order finasteride 5mg without prescription
wow mythic raid carry [url=https://kreativwerkstatt-esens.de/]wow mythic raid carry[/url] .
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
Где заказать диплом по нужной специальности?
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании.
https://pankasyno22.com/
[u][b] Рады оказаться полезными![u][b]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Приобрести диплом университета.
Наш сервис предлагает приобрести диплом в высоком качестве, который невозможно отличить от оригинала без участия специалиста высокой квалификации с дорогостоящим оборудованием.
[b]Где заказать диплом по необходимой специальности?[/b]
http://www.figarohair.ru/conf/posting.php?mode=post&f=11&sid=f3b0831a3c1f3a2e12fdc6cb5dd3f212
[b]Успешной учебы![/b]
Gerakl24: Квалифицированная Смена Основания, Венцов, Полов и Передвижение Домов
Фирма Gerakl24 специализируется на выполнении всесторонних услуг по смене основания, венцов, полов и переносу домов в населённом пункте Красноярском регионе и за его пределами. Наша группа профессиональных экспертов обещает превосходное качество выполнения различных типов восстановительных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасного типа, кирпичные постройки или бетонные строения.
Преимущества услуг Геракл24
Навыки и знания:
Все работы выполняются только профессиональными экспертами, с многолетним большой практику в направлении строительства и ремонта зданий. Наши сотрудники знают свое дело и реализуют проекты с безупречной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предоставляем все виды работ по реставрации и ремонту домов:
Реставрация фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что позволяет продлить срок службы вашего дома и избежать проблем, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Смена венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые чаще всего подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Установка новых покрытий: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает визуальное восприятие и функциональность помещения.
Перемещение зданий: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на новые локации, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и предотвращает лишние расходы на строительство нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Дома из дерева: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, защита от гниения и вредителей.
Дома с каркасом: укрепление каркасов и замена поврежденных элементов.
Дома из кирпича: ремонт кирпичных стен и укрепление стен.
Бетонные дома: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы используем только высококачественные материалы и новейшее оборудование, что гарантирует долгий срок службы и надежность всех выполненных работ. Каждый наш проект подвергаются строгому контролю качества на каждом этапе выполнения.
Персонализированный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем подходящие решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Мы стараемся, чтобы итог нашей работы соответствовал вашим запросам и желаниям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по восстановлению и ремонту вашего здания. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в установленные сроки и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы готовы предоставить консультацию и ответить на ваши вопросы. Звоните нам, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами.
https://gerakl24.ru/поднять-дом-красноярск/
[url=https://lasixor.com/]lasix 80 mg[/url]
buy generic leflunomide 10mg – buy generic alfacalcidol over the counter cartidin canada
NetTruyen ZZZ: Nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến dành cho mọi lứa tuổi
NetTruyen ZZZ là nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến miễn phí với số lượng truyện tranh lên đến hơn 30.000 đầu truyện với chất lượng hình ảnh và tốc độ tải cao. Nền tảng được xây dựng với mục tiêu mang đến cho người đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tranh tốt nhất, đồng thời tạo dựng cộng đồng yêu thích truyện tranh sôi động và gắn kết với hơn 11 triệu thành viên (tính đến tháng 7 năm 2024).
NetTruyen ZZZ – Kho tàng truyện tranh phong phú:
NetTruyen ZZZ sở hữu kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ với hơn 30.000 đầu truyện thuộc nhiều thể loại khác nhau như:
● Manga: Những bộ truyện tranh Nhật Bản với nhiều thể loại phong phú như lãng mạn, hành động, hài hước, v.v.
● NetTruyen anime: Hàng ngàn bộ truyện tranh anime chọn lọc được đăng tải đều đặn trên NetTruyen ZZZ được chuyển thể từ phim hoạt hình Nhật Bản với nội dung hấp dẫn và hình ảnh đẹp mắt.
● Truyện manga: Hơn 10.000 bộ truyện tranh manga hay nhất được đăng tải đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhua: Hơn 5000 bộ truyện tranh manhua được đăng tải trọn bộ đầy đủ trên NetTruyen ZZZ.
● Truyện manhwa: Những bộ truyện tranh manhwa Hàn Quốc được yêu thích nhất có đầy đủ trên NetTruyen với cốt truyện lôi cuốn và hình ảnh bắt mắt cùng với nét vẽ độc đáo và nội dung đa dạng.
● Truyện ngôn tình: Những câu chuyện tình yêu lãng mạn, ngọt ngào và đầy cảm xúc.
● Truyện trinh thám: Những câu chuyện ly kỳ, bí ẩn và đầy lôi cuốn xoay quanh các vụ án và quá trình phá án.
● Truyện tranh xuyên không: Những câu chuyện về những nhân vật du hành thời gian hoặc không gian đến một thế giới khác.
NetTruyen ZZZ không ngừng cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường, đảm bảo mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mới mẻ và thú vị nhất.
Chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao tại NetTruyenZZZ:
Với hơn 30 triệu lượt truy cập hằng tháng, NetTruyen ZZZ luôn chú trọng vào chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung của các bộ truyện tranh được đăng tải trên nền tảng. Hình ảnh được hiển thị sắc nét, rõ ràng, không bị mờ hay vỡ ảnh. Nội dung được dịch thuật chính xác, dễ hiểu và giữ nguyên vẹn ý nghĩa của tác phẩm gốc.
NetTruyen ZZZ hợp tác với đội ngũ dịch giả và biên tập viên chuyên nghiệp, giàu kinh nghiệm để đảm bảo chất lượng bản dịch tốt nhất. Nền tảng cũng có hệ thống kiểm duyệt nội dung nghiêm ngặt để đảm bảo nội dung lành mạnh, phù hợp với mọi lứa tuổi.
Trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi:
NetTruyen ZZZ được thiết kế với giao diện đẹp mắt, thân thiện với người dùng và dễ dàng sử dụng. Bạn đọc có thể đọc truyện tranh trên mọi thiết bị, từ máy tính, điện thoại thông minh đến máy tính bảng. Nền tảng cũng cung cấp nhiều tính năng tiện lợi như:
● Tìm kiếm truyện tranh theo tên, tác giả, thể loại, v.v.
● Lưu truyện tranh yêu thích để đọc sau.
● Đánh dấu trang để dễ dàng quay lại vị trí đang đọc.
● Chia sẻ truyện tranh với bạn bè.
● Tham gia bình luận và thảo luận về truyện tranh.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn nỗ lực để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
Định hướng phát triển:
NetTruyen ZZZ cam kết không ngừng phát triển và hoàn thiện để trở thành nền tảng đọc truyện tranh trực tuyến tốt nhất dành cho bạn đọc tại Việt Nam. Nền tảng sẽ tiếp tục cập nhật những bộ truyện tranh mới nhất và hot nhất trên thị trường thế giới, đồng thời nâng cao chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung. NetTruyen ZZZ cũng sẽ phát triển thêm nhiều tính năng mới để mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ luôn đặt lợi ích của bạn đọc lên hàng đầu. Nền tảng cam kết:
● Cung cấp kho tàng truyện tranh khổng lồ và đa dạng với chất lượng hình ảnh và nội dung đỉnh cao.
● Mang đến cho bạn đọc những trải nghiệm đọc truyện mượt mà, tiện lợi và thú vị nhất.
● Luôn lắng nghe ý kiến phản hồi của bạn đọc và không ngừng cải thiện để mang đến dịch vụ tốt nhất.
NetTruyen ZZZ hy vọng sẽ trở thành người bạn đồng hành không thể thiếu của bạn trong hành trình khám phá thế giới truyện tranh đầy màu sắc.
Kết nối với NetTruyen ZZZ ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng những trải nghiệm đọc truyện tuyệt vời.
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Купить диплом ВУЗа
[b]Наша компания предлагает[/b] выгодно и быстро приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен мокрыми печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Наш документ способен пройти любые проверки, даже с использованием специально предназначенного оборудования. Решите свои задачи быстро с нашим сервисом.
[b]Где приобрести диплом специалиста?[/b]
https://bery-optom.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=11289
[u][b] Будем рады вам помочь![u][b].
Геракл24: Опытная Замена Фундамента, Венцов, Полов и Передвижение Зданий
Фирма Геракл24 профессионально занимается на предоставлении полных сервисов по смене основания, венцов, настилов и передвижению строений в городе Красноярск и за его пределами. Наш коллектив опытных специалистов гарантирует отличное качество исполнения всех типов реставрационных работ, будь то из дерева, каркасного типа, кирпичные постройки или из бетона дома.
Преимущества работы с Геракл24
Квалификация и стаж:
Весь процесс выполняются исключительно опытными мастерами, имеющими многолетний стаж в направлении создания и ремонта зданий. Наши специалисты знают свое дело и осуществляют проекты с безупречной точностью и вниманием к деталям.
Полный спектр услуг:
Мы осуществляем полный спектр услуг по ремонту и реконструкции строений:
Замена фундамента: замена и укрепление фундамента, что гарантирует долговечность вашего строения и избежать проблем, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Смена венцов: реставрация нижних венцов из дерева, которые обычно подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: установка новых полов, что существенно улучшает внешний облик и функциональность помещения.
Перемещение зданий: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на новые локации, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избегает дополнительных затрат на создание нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Древесные строения: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, защита от разрушения и вредителей.
Каркасные дома: укрепление каркасов и замена поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные строения: восстановление кирпичной кладки и усиление стен.
Бетонные строения: реставрация и усиление бетонных элементов, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и прочность:
Мы применяем только высококачественные материалы и современное оборудование, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех работ. Все проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Личный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем персонализированные решения, учитывающие все особенности и пожелания. Мы стараемся, чтобы итог нашей работы полностью удовлетворял вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в сроки, оговоренные заранее и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Обратившись в Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и ответить на ваши вопросы. Звоните нам, чтобы обсудить детали и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы сохраним и улучшим ваш дом, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Gerakl24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами.
https://gerakl24.ru/поднять-дом-красноярск/
[url=https://мрикрнц.рф/wp-content/telm/Promokod_1hBet_Na_Segodnya_Besplatno_2021.html]1xbet промокод[/url]
[url=https://doctor-loder.ru/wp-content/inc/1xbet_promokod_na_segodnya___bonus_pri_registracii.html]промокод для 1xbet[/url]
[u][b] Привет, друзья![/b][/u]
Для некоторых людей, заказать [b]диплом[/b] университета – это острая потребность, уникальный шанс получить достойную работу. Но для кого-то – это понятное желание не терять время на учебу в институте. Что бы ни толкнуло вас на такой шаг, мы готовы помочь. Быстро, качественно и недорого изготовим диплом любого года выпуска на государственных бланках с реальными подписями и печатями.
[b]Мы предлагаем[/b] выгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями должностных лиц. Наш документ пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании профессиональных приборов. Достигайте цели максимально быстро с нашим сервисом.
[b]Где приобрести диплом по нужной специальности?[/b]
http://ukrevent.ru/kupit-diplom-rf-v-moskve-legko-i-dostupno/
[b]Удачи![/b]
купить диплом в кургане [url=https://diplomyx.com/]diplomyx.com[/url] .
аттестат за 9 класс купить [url=https://diplomasx.com/]аттестат за 9 класс купить[/url] .
WELCOME TO PUGACHEV LUXURY CAR RENTALS EXCLUSIVE MOTORING LUXURY & EXOTIC RENTALS
Dive into the ultimate driving experience with Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, your premier destination for luxury and exotic car rentals in Los Angeles. Whether you’re looking to impress at a corporate event, add a splash of glamour to your weekend, or simply enjoy the thrill of driving some of the world’s most sought-after vehicles, we’ve got you covered.
https://pugachev.la/
Our extensive fleet includes the pinnacle of automotive excellence from renowned brands such as Lamborghini, Rolls-Royce, Bentley, Ferrari, McLaren, and more. Indulge in the elegance of a Rolls-Royce Ghost, starting at $1,150 per day, or experience the exhilarating performance of a Lamborghini Huracan EVO, available from $875 per day. With options ranging from the powerful Ferrari GTB Red at $1,100 per day to the opulent Bentley Continental GT at $950 per day, our collection is meticulously curated to cater to the most discerning tastes and preferences.
Navigating the vibrant streets of Los Angeles or cruising along the scenic coastlines has never been more accessible or more stylish. At Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, we make it easy and efficient for you to rent the luxury car of your dreams with straightforward daily and weekly rental options—like the versatile Mercedes-Benz AMG G63, which can be yours for $790 daily or $4,424 weekly.
Embrace the luxury, power, and finesse of our elite vehicles and elevate your next Los Angeles visit into a truly memorable journey. Whether you’re seeking an exotic sports car for that extra special thrill, a luxury sedan for sophisticated travel, or a sumptuous SUV for family comfort and safety, our fleet promises the perfect match for every occasion and desire.
OUR COLLECTION OF LUXURY CARS FOR DISCERNING DRIVERS
Elegant Sedans for Business Executives
At Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals, we understand the importance of a strong first impression. Our fleet of luxury sedans is designed to cater to business executives who demand sophistication and functionality. Each vehicle, such as the Rolls-Royce Ghost Anthracite, available at $1,100 per day, offers a sublime mix of comfort and prestige, ensuring you arrive at your business engagements in unparalleled style. For a slightly different but equally impressive experience, consider the Bentley Flying Spur at $1,000 daily, which combines classic elegance with cutting-edge technology.
exotic car rental los angeles
[url=https://pugachev.la/lamborghini-rental/]lamborghini rental in los angeles[/url]
Sumptuous SUVs for Family and Leisure
Our selection of high-end SUVs blends luxury with practicality, making them perfect for family trips or stylish outings with friends. The Bentley Bentayga, starting from $700 per day, offers spaciousness and state-of-the-art amenities that ensure comfort without compromise. For those seeking a bolder statement, the Rolls-Royce Cullinan Black Badge provides an imposing presence and unrivaled luxury for $1,300 daily, ensuring every journey is an event in itself.
Prestige Convertibles for Scenic Drives
Los Angeles is renowned for its beautiful landscapes and stunning coastlines, best enjoyed in one of our prestige convertibles. Feel the exhilarating freedom of the open road in a Ferrari Portofino Spyder, available for $850 daily. Its breathtaking performance and sleek design are perfect for scenic drives along the Pacific Coast Highway. Alternatively, the BMW M4 Competition Cabrio, at $390 per day, offers a more accessible but equally thrilling option for cruising under the Californian sun.
Our fleet at Pugachev Luxury Car Rentals is meticulously maintained and regularly updated to ensure that each car looks and performs like new. This commitment to quality and excellence reflects our dedication to providing only the best for our clients, who return time and again for the reliability and prestige our services offer. Each model in our fleet is more than just a vehicle; it’s a part of an exclusive lifestyle made accessible to our discerning clientele. Whether you are looking to impress at a corporate event or simply indulge in the pleasure of driving a luxury car, our collection is guaranteed to enhance your experience in Los Angeles.
luxury car rental los angeles
[url=https://pugachev.la/]exotic car rental los angeles[/url]
[b]Здравствуйте[/b]!
Хочу поделиться своим опытом по заказу аттестата ПТУ. Думал, что это невозможно, и начал искать информацию в интернете по теме: купить диплом сантехника, купить диплом в челябинске, купить диплом в оренбурге, купить диплом университета, купить диплом в чапаевске. Постепенно углубляясь в тему, нашел отличный ресурс здесь: http://mastrerkon.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=27394 и остался очень доволен!
Теперь у меня есть диплом сварщика о среднем специальном образовании, и я обеспечен на всю жизнь!
Хорошей учебы!
Tributes flood in for BBC sport commentator whose wife and daughters were killed in suspected crossbow attack
[url=https://telltrue.net/eto-lohotron/chernyj-spisok-lohotronov-utl-coinexfom-uno-club-bitlans-profitcrypto/?ysclid=ly1sujvcbx993980390]гей порно видео[/url]
Figures from across the United Kingdom have offered their condolences to a BBC sport commentator, after his wife and two daughters were killed by an alleged crossbow attacker, in deaths that again drew attention to the epidemic of violence against women.
Carol Hunt, 61, wife of BBC horse racing commentator, John Hunt, and their daughters, Hannah Hunt, 28, and Louise Hunt, 25, died from injuries sustained in an attack in Bushey, just northwest of London, on Tuesday, according to police and Britain’s public broadcaster.
A 26-year-old suspect wanted in connection with the killings, and named as Kyle Clifford, was found by British police in Enfield, north London, on Wednesday, following a sprawling manhunt. There were no previous reports to the force over Clifford, who is in serious condition in hospital and is yet to speak with officers, Hertfordshire Police said in a statement.
A crossbow was recovered as part of the investigation, which police believe was used in a “targeted incident.”
Epidemic of violence against women
The killings of the three women rocked Britain, where mass murders are infrequent but violence against women and girls has been officially labeled as a national threat.
A woman is killed by a man every three days in the UK and one in four women will experience domestic violence in her lifetime, the United Nations’ special rapporteur on violence against women and girls, Reem Alsalem, said earlier this year.
Charities and human rights organizations have subsequently reiterated urgent demands to tackle femicide in the UK.
Tributes flood in for BBC sport commentator whose wife and daughters were killed in suspected crossbow attack
[url=https://forum-kpfu.ru/100624/novosti-vasilenko-roman-poslednie-novosti/]жесткое порно видео[/url]
Figures from across the United Kingdom have offered their condolences to a BBC sport commentator, after his wife and two daughters were killed by an alleged crossbow attacker, in deaths that again drew attention to the epidemic of violence against women.
Carol Hunt, 61, wife of BBC horse racing commentator, John Hunt, and their daughters, Hannah Hunt, 28, and Louise Hunt, 25, died from injuries sustained in an attack in Bushey, just northwest of London, on Tuesday, according to police and Britain’s public broadcaster.
A 26-year-old suspect wanted in connection with the killings, and named as Kyle Clifford, was found by British police in Enfield, north London, on Wednesday, following a sprawling manhunt. There were no previous reports to the force over Clifford, who is in serious condition in hospital and is yet to speak with officers, Hertfordshire Police said in a statement.
A crossbow was recovered as part of the investigation, which police believe was used in a “targeted incident.”
Epidemic of violence against women
The killings of the three women rocked Britain, where mass murders are infrequent but violence against women and girls has been officially labeled as a national threat.
A woman is killed by a man every three days in the UK and one in four women will experience domestic violence in her lifetime, the United Nations’ special rapporteur on violence against women and girls, Reem Alsalem, said earlier this year.
Charities and human rights organizations have subsequently reiterated urgent demands to tackle femicide in the UK.
Воины-пайщики оказались без защиты в тылу
Пайщики «Бест Вей» — участники СВО готовы защищать свой кооператив
[url=https://svpressa.ru/society/article/421904]ЖК Бествей[/url]
Многие пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» и те, в чьих интересах приобретаются квартиры в кооперативе, — участники СВО. И они сами, и их родственники возмущены событиями, происходящими вокруг кооператива. Ведь защищая интересы страны на фронте, в тылу они не защищены от того, что не могут приобрести недвижимость из-за того, что счета кооператива с почти 4 млрд рублей уже более двух лет находятся под арестом — притом, что сумма ущерба по уголовному делу, рассматриваемому Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга, согласно обвинительному заключению, составляет 282 млн рублей.
«Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию»
Наталья Пригаро, мать пайщика кооператива — участника СВО из Нефтеюганска Даниила Пригаро:
— Сын расплатился за однокомнатную квартиру, приобретенную с помощью кооператива, еще два года назад, подал пакет документов на оформление квартиры в собственность в Росреестр в начале сентября 2022 года — и все это время не может зарегистрировать собственность на нее из-за того, что в Росреестре она значится как арестованная. В конце сентября 2022 года он был мобилизован. Сын брал кредит, чтобы расплатиться за квартиру с кооперативом. Планировал продать эту квартиру и взять квартиру побольше в ипотеку. Однако неоднократно накладывался арест на недвижимость кооператива, несмотря на то что сейчас ареста нет — последний арест, накладывавшийся осенью 2023 года, 19 февраля истек, ходатайства о новом аресте дважды отклонены судом, по Росреестру арест с квартиры до сих пор не снят. В результате кредит приходится платить, квартира в собственность до сих пор не оформлена.
У сына нет никакой физической и финансовой возможности выяснять отношения с Росреестром — в административном или судебном порядке, он приезжает в отпуска на неделю-полторы, ему не до сутяжничества. Я нахожусь в Анапе, приобрела квартиру с помощью кооператива — сын не имеет возможности сделать на меня генеральную доверенность, а я не могу из Анапы приехать в Нефтеюганск и решать вопросы в Росреестре — кроме поезда, сейчас, сами понимаете, ничего не ходит (конец цитаты).
«На безобразие, которое происходит с кооперативом, мы пишем жалобы во все инстанции, — говорит она. — Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию».
«Надежда, что все разрешится, остается — не может же все быть коррумпировано»
Елена Бойко — пайщик кооператива из Новосибирска и мать солдата, воющего в СВО, для которого она собиралась приобрести одну из двух квартир в кооперативе. «Я стала пайщиком кооператива в 2021 году. В январе 2021 года подала заявление на покупку двух квартир с помощью кооператива по накопительной программе. У меня двое детей — сын и дочь, им нужно жилье. В 2020 году взяли в ипотеку загородный дом — причем оформили на сына как единственного, кому ее могли одобрить, а в 2021 году он ушел в армию как призывник, а потом подписал контракт. Его относительно недавно отправили „за ленточку“. Думали, что поживем в ипотечном доме, и тут как раз подойдет очередь приобретать квартиры с помощью кооператива. Мы останемся жить в частном доме, а дети въедут в кооперативные квартиры».
«Ипотека — это разорительно, — подчеркивает Елена, — мы взяли 2,5 млн, а за 30 лет отдадим 6 млн. Когда появился кооператив, для нас это была возможность предоставить каждому из детей жилье: за 10 лет или раньше они расплатятся с кооперативом, причем с минимальной по сравнению ипотекой переплатой, и у них будет собственное жилье. Из-за репрессий в отношении кооператива мы можем быть этой возможности лишены».
«Я всем сердцем переживаю за ситуацию с кооперативом, заявление о выходе из кооператива пока не пишу — надеюсь, что его деятельность „разморозится“, — говорит Елена. — Обращаемся во все инстанции, в прокуратуру — приходят отписки. Смысл происходящего я понимаю хорошо — когда-то занималась кредитным потребительским кооперативом: нас тогда закрыл Центральный банк. Нашел формальный повод. Но настоящая причина была в том, что мы мешали банкам обирать клиентов. Но надежда на то, что все разрешится, остается — не может же быть все коррумпировано».
«Больше всего в нашей ситуации возмущает то, что наши воины стоят на стороне государства на фронте, а здесь, в тылу, их интересы нарушаются государственными структурами. Такого быть не должно!»
«Для многих кооператив — единственная возможность приобрести квартиру»
Лариса Зискинд — пайщица «Бест Вей», переехавшая с помощью кооператива с семьей — с дочерью, зятем и маленьким внуком - с Дальнего Востока в Белгородскую область. Ее зять, живущий в кооперативной квартире, находится на фронте СВО. «С помощью кооператива я приобрела квартиру в двухэтажном доме в селе Пушкарное Белгородской области — мы с дочерью переехали сюда. Мы уже два года расплачиваемся за него с кооперативом. Не до конца сделали ремонт, кухни фактически нет: моем посуду в ванной. Финансовых средств не хватает, так как зять уже год на СВО, пока ни разу не был в отпуске, и перевести деньги с его карты в ВТБ сейчас непросто, потому что карта — в расположении, до ближайшего банка ехать далеко, а он сам — на линии фронта. Мы фактически живем с выплат на ребенка, на мне кредиты — у меня полпенсии уходит на их оплату. Квартира по Росреестру находится под арестом, хотя арест по квартирам кооператива арест истек — а я боюсь ехать в Белгород, чтобы решать по ней вопрос. Я с ребенком на улицу гулять не выхожу в нынешней военной обстановке — сирены воздушной тревоги постоянные. Побыстрее бы наши войска создали санитарную зону в Харьковской области!»
По поводу покупки квартиры Лариса сообщает, что «ипотека точно никак не светила. Кооператив — это 14 тыс. в месяц и всего лишь 10 лет. В кооперативе даже студентка может приобрести квартиру, почти не переплачивая. При покупке через банк придется заплатить еще как минимум за одну квартиру».
«Среди пайщиков кооператива очень много пенсионеров, социально незащищенных людей, это была их единственная возможность приобрести квартиру, — говорит Лариса. — Из-за репрессий против кооператива мы можем лишиться единственного жилья. Мы куда только не писали в защиту кооператива. Но, видимо, слишком большой куш. Кооперативу не дают даже платить налоги. Надеемся, что отношение к кооперативу в результате справедливого разбирательства изменится в лучшую сторону».
«Мы очень устали. Но боремся»
Людмила Гарина — пайщица кооператива из Саратова, зять которой, проживающий вместе с ней в кооперативной квартире, участвует в СВО. «Я проживаю в кооперативной квартире почти три года вместе с дочерью и внуком, вносим ежемесячные платежи через госуслуги».
«Возможности взять ипотеку не было, — говорит Людмила. — Фактически у нас один работающий человек — дочь, зять мобилизован, внук — студент, внучке — четыре года. Мы с мужем пенсионеры».
«У нас с кооперативом проблем не было никаких, — говорит она, — но сейчас уверенности в завтрашнем дне нет. Пишем во все возможные инстанции, в том числе в Администрацию президента, ходили на прием к Володину. Пока ничего не помогает. Вся надежда на то, что суд разберется».
«Хотелось, чтобы вопрос о возобновлении работы кооператива быстрее решился, — говорит она, — тогда стало бы проще. Когда кооператив заработает, будет совершенно иная ситуация. Мы очень устали. Но боремся».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить»
Алла Яровая — пайщик кооператива из Пятигорска и представитель пайщицы Людмилы Дворцовой, сын которой, Игорь Дворцов, находился на СВО, а теперь служит внутри страны. «Людмила приобрела с помощью кооператива в Пятигорске квартиру для своего сына. Вступила в кооператив она в 2017 году, сначала находилась в накопительной программе — накапливала на первоначальный паевый взнос, накопила, потом стояла в очереди на приобретение жилье, приобрела с помощью кооператива однокомнатную квартиру за 1450 тыс. рублей. Потом приобрела квартиру и постепенно полностью за нее расплатилась. Работала для этого на двух работах, в том числе санитаркой в инфекционном отделении».
Но оформить квартиру в собственность не удалось, так как она оказалась под арестом, поясняет Алла. И хотя арест 19 февраля истек и больше не накладывался, суд первой инстанции в Пятигорске этот арест подтвердил. «По вопросу получения права собственности и снятия ареста мы обратились в Пятигорский городской суд, где судья очень предвзято отнесся к решению вопроса и мы получили отказ, — говорит Алла, — Хотя аналогичный вопрос рассматривался в Минераловодском суде и там судья вынесла положительное решение и в настоящий момент пайщик получил право собственности на свою квартиру. Предстоит рассмотрение в апелляционной инстанции — несмотря на то, что рассматривать нечего: ареста на недвижимость кооператива сейчас нет. А на квартиру Людмилы Дворцовой — почему-то есть».
«Кооператив — единственная возможность для людей со средним достатком получить жилье, — говорит Алла, — Нерешенный вопрос — налоги. Мы вынуждены платить налоги с юридических лиц, но мы же физические лица. К депутатам — с нас берут налог как с юрлица. Почему мы должны оплачивать — мы же физлица? Во многих регионах это сделано. Надеемся добиться того, чтобы это было сделано по всей стране».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить, — подчеркивает пайщица. — Это наши деньги, и мы за них боремся. Обязательно отстоим наш кооператив!»
«Активно участвую в защите кооператива»
У пайщицы кооператива, жительницы из Ленинградской области Татьяны Власенко старший сын находится на СВО с сентября 2022 года. «Три месяца проходил обучение, а потом оказался „за ленточкой“, — говорит Татьяна. — Мы должны были в конце лета 2022 года купить квартиру с помощью кооператива — квартиру планировали большую. Но работа кооператива оказалась заблокирована, и кооператив не может ничего купить уже более двух лет, так как и его счета, и его деятельность заблокированы. Деньги пайщиков, собранные для приобретения квартир, при этом обесцениваются».
«Я активно участвую в защите нашего кооператива, — говорит Татьяна. — Езжу на все суды в Санкт-Петербурге, хотя живу в деревне — ехать два с половиной, а то и три часа, мне 64 года, а путь неблизкий. И сын в этом поддерживает меня».
«Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются»
У пайщицы из Хабаровска Натальи Ромашко на СВО было два племянника — один, к сожалению, погиб. Планировалась покупка большой квартиры в Хабаровске, Наталья состояла в накопительной программе. «Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются, — говорит Наталья. — Я участвую в защите кооператива, пишу письма в прокуратуру, в высшие государственные инстанции, потому что нарушаются наши права, нас лишают возможности приобрести квартиру вне ипотечной системы. Пока приходят одни отписки, но борьбу мы продолжаем!»
«Ситуация — как на СВО»
Пайщица Светлана Иванова из Новосибирска, волонтер СВО, планировала приобрести с помощью кооператива две квартиры — для себя и для сына, который воюет на СВО добровольцем. «До этого я продала квартиру и сейчас вообще без собственного жилья, — говорит она. — Вступила в кооператив по накопительной программе, рассматривали для приобретения квартиры Крым и Новосибирск. В СВО участвую как волонтер — не остаюсь в стороне, когда Родине нужна помощь».
«От ситуации с кооперативом очень многие люди пострадали, — говорит Светлана. — Ситуация — как на СВО. И еще больше пострадают, если реализуется плохой сценарий. Хочется надеяться на то, что все образуется, правда восторжествует. Заявление о выходе из кооператива и возврате паевых средств я не подавала. Готова продолжить участие в нем, готова приобрести недвижимость с его помощью: это самый лучший вариант покупки квартиры».
«Сдаваться в планах нет»
Пайщица Марина Янковская родом из Хабаровска, она переехала в Новороссийск, ее супруг погиб на СВО. «У нас уже подходила очередь на покупку квартиры в Новороссийске для нашей семьи, мы должны были подбирать объект, — рассказывает она. — Но два года назад все остановилось. Хотели приобрести двухкомнатную квартиру в Новороссийске. Деньги лежат на арестованных счетах кооператива — а недвижимость за это время подорожала. Надеемся хоть что-то приобрести после того, как счета разблокируют».
«Мы всячески поддерживаем кооператив, — говорит Марина. — Записывали видео, что мы не обманутые, а вполне довольные пайщики, объясняли, что это никакая не пирамида, а организация, созданная в помощь людям. Ждем, когда снимут эти аресты. Сдаваться в планах нет».
Воины-пайщики оказались без защиты в тылу
Пайщики «Бест Вей» — участники СВО готовы защищать свой кооператив
[url=https://svpressa.ru/society/article/421904]Уголовное дело Бест Вей[/url]
Многие пайщики кооператива «Бест Вей» и те, в чьих интересах приобретаются квартиры в кооперативе, — участники СВО. И они сами, и их родственники возмущены событиями, происходящими вокруг кооператива. Ведь защищая интересы страны на фронте, в тылу они не защищены от того, что не могут приобрести недвижимость из-за того, что счета кооператива с почти 4 млрд рублей уже более двух лет находятся под арестом — притом, что сумма ущерба по уголовному делу, рассматриваемому Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга, согласно обвинительному заключению, составляет 282 млн рублей.
«Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию»
Наталья Пригаро, мать пайщика кооператива — участника СВО из Нефтеюганска Даниила Пригаро:
— Сын расплатился за однокомнатную квартиру, приобретенную с помощью кооператива, еще два года назад, подал пакет документов на оформление квартиры в собственность в Росреестр в начале сентября 2022 года — и все это время не может зарегистрировать собственность на нее из-за того, что в Росреестре она значится как арестованная. В конце сентября 2022 года он был мобилизован. Сын брал кредит, чтобы расплатиться за квартиру с кооперативом. Планировал продать эту квартиру и взять квартиру побольше в ипотеку. Однако неоднократно накладывался арест на недвижимость кооператива, несмотря на то что сейчас ареста нет — последний арест, накладывавшийся осенью 2023 года, 19 февраля истек, ходатайства о новом аресте дважды отклонены судом, по Росреестру арест с квартиры до сих пор не снят. В результате кредит приходится платить, квартира в собственность до сих пор не оформлена.
У сына нет никакой физической и финансовой возможности выяснять отношения с Росреестром — в административном или судебном порядке, он приезжает в отпуска на неделю-полторы, ему не до сутяжничества. Я нахожусь в Анапе, приобрела квартиру с помощью кооператива — сын не имеет возможности сделать на меня генеральную доверенность, а я не могу из Анапы приехать в Нефтеюганск и решать вопросы в Росреестре — кроме поезда, сейчас, сами понимаете, ничего не ходит (конец цитаты).
«На безобразие, которое происходит с кооперативом, мы пишем жалобы во все инстанции, — говорит она. — Надеемся, новое руководство Министерства обороны поможет урегулировать ситуацию».
«Надежда, что все разрешится, остается — не может же все быть коррумпировано»
Елена Бойко — пайщик кооператива из Новосибирска и мать солдата, воющего в СВО, для которого она собиралась приобрести одну из двух квартир в кооперативе. «Я стала пайщиком кооператива в 2021 году. В январе 2021 года подала заявление на покупку двух квартир с помощью кооператива по накопительной программе. У меня двое детей — сын и дочь, им нужно жилье. В 2020 году взяли в ипотеку загородный дом — причем оформили на сына как единственного, кому ее могли одобрить, а в 2021 году он ушел в армию как призывник, а потом подписал контракт. Его относительно недавно отправили „за ленточку“. Думали, что поживем в ипотечном доме, и тут как раз подойдет очередь приобретать квартиры с помощью кооператива. Мы останемся жить в частном доме, а дети въедут в кооперативные квартиры».
«Ипотека — это разорительно, — подчеркивает Елена, — мы взяли 2,5 млн, а за 30 лет отдадим 6 млн. Когда появился кооператив, для нас это была возможность предоставить каждому из детей жилье: за 10 лет или раньше они расплатятся с кооперативом, причем с минимальной по сравнению ипотекой переплатой, и у них будет собственное жилье. Из-за репрессий в отношении кооператива мы можем быть этой возможности лишены».
«Я всем сердцем переживаю за ситуацию с кооперативом, заявление о выходе из кооператива пока не пишу — надеюсь, что его деятельность „разморозится“, — говорит Елена. — Обращаемся во все инстанции, в прокуратуру — приходят отписки. Смысл происходящего я понимаю хорошо — когда-то занималась кредитным потребительским кооперативом: нас тогда закрыл Центральный банк. Нашел формальный повод. Но настоящая причина была в том, что мы мешали банкам обирать клиентов. Но надежда на то, что все разрешится, остается — не может же быть все коррумпировано».
«Больше всего в нашей ситуации возмущает то, что наши воины стоят на стороне государства на фронте, а здесь, в тылу, их интересы нарушаются государственными структурами. Такого быть не должно!»
«Для многих кооператив — единственная возможность приобрести квартиру»
Лариса Зискинд — пайщица «Бест Вей», переехавшая с помощью кооператива с семьей — с дочерью, зятем и маленьким внуком - с Дальнего Востока в Белгородскую область. Ее зять, живущий в кооперативной квартире, находится на фронте СВО. «С помощью кооператива я приобрела квартиру в двухэтажном доме в селе Пушкарное Белгородской области — мы с дочерью переехали сюда. Мы уже два года расплачиваемся за него с кооперативом. Не до конца сделали ремонт, кухни фактически нет: моем посуду в ванной. Финансовых средств не хватает, так как зять уже год на СВО, пока ни разу не был в отпуске, и перевести деньги с его карты в ВТБ сейчас непросто, потому что карта — в расположении, до ближайшего банка ехать далеко, а он сам — на линии фронта. Мы фактически живем с выплат на ребенка, на мне кредиты — у меня полпенсии уходит на их оплату. Квартира по Росреестру находится под арестом, хотя арест по квартирам кооператива арест истек — а я боюсь ехать в Белгород, чтобы решать по ней вопрос. Я с ребенком на улицу гулять не выхожу в нынешней военной обстановке — сирены воздушной тревоги постоянные. Побыстрее бы наши войска создали санитарную зону в Харьковской области!»
По поводу покупки квартиры Лариса сообщает, что «ипотека точно никак не светила. Кооператив — это 14 тыс. в месяц и всего лишь 10 лет. В кооперативе даже студентка может приобрести квартиру, почти не переплачивая. При покупке через банк придется заплатить еще как минимум за одну квартиру».
«Среди пайщиков кооператива очень много пенсионеров, социально незащищенных людей, это была их единственная возможность приобрести квартиру, — говорит Лариса. — Из-за репрессий против кооператива мы можем лишиться единственного жилья. Мы куда только не писали в защиту кооператива. Но, видимо, слишком большой куш. Кооперативу не дают даже платить налоги. Надеемся, что отношение к кооперативу в результате справедливого разбирательства изменится в лучшую сторону».
«Мы очень устали. Но боремся»
Людмила Гарина — пайщица кооператива из Саратова, зять которой, проживающий вместе с ней в кооперативной квартире, участвует в СВО. «Я проживаю в кооперативной квартире почти три года вместе с дочерью и внуком, вносим ежемесячные платежи через госуслуги».
«Возможности взять ипотеку не было, — говорит Людмила. — Фактически у нас один работающий человек — дочь, зять мобилизован, внук — студент, внучке — четыре года. Мы с мужем пенсионеры».
«У нас с кооперативом проблем не было никаких, — говорит она, — но сейчас уверенности в завтрашнем дне нет. Пишем во все возможные инстанции, в том числе в Администрацию президента, ходили на прием к Володину. Пока ничего не помогает. Вся надежда на то, что суд разберется».
«Хотелось, чтобы вопрос о возобновлении работы кооператива быстрее решился, — говорит она, — тогда стало бы проще. Когда кооператив заработает, будет совершенно иная ситуация. Мы очень устали. Но боремся».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить»
Алла Яровая — пайщик кооператива из Пятигорска и представитель пайщицы Людмилы Дворцовой, сын которой, Игорь Дворцов, находился на СВО, а теперь служит внутри страны. «Людмила приобрела с помощью кооператива в Пятигорске квартиру для своего сына. Вступила в кооператив она в 2017 году, сначала находилась в накопительной программе — накапливала на первоначальный паевый взнос, накопила, потом стояла в очереди на приобретение жилье, приобрела с помощью кооператива однокомнатную квартиру за 1450 тыс. рублей. Потом приобрела квартиру и постепенно полностью за нее расплатилась. Работала для этого на двух работах, в том числе санитаркой в инфекционном отделении».
Но оформить квартиру в собственность не удалось, так как она оказалась под арестом, поясняет Алла. И хотя арест 19 февраля истек и больше не накладывался, суд первой инстанции в Пятигорске этот арест подтвердил. «По вопросу получения права собственности и снятия ареста мы обратились в Пятигорский городской суд, где судья очень предвзято отнесся к решению вопроса и мы получили отказ, — говорит Алла, — Хотя аналогичный вопрос рассматривался в Минераловодском суде и там судья вынесла положительное решение и в настоящий момент пайщик получил право собственности на свою квартиру. Предстоит рассмотрение в апелляционной инстанции — несмотря на то, что рассматривать нечего: ареста на недвижимость кооператива сейчас нет. А на квартиру Людмилы Дворцовой — почему-то есть».
«Кооператив — единственная возможность для людей со средним достатком получить жилье, — говорит Алла, — Нерешенный вопрос — налоги. Мы вынуждены платить налоги с юридических лиц, но мы же физические лица. К депутатам — с нас берут налог как с юрлица. Почему мы должны оплачивать — мы же физлица? Во многих регионах это сделано. Надеемся добиться того, чтобы это было сделано по всей стране».
«20 тыс. пайщиков кооператива не так просто остановить, — подчеркивает пайщица. — Это наши деньги, и мы за них боремся. Обязательно отстоим наш кооператив!»
«Активно участвую в защите кооператива»
У пайщицы кооператива, жительницы из Ленинградской области Татьяны Власенко старший сын находится на СВО с сентября 2022 года. «Три месяца проходил обучение, а потом оказался „за ленточкой“, — говорит Татьяна. — Мы должны были в конце лета 2022 года купить квартиру с помощью кооператива — квартиру планировали большую. Но работа кооператива оказалась заблокирована, и кооператив не может ничего купить уже более двух лет, так как и его счета, и его деятельность заблокированы. Деньги пайщиков, собранные для приобретения квартир, при этом обесцениваются».
«Я активно участвую в защите нашего кооператива, — говорит Татьяна. — Езжу на все суды в Санкт-Петербурге, хотя живу в деревне — ехать два с половиной, а то и три часа, мне 64 года, а путь неблизкий. И сын в этом поддерживает меня».
«Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются»
У пайщицы из Хабаровска Натальи Ромашко на СВО было два племянника — один, к сожалению, погиб. Планировалась покупка большой квартиры в Хабаровске, Наталья состояла в накопительной программе. «Вот уже более двух лет работа кооператива заблокирована, деньги обесцениваются, — говорит Наталья. — Я участвую в защите кооператива, пишу письма в прокуратуру, в высшие государственные инстанции, потому что нарушаются наши права, нас лишают возможности приобрести квартиру вне ипотечной системы. Пока приходят одни отписки, но борьбу мы продолжаем!»
«Ситуация — как на СВО»
Пайщица Светлана Иванова из Новосибирска, волонтер СВО, планировала приобрести с помощью кооператива две квартиры — для себя и для сына, который воюет на СВО добровольцем. «До этого я продала квартиру и сейчас вообще без собственного жилья, — говорит она. — Вступила в кооператив по накопительной программе, рассматривали для приобретения квартиры Крым и Новосибирск. В СВО участвую как волонтер — не остаюсь в стороне, когда Родине нужна помощь».
«От ситуации с кооперативом очень многие люди пострадали, — говорит Светлана. — Ситуация — как на СВО. И еще больше пострадают, если реализуется плохой сценарий. Хочется надеяться на то, что все образуется, правда восторжествует. Заявление о выходе из кооператива и возврате паевых средств я не подавала. Готова продолжить участие в нем, готова приобрести недвижимость с его помощью: это самый лучший вариант покупки квартиры».
«Сдаваться в планах нет»
Пайщица Марина Янковская родом из Хабаровска, она переехала в Новороссийск, ее супруг погиб на СВО. «У нас уже подходила очередь на покупку квартиры в Новороссийске для нашей семьи, мы должны были подбирать объект, — рассказывает она. — Но два года назад все остановилось. Хотели приобрести двухкомнатную квартиру в Новороссийске. Деньги лежат на арестованных счетах кооператива — а недвижимость за это время подорожала. Надеемся хоть что-то приобрести после того, как счета разблокируют».
«Мы всячески поддерживаем кооператив, — говорит Марина. — Записывали видео, что мы не обманутые, а вполне довольные пайщики, объясняли, что это никакая не пирамида, а организация, созданная в помощь людям. Ждем, когда снимут эти аресты. Сдаваться в планах нет».
русское порно онлайн худые [url=www.russkie-hudyshki.ru]русское порно онлайн худые[/url] .
купить диплом нового образца [url=http://diploms-x.com]купить диплом нового образца[/url] .
buy generic calan 120mg – buy diltiazem generic generic tenoretic
[url=http://asynthroid.online/]synthroid 20 mcg[/url]
Купить диплом о среднем полном образовании, в чем подвох и как избежать обмана?
[url=http://diploms-x.com/kupit-diplom-nizhnij-novgorod/]diploms-x.com/kupit-diplom-nizhnij-novgorod[/url]
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for! “Being rich is having money being wealthy is having time.” by Margaret Bonnano.
диплом купит заказать [url=https://ast-diploms.com/]ast-diploms.com[/url] .
[url=http://vermox.company/]mebendazole price[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://webmontag.de/doku.php?id=landsdiplomy/]webmontag.de/doku.php?id=landsdiplomy[/url]
[url=http://marandola.net/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=diplomandoci/]marandola.net/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=diplomandoci[/url]
[url=http://мипак.рф/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ezisimip/]мипак.рф/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ezisimip[/url]
[url=http://fire-team.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=35356#post35356/]fire-team.ru/forum/showthread.php?p=35356#post35356[/url]
[url=http://carforum.info/topic/2712-купить-диплом-цена-x31f//]carforum.info/topic/2712-купить-диплом-цена-x31f/[/url]
Компания Септик-Нара-[url=https://septik-nara.ru/]купить септик для частного дома[/url]
занимается продажей, установкой и обслуживанием септиков в Наро-Фоминске Наро-Фоминском районе. Основное направление деятельности нашей компании именно установка под ключ септиков любых видов и размеров. С момента основания нашей компании, мы произвели монтаж более 1000 септиков по Московской и Калужской области. Благодаря этому у нас огромный опыт работы с любыми станциями, представленными в нашем регионе!
Если Вы решили купить септик для дома или дачи, мы с радостью поможем Вам с выбором модели, доставим и установим септик на вашем участке в кратчайшие сроки.
Мы занимаемся продажей септиков таких марок: Топас Юнилос Астра Евролос Тверь Аквалос Дочиста Фекалов Волгарь Удача. Мы работаем напрямую с производителями септиков, поэтому Вы можете быть уверены, что не переплачиваете ни копейки. Вся продукция в нашей компании имеет соответствующие сертификаты и лицензии. Время выезда на осмотр, установки или привоза оборудования согласовывается с клиентами и выполняется в срок. Мы заботимся о своей репутации, поэтому выполняем работу надежно и быстро.
Если Вы не знаете, какой септик больше всего Вам подходит, мы предоставим консультацию и выезд специалиста на Ваш участок абсолютно бесплатно!
Благодаря приобретению качественных септиков в нашей компании, каждый клиент получает большое количество преимуществ:
» компактные размеры и небольшой вес устройства;
» доступная стоимость очистной установки;
» быстрый и простой монтаж;
» невысокая стоимость эксплуатации;
» отсутствие неприятных запахов;
» высокая производительность;
» длительный срок эксплуатации;
» высокая степень очистки;
» практически полностью автономный режим работы.
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
[b]Купить документ[/b] о получении высшего образования можно в нашей компании в столице.
[url=http://ast-diploms.com/kupit-diplom-kazan /]ast-diploms.com/kupit-diplom-kazan [/url]
[b]Приобрести диплом университета.[/b]
[url=http://make-coin.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-garantiya-kachestva-i-podlinnosti/]make-coin.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-garantiya-kachestva-i-podlinnosti[/url]
[url=http://linux.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=483/]linux.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=483[/url]
[url=http://mymink.5bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=8884#p454993/]mymink.5bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=8884#p454993[/url]
[url=http://bn.tobase.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=3346/]bn.tobase.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=3346[/url]
[url=http://noo.by/wiki/Ћегальна€_ѕокупка_?ипломов_ќнлайн/]noo.by/wiki/Ћегальна€_ѕокупка_?ипломов_ќнлайн[/url]
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
Мы можем предложить дипломы.
[url=http://blogs.rufox.ru/~worksale/48191.htm/]blogs.rufox.ru/~worksale/48191.htm[/url]
[url=http://ukrevents.ru/nastoyashhie-diplomyi-bez-lishnih-voprosov//]ukrevents.ru/nastoyashhie-diplomyi-bez-lishnih-voprosov/[/url]
[url=http://wegug.in/blogs/940/ упить-?иплом-Ѕыстро-и-Ћегально/]wegug.in/blogs/940/ упить-?иплом-Ѕыстро-и-Ћегально[/url]
[url=http://g95334gq.beget.tech/2024/07/06/nastoyaschie-diplomy-bystro-legalno-nadezhno.html/]g95334gq.beget.tech/2024/07/06/nastoyaschie-diplomy-bystro-legalno-nadezhno.html[/url]
[url=http://igenplan.ru/forum/user/94133//]igenplan.ru/forum/user/94133/[/url]
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
[b]Мы можем предложить документы ВУЗов[/b], расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Можно заказать диплом от любого заведения, за любой год, указав подходящую специальность и оценки за все дисциплины. Дипломы и аттестаты печатаются на бумаге самого высокого качества. Это дает возможность делать настоящие дипломы, не отличимые от оригинала. Документы заверяются всеми обязательными печатями и штампами.
[url=http://balacixynu.trexgame.net/bystro-pokupaem-attestat-v-lucsem-internet-magazine-russian-diplom/]balacixynu.trexgame.net/bystro-pokupaem-attestat-v-lucsem-internet-magazine-russian-diplom[/url]
новые порно видео [url=http://www.apteka-porno.ru]http://www.apteka-porno.ru[/url] .
A fairly new player in the Russian darknet arena, [url=https://bs-gl-darknet.com]blacksprut[/url] Blacksprut has quickly gained attention for its interesting features and growing popularity. While some aspects raise questions, it has the potential to become a prominent figure in the darknet scene.
Features:
Blacksprut https://bs-gl-darknet.com offers an “Instant Transactions” feature, inspired by the success of similar systems on other platforms like Hydra. Couriers hide goods within the city and provide buyers with coordinates, adding an adventurous element to the purchasing process.
порно коллекции бесплатно [url=http://porn-library.ru]http://porn-library.ru[/url] .
[b]Привет, друзья![/b]
Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании
[url=http://landik-diploms-srednee.ru/kupit-diplom-volgograd В ]landik-diploms-srednee.ru/kupit-diplom-volgograd В [/url]
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
[b]Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании.[/b]
[url=http://dev.spooo.ru/post/article/217862/]dev.spooo.ru/post/article/217862[/url]
[u][b] Привет, друзья![/b][/u]
Купить документ университета можно в нашей компании в Москве. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов Российской Федерации. Вы сможете получить диплом по любой специальности, включая документы старого образца. Даем гарантию, что при проверке документов работодателями, никаких подозрений не возникнет.
[url=http://deviva.ru/viewtopic.php?id=9081#p62009/]deviva.ru/viewtopic.php?id=9081#p62009[/url]
[url=http://www.hip-hop.ru/forum/id298234-worksale/]www.hip-hop.ru/forum/id298234-worksale[/url]
[url=http://rusere.ru/communication/forum/messages/forum11/message3684/2971-chetyre-glavnykh-gruppy-onlayn_magazinov_-chto-realizuyut-dokumenty?result=new/]rusere.ru/communication/forum/messages/forum11/message3684/2971-chetyre-glavnykh-gruppy-onlayn_magazinov_-chto-realizuyut-dokumenty?result=new[/url]
[url=http://meco.eeconme.com/read-blog/3642/]meco.eeconme.com/read-blog/3642[/url]
[url=http://mamuli.club/forum/topic/24661//]mamuli.club/forum/topic/24661/[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа
[b]Наша компания предлагает[/b] выгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на оригинальном бланке и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти любые проверки, даже с применением специальных приборов. Достигайте своих целей быстро с нашим сервисом.
[b]Где приобрести диплом по необходимой специальности?[/b]
[url=http://socialnetwork.cloudyzx.com/read-blog/12267/]socialnetwork.cloudyzx.com/read-blog/12267[/url]
[url=http://vip.7bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3028#p7121/]vip.7bb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=3028#p7121[/url]
[url=http://followgrown.com/read-blog/2702/]followgrown.com/read-blog/2702[/url]
[url=http://russianecuador.com/forum/member.php?u=13207/]russianecuador.com/forum/member.php?u=13207[/url]
[url=http://lighttur.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-podlinnost-i-nadezhnost/]lighttur.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-podlinnost-i-nadezhnost[/url]
[u][b] Привет, друзья![/b][/u]
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании
[b]Наша компания предлагает[/b] выгодно приобрести диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями. Наш диплом способен пройти любые проверки, даже с использованием профессиональных приборов. Достигайте своих целей быстро и просто с нашими дипломами.
[b]Где купить диплом специалиста?[/b]
[url=http://www.hristianka.ru/forum/r/prev_loaded/1//]www.hristianka.ru/forum/r/prev_loaded/1/[/url]
[url=http://blogs.rufox.ru/~worksale/47159.htm/]blogs.rufox.ru/~worksale/47159.htm[/url]
[url=http://rodina.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=502/]rodina.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=502[/url]
[url=http://macadamlab.ru/wiki/index.php?title=пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ/]macadamlab.ru/wiki/index.php?title=пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ_пїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅпїЅ[/url]
[url=http://molbiol.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=1179953/]molbiol.ru/forums/index.php?showtopic=1179953[/url]
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
Мы можем предложить документы техникумов
[url=http://paintball-keller-lev.de/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=100162&sid=fd2e6dd5990fe8ead88d351d7e143aa6/]paintball-keller-lev.de/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=100162&sid=fd2e6dd5990fe8ead88d351d7e143aa6[/url]
[url=http://hebergementweb.org/forums/discussions-generales.15/create-thread/]hebergementweb.org/forums/discussions-generales.15/create-thread[/url]
[url=http://worksale777.blogspot.com/2024/07/blog-post_53.html/]worksale777.blogspot.com/2024/07/blog-post_53.html[/url]
[url=http://mf.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=664/]mf.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=664[/url]
[url=http://newspromworld.ru/byistroe-poluchenie-diplomov-vseh-spetsialnostey/]newspromworld.ru/byistroe-poluchenie-diplomov-vseh-spetsialnostey[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
[b]Полезные советы по безопасной покупке диплома о высшем образовании [/b]
[url=http://sgs-penza.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=yvoriz/]sgs-penza.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=yvoriz[/url]
[u][b] Рады помочь![u][b].
порно тренер пристает [url=https://pornotrenery.ru]порно тренер пристает[/url] .
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Приобрести документ университета можно в нашем сервисе. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов России.
[url=http://cookownfood.blogspot.com/2012/11/cold-bean-thread-noodles-with-spinach.html/]cookownfood.blogspot.com/2012/11/cold-bean-thread-noodles-with-spinach.html[/url]
[url=http://torgteh-rzn.ru/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=11559/]torgteh-rzn.ru/index.php?option=com_k2&view=itemlist&task=user&id=11559[/url]
[url=http://ka4nem.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=isivyfati/]ka4nem.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=isivyfati[/url]
[url=http://bumblebeeco.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=axesavu/]bumblebeeco.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=axesavu[/url]
[url=http://ds2.edu.sbor.net/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=icodozan/]ds2.edu.sbor.net/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=icodozan[/url]
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
Мы предлагаем [b]дипломы[/b] любой профессии по приятным ценам. [b]Стоимость[/b] зависит от выбранной специальности, года получения и образовательного учреждения. Стараемся поддерживать для клиентов адекватную политику тарифов. Для нас важно, чтобы дипломы были доступными для подавляющей массы граждан.
[url=http://bookmarkick.com/story17122005/купить-диплом-в-Челябинске/]bookmarkick.com/story17122005/купить-диплом-в-Челябинске[/url]
смотреть порно гимнастки онлайн [url=sexygimnastky.ru]sexygimnastky.ru[/url] .
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
[b]Заказать диплом ВУЗа.[/b]
[url=http://mysmart.ru/index.php?/gallery/image/655-%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%8B%D1%80%D0%B5-%D0%BA%D0%BB%D1%8E%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%B2%D1%8B%D1%85-%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%BF%D1%8B-%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B7%D1%83%D1%8E%D1%89%D0%B8%D1%85-%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%8B//]mysmart.ru/index.php?/gallery/image/655-%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%8B%D1%80%D0%B5-%D0%BA%D0%BB%D1%8E%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%B2%D1%8B%D1%85-%D0%B3%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%BF%D1%8B-%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BD-%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2-%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B7%D1%83%D1%8E%D1%89%D0%B8%D1%85-%D0%B4%D0%BE%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%8B/[/url]
Discover your perfect stay with WorldHotels-in.com, your ultimate destination for finding the best hotels worldwide! Our user-friendly platform offers a vast selection of accommodations to suit every traveler’s needs and budget. Whether you’re planning a luxurious getaway or a budget-friendly adventure, we’ve got you covered with our extensive database of hotels across the globe. Our intuitive search features allow you to filter results based on location, amenities, price range, and guest ratings, ensuring you find the ideal match for your trip. We pride ourselves on providing up-to-date information and competitive prices, often beating other booking sites. Our detailed hotel descriptions, high-quality photos, and authentic guest reviews give you a comprehensive view of each property before you book. Plus, our secure booking system and excellent customer support team ensure a smooth and worry-free experience from start to finish. Don’t waste time jumping between multiple websites – http://www.WorldHotels-in.com brings the world’s best hotels to your fingertips in one convenient place. Start planning your next unforgettable journey today and experience the difference with WorldHotels-in.com!
конференционный зал [url=http://oborudovanie-dlja-konferenc-zalov.ru/]http://oborudovanie-dlja-konferenc-zalov.ru/[/url] .
капперы рейтинг [url=http://rejting-kapperov12.ru/]http://rejting-kapperov12.ru/[/url] .
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов
[url=http://pnevmokzn.80lvl.ru/search.php?search_id=egosearch/]pnevmokzn.80lvl.ru/search.php?search_id=egosearch[/url]
[url=http://worksale777.blogspot.com/2024/07/blog-post_20.html/]worksale777.blogspot.com/2024/07/blog-post_20.html[/url]
[url=http://energypowerworld.co.uk/read-blog/9187/]energypowerworld.co.uk/read-blog/9187[/url]
[url=http://shuvalduet.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=609/]shuvalduet.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=609[/url]
[url=http://niecewicz.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=34&t=894/]niecewicz.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=34&t=894[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
[b]Купить диплом о высшем образовании.[/b]
[url=http://forum.rucarp.ru/album.php?albumid=128&attachmentid=35737&commentid=1961/]forum.rucarp.ru/album.php?albumid=128&attachmentid=35737&commentid=1961[/url]
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании
[url=http://mongolsmc.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=412/]mongolsmc.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=412[/url]
[url=http://newsbizlife.ru/poluchite-diplom-za-korotkiy-srok/]newsbizlife.ru/poluchite-diplom-za-korotkiy-srok[/url]
[url=http://ic-info.ru/forum/user/166644//]ic-info.ru/forum/user/166644/[/url]
[url=http://digdroid.com/forums/entry/signin/]digdroid.com/forums/entry/signin[/url]
[url=http://seriallove.bbok.ru/viewtopic.php?id=7232#p123278/]seriallove.bbok.ru/viewtopic.php?id=7232#p123278[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Диплом бакалавра
[url=http://roseninsel.kz/forum/topic/add/forum7//]roseninsel.kz/forum/topic/add/forum7/[/url]
[url=http://bideew.com/create-blog//]bideew.com/create-blog/[/url]
[url=http://academy4elements.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=963#p2097/]academy4elements.mybb.ru/viewtopic.php?id=963#p2097[/url]
[url=http://neoncity.gtaserv.ru/viewtopic.php?f=38&t=1997/]neoncity.gtaserv.ru/viewtopic.php?f=38&t=1997[/url]
[url=http://awaytravel.ru/content/Быстрое-получение-диплома-без-бюрократии/]awaytravel.ru/content/Быстрое-получение-диплома-без-бюрократии[/url]
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
[b]Мы готовы предложить дипломы[/b] любых профессий по приятным тарифам.
[url=http://stlvolleyball.com/купить-главу-диплома//]stlvolleyball.com/купить-главу-диплома/[/url]
звуковое оборудование для конференц зала [url=https://oborudovanie-konferenc-zalov.ru/]https://oborudovanie-konferenc-zalov.ru/[/url] .
переговорные комнаты в москве [url=www.oborudovanie-dlja-peregovornoj-komnaty.ru/]www.oborudovanie-dlja-peregovornoj-komnaty.ru/[/url] .
The Unseen Story About Solana Founder Toly’s Accomplishment
Post Two Servings of Java and a Beer
Yakovenko, the innovator behind Solana, commenced his path with an ordinary habit – two cups of coffee and a beer. Little did he realize, those moments would set the cogs of fate. Nowadays, Solana is as a significant competitor in the crypto sphere, featuring a market value of billions.
Ethereum ETF First Sales
The new Ethereum ETF recently was introduced with a staggering trading volume. This landmark occasion experienced various spot Ethereum ETFs from various issuers begin trading on U.S. exchanges, injecting extraordinary activity into the usually calm ETF trading environment.
SEC Approved Ethereum ETF
The SEC has given the nod to the spot Ethereum ETF for being listed. As a digital asset with smart contracts, Ethereum is expected to deeply influence on the cryptocurrency industry following this approval.
Trump’s Crypto Maneuver
As the election approaches, Trump frames himself as the “President of Crypto,” frequently displaying his advocacy for the crypto sector to garner votes. His method is different from Biden’s approach, seeking to capture the focus of the blockchain community.
Elon Musk’s Influence
Musk, a famous figure in the crypto community and a proponent of Trump, caused a stir again, propelling a meme coin connected to his actions. His participation continues to shape market trends.
Recent Binance News
Binance’s subsidiary, BAM, is now allowed to invest customer funds into U.S. Treasury instruments. In addition, Binance observed its 7th anniversary, showcasing its path and obtaining numerous regulatory approvals. In the meantime, the company also announced plans to take off several significant crypto trading pairs, impacting various market participants.
AI and Market Trends
A top stock analyst from Goldman Sachs recently observed that AI won’t spark an economic transformation
ключ от комнаты совещаний [url=http://oborudovanie-peregovornyh-komnat.ru]ключ от комнаты совещаний[/url] .
[b]Купить диплом любого ВУЗа.[/b]
[url=http://nowoczesna.phorum.pl/posting.php?mode=newtopic&f=2&sid=cdf439e7c78e8b1e73f44022db29ae31/]nowoczesna.phorum.pl/posting.php?mode=newtopic&f=2&sid=cdf439e7c78e8b1e73f44022db29ae31[/url]
[url=http://ledsoft.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=message&FID=3&TID=13929&TITLE_SEO=13929-nastoyashchie-diplomy-bystro-i-legalno&MID=14733&result=new#message14733/]ledsoft.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=message&FID=3&TID=13929&TITLE_SEO=13929-nastoyashchie-diplomy-bystro-i-legalno&MID=14733&result=new#message14733[/url]
[url=http://forummichiganrp.moibb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=21&t=431/]forummichiganrp.moibb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=21&t=431[/url]
[url=http://teplichnaya.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=638231/]teplichnaya.ru/viewtopic.php?f=18&t=638231[/url]
[url=http://bn.tobase.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=3360/]bn.tobase.ru/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=3360[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Заказать документ университета
[url=http://ast-diplomy24.ru/kupit-diplom-magistra]ast-diplomy24.ru/kupit-diplom-magistra[/url]
МОСКВА, 7 мая — РИА Новости. Правительство России, возглавляемое Михаилом Мишустиным, уйдет в отставку во вторник.
Сразу после инаугурации президента Владимира Путина нынешний кабинет министров сложит полномочия перед вступившим в должность главой государства.
[url=https://xrumer.us/]Прогон по комментария[/url]
Кооператив для военных
Как пайщики — участники СВО относятся к событиям вокруг «Бест Вей»
[url=https://svpressa.ru/society/article/423652]Приморский районный суд Бест Вей[/url]
Потребительский кооператив «Бест Вей» оказался затронут уголовным делом, касающимся в основном иностранной инвесткомпании «Гермес», которое сейчас рассматривается Приморским районным судом Санкт-Петербурга. Более двух лет более 3,5 млрд рублей на счетах кооператива почти непрерывно арестованы по ходатайству сначала ГСУ ГУ МВД по Санкт-Петербургу, а затем Прокуратуры Санкт-Петербурга: пайщики не имеют возможности ни приобрести недвижимость, ни вернуть средства.
По данным совета потребительского кооператива «Бест Вей», в числе его пайщиков, страдающих от блокировки средств, тысячи военнослужащих, в том числе сотни участников СВО, часть из которых успела приобрести квартиру, часть собирает или собрала первоначальный взнос, а часть — планировала вступить в кооператив. «СП» пообщалась с некоторыми из них и их родственниками, чтобы узнать отношение к «Бест Вей» и событиям вокруг кооператива.
«К кооперативу отношение очень хорошее»
Александр Голдман на СВО с мая 2022 года как доброволец, три ранения. Пришел на СВО рядовым, сейчас — начальник штаба батальона. Был пайщиком кооператива, сейчас пайщик — его мама.
«С помощью кооператива в 2019 году приобретена двухкомнатная квартира во Владивостоке, в которой проживает мама, — рассказывает он. — Расплачиваемся за нее, в ближайшие месяцы намерены погасить задолженность перед кооперативом и оформить квартиру в собственность. К кооперативу отношение очень хорошее, полностью его поддерживаю — он дает возможность без больших переплат приобрести недвижимость. К действиям в отношении кооператива отношусь отрицательно, так как „Бест Вей“ — единственная возможность приобрести жилье в рассрочку».
«Происходящее вокруг кооператива вызывает шок»
Гвардии рядовой Глушков Иван Васильевич — пайщик кооператива из Челябинской области. Танкист, мобилизованный, проходил службу в 15-й отдельной гвардейской мотострелковой Александрийской бригаде 2-й гвардейской общевойсковой армии ЦВО. Погиб 11 октября 2023 года.
Рассказывает его вдова Татьяна Неручева:
«Мы внесли первоначальный паевый взнос и во второй половине 2021 года встали в очередь на приобретение квартиры в Челябинске, когда начались события вокруг кооператива — была заблокирована его возможность приобретать недвижимость и заблокированы его счета. Наша очередь должна была подойти примерно через год. Мы заявили для приобретения небольшую квартиру, но планировали при покупке увеличить ее стоимость до 3 млн и купить двухкомнатную квартиру — с увеличением первоначального паевого взноса: уставом кооператива это позволяется, а затем переехать из Коркино в Челябинск. Сейчас 3 млн хватит только на небольшую квартиру-студию метров 25, то есть мы понесли материальный ущерб из-за блокирования деятельности кооператива, так как лишены были возможности приобрести квартиру, на которую собрали первоначальный паевый взнос. Работа кооператива заблокирована, счета арестованы уже более двух лет. В наследование пая я только вступаю, так как муж очень долго считался пропавшим без вести — долго шла экспертиза, и свидетельство о смерти мы получили только 18 июня этого года».
Татьяна — юрист: «Как у юриста у меня происходящее вокруг кооператива вызывает шок, и любой непредвзятый юрист вам скажет то же самое». «Кооператив, — подчеркивает она, — абсолютно прозрачен, он полностью соответствует законодательству о кооперации — что и подтверждалось многократно государственными органами и судами. Если бы мы с мужем не были уверены, что все прозрачно и законно, мы бы не вкладывали в него деньги. Мы не подавали заявление о выходе из кооператива. Я, несмотря ни на что, жду счастливого завершения рукотворного кризиса вокруг кооператива. Для меня это еще и память о муже — он продал долю в квартире, которая ему принадлежала, чтобы вложиться в кооператив. Кроме того, мне хочется понять — до какого маразма может дойти ситуация у нас в государстве в плане незаконных действий в отношении организации, которая по тем или иным причинам не понравилась каким-то чиновникам?».
«Рассчитываю, что ситуация закончится благополучно»
Сергей Логинов, рядовой, мобилизованный, представлен к награде «Честь и доблесть».
«Пять лет назад я стал пайщиком кооператива, участвовал в накопительной программе, планировал прибрести однокомнатную квартиру в Самарской области. Уже нужно было подбирать объект недвижимости и вставать в очередь на покупку, как работа кооператива была заблокирована по инициативе правоохранительных органов, и это продолжается уже более двух лет. По-прежнему надеюсь получить квартиру и рассчитываю, что ситуация закончится благополучно. Поддерживаю кооператив».
«В кооперативе минимум переплат — несопоставимо с ипотекой»
Егор Ивков, офицер флота, дирижер военного оркестра, пайщик кооператива с 2019 года.
«Я нахожусь в накопительной программе — планировал покупку квартиры в Санкт-Петербурге. До постановки в очередь на покупку дело не дошло, но сумма внесена серьезная — и на два года все зависло. Есть друзья-военнослужащие, которые также являются пайщиками и тоже накапливали деньги на первоначальный паевый взнос — они, как и я, не могут ни продолжать накапливать, ни получить деньги обратно, потому что счета арестованы. Отношение наше к ситуации, создавшейся вокруг кооператива, крайне негативное».
«Кооператив поддерживаю, — говорит пайщик. — Моя сестра живет в квартире, приобретенной с помощью „Бест Вей“ — у нее многодетная семья, сейчас кооперативная квартира переходит в ее собственность. Минимум переплат — несопоставимо с ипотекой. Надеюсь, что ситуация с арестом счетов разрешится в ближайшее время».
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
Купить документ ВУЗа вы сможете в нашей компании в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации. Вы сможете получить необходимый диплом по любым специальностям, любого года выпуска, в том числе документы СССР. Гарантируем, что при проверке документа работодателями, каких-либо подозрений не появится.
[url=http://www.zooclub.com.ua/o-proekte/]www.zooclub.com.ua/o-proekte[/url]
[url=http://vnuci.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=530/]vnuci.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=530[/url]
[url=http://iqtorg.ru/forum/messages/forum2/topic626/message700/?result=new#message700/]iqtorg.ru/forum/messages/forum2/topic626/message700/?result=new#message700[/url]
[url=http://censornet.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-kachestvo-i-legalnost//]censornet.ru/ofitsialnyie-diplomyi-kachestvo-i-legalnost/[/url]
[url=http://gracebook.app/blogs/1192/Что-потребуется-для-создания-качественного-документа/]gracebook.app/blogs/1192/Что-потребуется-для-создания-качественного-документа[/url]
[url=http://amoxicillinir.online/]amoxicillin 875 mg cost[/url]
It’s impressive that you are getting ideas from this article as well as from our argument made here.
видеостена оборудование [url=https://videosteny-dlja-sozdanija-jekranov.ru/]видеостена оборудование[/url] .
Оборудование актовых залов [url=https://www.oborudovanie-aktovogo-zala.ru]https://www.oborudovanie-aktovogo-zala.ru[/url] .
[u][b] Привет, друзья![/b][/u]
[b]Купить документ[/b] института вы можете у нас.
[url=http://diploms-x24.ru/kupit-diplom-voronezh/]diploms-x24.ru/kupit-diplom-voronezh[/url]
[b]Успехов в учебе![/b]
Как купить диплом о высшем образовании с минимальными рисками
[url=http://eoovbook.com/read-blog/10884/]eoovbook.com/read-blog/10884[/url]
[url=http://politictoday.ru/vash-shans-na-uspeh-diplom-bez-truda/]politictoday.ru/vash-shans-na-uspeh-diplom-bez-truda[/url]
[url=http://z3xoqn2f3.bloggin-ads.com/51705104/Читайте-наш-обзор-в-случае-если-требуется-заказать-диплом-в-сети/]z3xoqn2f3.bloggin-ads.com/51705104/Читайте-наш-обзор-в-случае-если-требуется-заказать-диплом-в-сети[/url]
[url=http://bawabetalquds.com/wall/blogs/364/Прочитайте-наш-обзор-если-требуется-купить-диплом-в-сети-интернет/]bawabetalquds.com/wall/blogs/364/Прочитайте-наш-обзор-если-требуется-купить-диплом-в-сети-интернет[/url]
[url=http://face2face.club/blogs/21/Изучите-наш-материал-в-случае-если-надо-заказать-диплом-в/]face2face.club/blogs/21/Изучите-наш-материал-в-случае-если-надо-заказать-диплом-в[/url]
оборудование для актовых залов [url=https://www.oborudovanija-dlja-aktovyh-zalov.ru]оборудование для актовых залов[/url] .
[u][b] Привет![/b][/u]
[b]Узнайте, как приобрести диплом о высшем образовании без рисков[/b]
[url=http://gamesfortop.ru/vash-diplom-garantiya-kachestva-i-podlinnosti/]gamesfortop.ru/vash-diplom-garantiya-kachestva-i-podlinnosti[/url]
[u][b] Здравствуйте![/b][/u]
[b]Заказать диплом ВУЗа.[/b]
[url=http://stroimarket-komi.ru/club/user/54/blog/38295//]stroimarket-komi.ru/club/user/54/blog/38295/[/url]
[u][b] Добрый день![/b][/u]
[b]Мы готовы предложить дипломы[/b] любых профессий по доступным ценам.
[url=http://sportraketka.ru/vash-diplom-kachestvo-i-autentichnost/]sportraketka.ru/vash-diplom-kachestvo-i-autentichnost[/url]