The EOS Model® provides a useful foundation for businesses, but it falls short in addressing key aspects of creating an growth. By incorporating additional elements from the Gravitas 7 Attributes of Agile Growth® model, businesses can create a more comprehensive system that promotes growth while maintaining smooth operations. Focusing on Leadership, Strategy, Execution, Customer, Profit, Systems, and Talent, the 7 Attributes of Agile Growth® offer a more encompassing approach to achieving success.

To Buyback or Not Buyback, That is the Question?
As part of The CARES Act, Congress imposed restrictions on stock buybacks. There was bipartisan support for this idea. Billionaire Mark Cuban argued that the rule for any company that receives federal assistance is, “No buybacks. Not now. Not a year from now. Not 20 years from now. Not ever.” Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer declared on-air: “Our motto in this is ‘workers first.’ …. These buybacks, they infuriate me. We should not be allowing them to do buybacks, raise corporate salaries.” Sen. Elizabeth Warren said that any corporate recipient of government assistance should be “permanently prohibited from engaging in share repurchases.” President Trump joined the chorus arguing, “I am strongly recommending a buyback exclusion. You can’t take a billion dollars of the money and just buy back your stock and increase the value.” However, others have argued that this policy is “The Worst Coronavirus Idea.”
How it Happened
The airline industry was the poster child for arguments against buybacks. Airlines for America, which represents major U.S. passenger and cargo air carrier companies, requested government assistance because of (i) the coronavirus crisis, and (ii) several of the largest carriers had used the majority of their free cash flow on share buybacks over the last decade. Given that airlines have a propensity for going bankrupt with over 60 since 1991, and being unprepared for hard times including the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks and the volcanic eruption in Iceland in 2010 that disrupted air travel, building up cash for a rainy day hasn’t been part of their plan.
| Airline | Free Cash Flow ($MM) | Share Buybacks ($MM) | Buybacks/FCF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southwest Airlines Co. | 15,103 | 10,650 | 71% |
| Alaska Air Group, Inc. | 4,948 | 1,590 | 32 |
| Delta Air Lines, Inc. | 23,186 | 11,430 | 49% |
| United Airlines Holdings, Inc. | 11,526 | 8,883 | 77% |
| American Airlines Group, Inc. | (7,935) | 12,957 | N/A |
| JetBlue Airways Corporation | 2,347 | 1,771 | 75% |
Source: FactSet
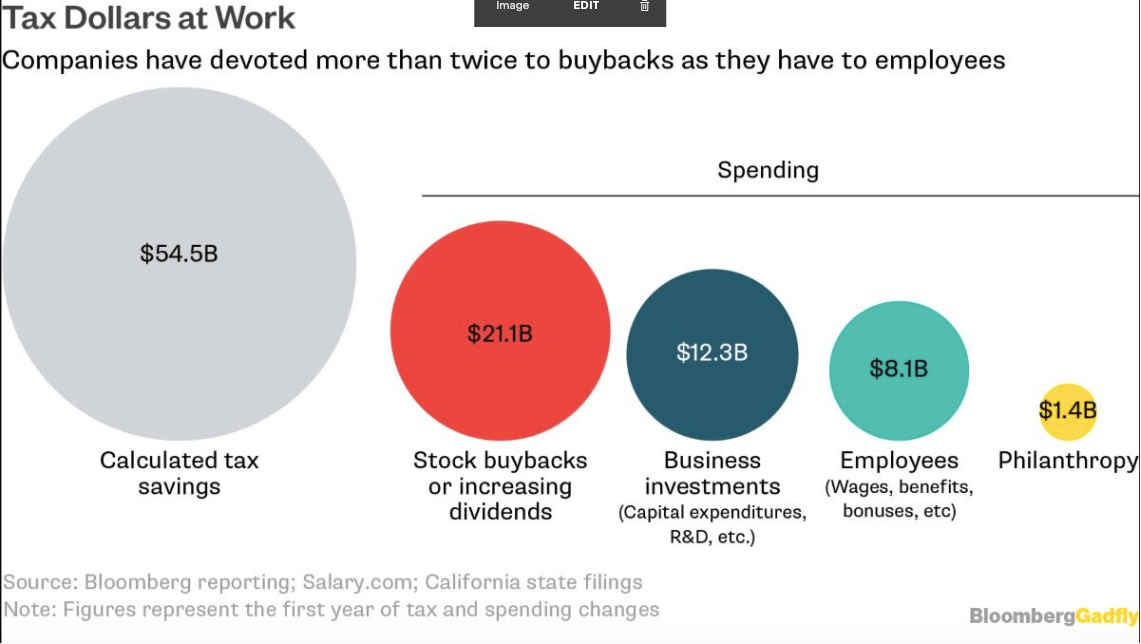
However, airlines weren’t the only ones spending free cash flow on share buybacks. As can be seen below, nearly 50% of the saving from the 2017 Tax Cut and Jobs Act went to share buybacks.
Arguments For Buybacks
Share buybacks are very popular. According to Federal Reserve data compiled by Goldman Sachs, over the past nine years, corporations have acquired more of their stocks – $3.8 trillion—than every other type of investor (individuals, mutual funds, pension funds, foreign investors) combined. So why do they do it?
-
An efficient way to return money to shareholders. By reducing the number of shares outstanding in the market, a buyback lifts the price of each remaining shares.
-
A Valuable source of cash. Donald L. Luskin and Chris Hynes made this argument in a Wall Street Opinion Editorial. It has to be the worst reason I have heard. If people need cash, they can sell their shares on the market; they don’t need the company to repurchase them.
-
More tax-efficient than dividends. If the shareholder has held the shares long enough to qualify for long term capital gains treatment, this is true. Dividends are taxed at 22% while the tax rate for capital gains is 0%,15%, or 20% depending on the taxpayers’ level of income.
-
Management captures the share bump. An analysis by the SEC revealed that executives, on average, sold five times as much stock in the eight days following a buyback announcement as they had on an ordinary day. According to SEC Commissioner Robert Jackson Jr., “Thus, executives personally capture the benefit of the short-term stock-price pop created by the buyback announcement.”
-
Boost management’s compensation. Following the adoption of Milton Friedman’s idea of “creating shareholder value,” more and more companies granted CEOs large blocks of company stock and stock options to align management with the corporate goal. However, with large portfolios of their own company’s stock, the desire to manipulate the share price with share buybacks was a temptation few CEOs could resist. As a recent article noted, “Today, the abuse of stock buybacks is so widespread that naming abusers is a bit like singling out snowflakes for ruining the driveway.”
Arguments Against Buybacks
-
Deprives companies of liquidity. As a recent Harvard Business Review article noted, when companies undertake buybacks, they deprive themselves of the cash that might help them cope when sales and profits decline in an economic downturn.
-
The share price boost is short-lived. A study by the research firm Fortuna Advisors found that five years out, the stocks of companies that engaged in substantial buybacks performed worse for shareholders than the shares of companies that didn’t.
-
The propensity to buy when the price is high and not when it’s low. Companies tend to overpay for their shares, diluting return to shareholders. The is overwhelming evidence that substantial buyback companies usually create less value for shareholders over time.
-
Lack of investment in things that grow shareholder value. Those companies that reinvested a higher percentage of their cash generation into capital expenditures, research and development, cash acquisitions, and working capital delivered substantially higher total shareholder return than those that reinvested less.
-
Lack of Imagination by Management. If the best use of the company’s money is share buybacks, then unless the shares are undervalued (20%+), management has effectively given up on planning to grow the company in new markets or products, through acquisition or investment. Such a strategy is a reflection of failed management.
Conclusion
From the above, it is apparent that there are few good reasons for share buybacks other than to boost management’s earnings. Hopefully, the current environment will cause management to reflect and do their jobs more efficiently so that there is real shareholder growth. As the Atlantic article pointed out.
“Craig Menear, the chairman and CEO of Home Depot mentioned on a conference call with investors in February 2018, their “plan to repurchase approximately $4 billion of outstanding shares during the year.” The next day, he sold 113,687 shares, netting $18 million. The following day, he was granted 38,689 new shares and promptly sold 24,286 shares for a profit of $4.5 million. Though Menear’s stated compensation in SEC filings was $11.4 million for 2018, stock sales helped him earn an additional $30 million for the year.
By contrast, the median worker pay at Home Depot is $23,000 a year. If the money spent on buybacks had been used to boost salaries, the Roosevelt Institute and the National Employment Law Project calculated, each worker would have made an additional $18,000 a year. But buybacks are more than just unfair. They’re myopic. Amazon (which hasn’t repurchased a share in seven years) is presently making the sort of investments in people, technology, and products that could eventually make Home Depot irrelevant. When that happens, Home Depot will probably wish it hadn’t spent all those billions on buying back 35 percent of its shares. “When you’ve got a mature company when everything seems to be going smoothly, that’s the exact moment you need to start worrying Jeff Bezos is going to start eating your lunch,” said the shareholder activist Nell Minow.”
Copyright (c) 2020, Marc A. Borrelli
Recent Posts
EOS is just that, an Operating System
What has COVID done to Company Culture?
COVID has affected everyone. However, companies need to examine if they have lived their core values during COVID, how they are reinforcing them in a WFH environment, and especially with the onboarding of new hires.
Profit ≠ Cash Flow
Knowing how much cash you generate is essential for planning for growth. Too many companies don’t know and when they grow they find they are continually running out of cash. Understand your cash flow generation and how to improve it through improvements in your Cash Conversion Cycle and using the Power of One.
What Are Your Critical and Counter Critical Numbers?
The key to achieving long term goals is to define short term goals that lead you there. Focusing those short term goals around a key metric is essential. However, ensure that the metric will not lead other areas astray by having an appropriate counter critical metric act as a counter balance.
Rethinking ‘Family’ Culture in Business: Fostering Performance and Success
Explore the importance of company culture and the potential pitfalls of adopting a “Family” culture in organizations. Learn how to foster a high-performance culture while maintaining key family values and discover success factors for family businesses. Rethink the “Family” culture concept and create a thriving environment for your organization.
Do You Truly Know Your Core Customer?
Knowing the profit of your core customers is key to building a growth model. Many companies have identified core customers that are generating a sub-optimal profit and so they cannot realize the profits they seek. Identifying the correct core customer allows you to generate profits and often operate in “Blue Ocean.”
The Spectacular Rise and Fall of the European Super League
The European Super League (ESL) collapsed within 48 hours of its announcement due to hubris, a lack of value creation, and fan backlash. The founders’ arrogance led them to disregard European football’s deep-rooted traditions and culture. At the same time, the focus on wealthy club owners instead of merit undermined the essence of the competition. The fierce backlash from fans, who felt betrayed by their clubs, demonstrated the importance of prioritizing supporters’ interests in football.
When Should I Sell My Business?
Many business owners want to sell at the top of the market. However, market timing is tough. Is this the best strategy? Probably not.
Does Your Financial Model Drive Growth?
Working with many companies looking to grow, I am always surprised how many have not built a financial model that drives growth. I have mentioned before a financial model that drives growth? Here I am basing on Jim Collin's Profit/X, which he laid out in Good to...
COVID = Caught Inside
As we emerge from COVID, the current employment environment makes me think of a surfing concept: “Being Caught Inside When a Big Set Comes Through.” Basically, the phrase refers to when you paddle like crazy to escape the crash of one wave, only to find that the next wave in the set is even bigger—and you’re exhausted. 2020 was the first wave, leaving us tired and low. But looking forward, there are major challenges looming on the horizon as business picks up in 2021. You are already asking a lot of your employees, who are working flat out and dealing with stress until you are able to hire more. But everyone is looking for employees right now, and hiring and retention for your organization is growing more difficult.










