The EOS Model® provides a useful foundation for businesses, but it falls short in addressing key aspects of creating an growth. By incorporating additional elements from the Gravitas 7 Attributes of Agile Growth® model, businesses can create a more comprehensive system that promotes growth while maintaining smooth operations. Focusing on Leadership, Strategy, Execution, Customer, Profit, Systems, and Talent, the 7 Attributes of Agile Growth® offer a more encompassing approach to achieving success.

The “Flaw of Averages” Causes Havoc for Businesses
Introduction: The Importance of Accurate Data Analysis
The “Flaw of Averages” is a term popularized by Sam Savage, referring to the misleading nature of averages in business decision-making. Averages often misstate the true situation within a company, leading to misallocation of resources and, ultimately, reduced profitability. In this blog post, we will discuss how the flaw of averages can impact businesses, using hypothetical examples to illustrate the consequences and offer suggestions for more accurate data analysis.
- The Flaw of Averages in Product Analysis
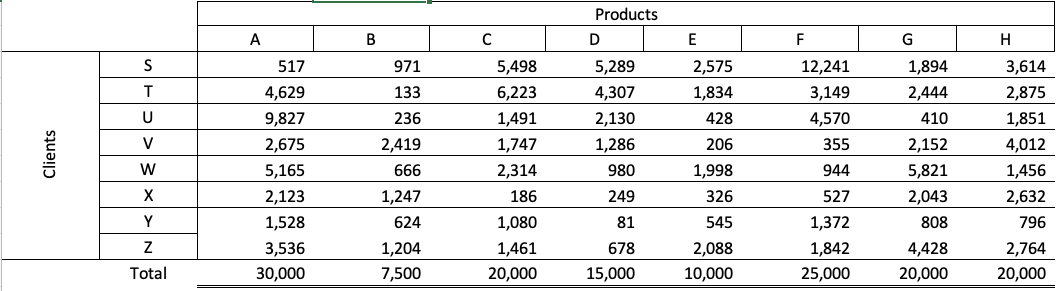
Consider a hypothetical business, ABC Inc., which sells a variety of products with different units sold, unit prices, and gross profits per unit.
| Product |
Units Sold |
Price/Unit |
Gross Profit/Unit |
| A |
30,000 |
$ 100.00 |
$ 12.50 |
| B |
7,500 |
$ 90.00 |
$ 75.00 |
| C |
20,000 |
$ 80.00 |
$ 37.50 |
| D |
15,000 |
$ 70.00 |
$ 45.00 |
| E |
10,000 |
$ 60.00 |
$ 25.00 |
| F |
25,000 |
$ 50.00 |
$ 12.50 |
| G |
20,000 |
$ 40.00 |
$ 20.00 |
| H |
20,000 |
$ 30.00 |
$ 25.00 |
When examining the product portfolio, looking beyond the total revenue and gross profit margin is essential. Focusing solely on averages can lead to misconceptions about the importance of certain products to the company’s profitability.
a. Rethinking Product Prioritization
For example, if ABC Inc. were to stop selling its largest revenue-generating product, its gross profit margin would increase substantially. By looking at average margins, the full impact of this product on the business is not apparent. A more detailed analysis may reveal additional costs associated with the production of this product, such as factory space, warehouse storage, staff, and shipping costs.
b. Bundling and Pricing Strategies
With a better understanding of the true profitability of each product, ABC Inc. can explore more effective pricing strategies, such as increasing the price of lower-margin products or bundling them with more profitable ones.
- The Flaw of Averages in Customer Analysis
Examining customers’ revenue and gross profit contributions can also reveal valuable insights. By ranking customers according to their gross margin contributions, businesses can identify the most profitable clients and those that may be dragging down overall profitability.
Now, if we examine the purchase and gross profits of each customer, we get:
| Customer |
Revenue |
Gross Profit |
|
S |
1,899,890 |
869,085 |
|
T |
1,725,700 |
700,983 |
|
U |
1,598,430 |
414,600 |
|
V |
951,540 |
491,173 |
|
W |
1,273,760 |
459,958 |
|
X |
563,430 |
259,640 |
|
Y |
458,530 |
176,880 |
|
Z |
1,103,720 |
452,683 |
|
Total |
9,575,000 |
3,825,000 |
Sorting that into the order of gross margin, we can see the following:
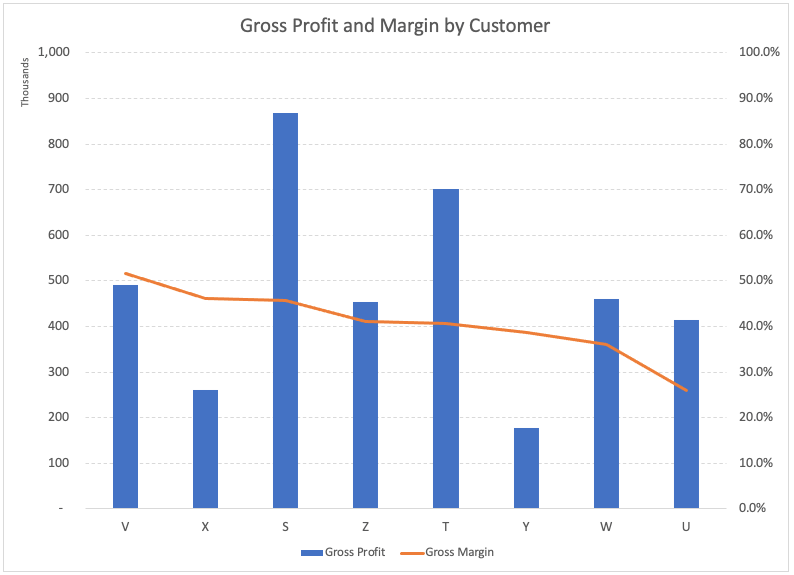
a. Identifying High-Value Customers
For example, if ABC Inc. were to lose its most profitable customer, its gross margin would decrease significantly. By contrast, losing a less profitable customer would lead to an increase in the overall gross margin. Understanding the value of each customer allows the company to focus its resources on retaining and attracting high-value clients.
b. Analyzing Customer Purchase Patterns
In addition to evaluating each customer’s profitability, examining their purchase patterns is essential. Businesses can better target their marketing and sales efforts by identifying clients with higher-margin purchase combinations.
- Improving Business Performance Through Better Data Analysis
To overcome the flaw of averages and make more informed decisions, businesses should:
a. Regularly analyze product and customer data. Examine each product’s and customer’s profitability to identify improvement areas and make better resource allocation decisions.
b. Focus on profitability, not just revenue. While revenue is essential, focusing solely on it can lead to misconceptions about the true value of products and customers. Prioritize profitability to drive sustainable growth.
c. Use data to inform pricing and bundling strategies. Identify opportunities to increase the price of lower-margin products or bundle them with more profitable ones to improve overall profitability.
d. Monitor and adapt to changes in the market. Regularly review product and customer data to stay up-to-date with market trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Conclusion: The Power of Proper Data Analysis
The flaw of averages can lead businesses to make misguided decisions based on misleading data. By delving deeper into product and customer data, businesses can better understand their true profitability, allocate resources more effectively, and ultimately drive sustainable growth. Don’t let the flaw of averages hold your business back – embrace the power of accurate data analysis to improve your decision-making and achieve success.
Recommended Reading:
-
The Flaw of Averages: Why We Underestimate Risk in the Face of Uncertainty, by Sam Savage This book provides an in-depth look at the limitations of averages and how they can lead to misguided decisions in various fields, including business, finance, and engineering. It also offers practical techniques for better understanding and managing risk through probabilistic thinking.
-
Why Can’t You Just Give Me The Number?: An Executive’s Guide to Using Probabilistic Thinking to Manage Risk and to Make Better Decisions, by Patrick Leach. This guide is designed for executives and decision-makers who want to improve their understanding of risk and uncertainty. It introduces the concept of probabilistic thinking, demonstrating how it can lead to better decision-making and risk management in a variety of business scenarios.
Recent Posts
EOS is just that, an Operating System
What has COVID done to Company Culture?
COVID has affected everyone. However, companies need to examine if they have lived their core values during COVID, how they are reinforcing them in a WFH environment, and especially with the onboarding of new hires.
Profit ≠ Cash Flow
Knowing how much cash you generate is essential for planning for growth. Too many companies don’t know and when they grow they find they are continually running out of cash. Understand your cash flow generation and how to improve it through improvements in your Cash Conversion Cycle and using the Power of One.
What Are Your Critical and Counter Critical Numbers?
The key to achieving long term goals is to define short term goals that lead you there. Focusing those short term goals around a key metric is essential. However, ensure that the metric will not lead other areas astray by having an appropriate counter critical metric act as a counter balance.
Rethinking ‘Family’ Culture in Business: Fostering Performance and Success
Explore the importance of company culture and the potential pitfalls of adopting a “Family” culture in organizations. Learn how to foster a high-performance culture while maintaining key family values and discover success factors for family businesses. Rethink the “Family” culture concept and create a thriving environment for your organization.
Do You Truly Know Your Core Customer?
Knowing the profit of your core customers is key to building a growth model. Many companies have identified core customers that are generating a sub-optimal profit and so they cannot realize the profits they seek. Identifying the correct core customer allows you to generate profits and often operate in “Blue Ocean.”
The Spectacular Rise and Fall of the European Super League
The European Super League (ESL) collapsed within 48 hours of its announcement due to hubris, a lack of value creation, and fan backlash. The founders’ arrogance led them to disregard European football’s deep-rooted traditions and culture. At the same time, the focus on wealthy club owners instead of merit undermined the essence of the competition. The fierce backlash from fans, who felt betrayed by their clubs, demonstrated the importance of prioritizing supporters’ interests in football.
When Should I Sell My Business?
Many business owners want to sell at the top of the market. However, market timing is tough. Is this the best strategy? Probably not.
Does Your Financial Model Drive Growth?
Working with many companies looking to grow, I am always surprised how many have not built a financial model that drives growth. I have mentioned before a financial model that drives growth? Here I am basing on Jim Collin's Profit/X, which he laid out in Good to...
COVID = Caught Inside
As we emerge from COVID, the current employment environment makes me think of a surfing concept: “Being Caught Inside When a Big Set Comes Through.” Basically, the phrase refers to when you paddle like crazy to escape the crash of one wave, only to find that the next wave in the set is even bigger—and you’re exhausted. 2020 was the first wave, leaving us tired and low. But looking forward, there are major challenges looming on the horizon as business picks up in 2021. You are already asking a lot of your employees, who are working flat out and dealing with stress until you are able to hire more. But everyone is looking for employees right now, and hiring and retention for your organization is growing more difficult.










